Deposition Date
2019-04-02
Release Date
2019-08-14
Last Version Date
2023-09-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6R8N
Keywords:
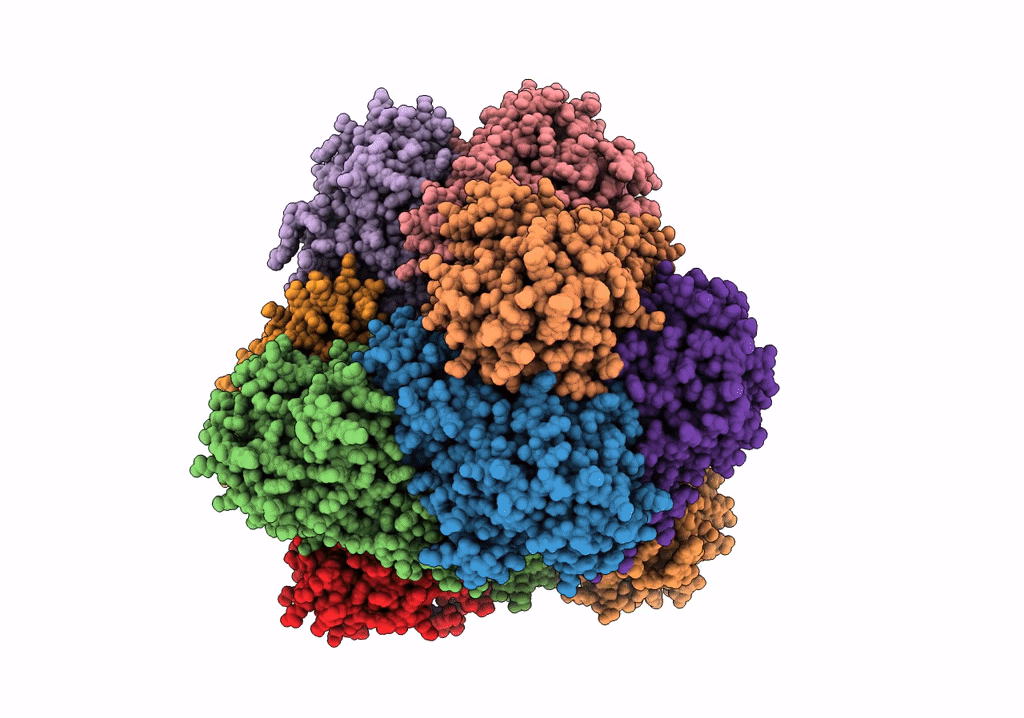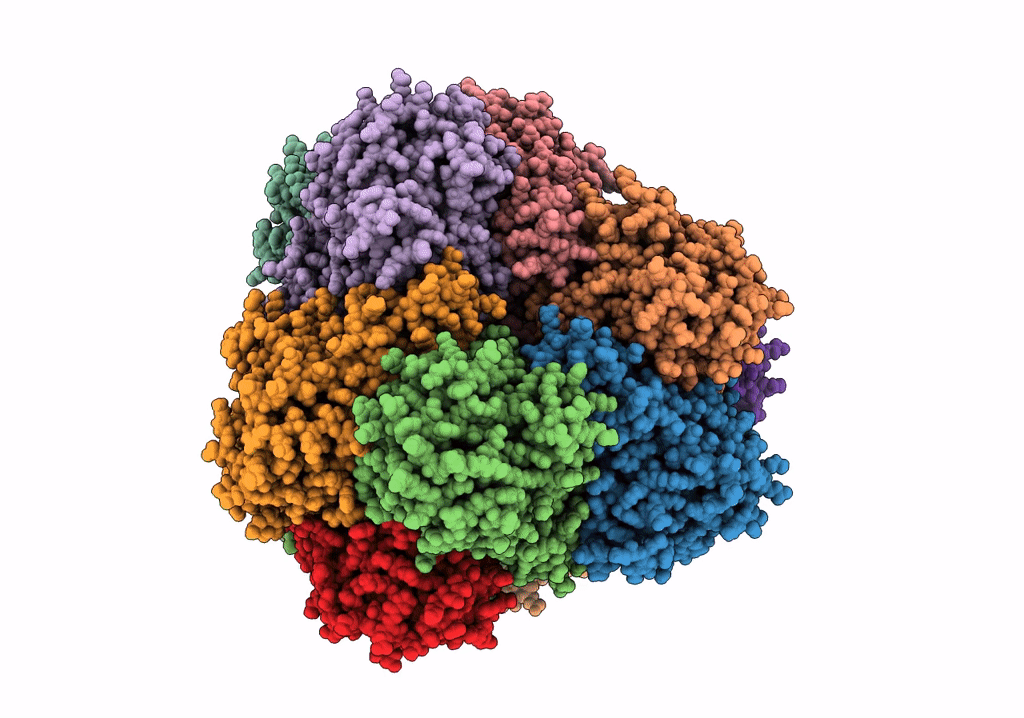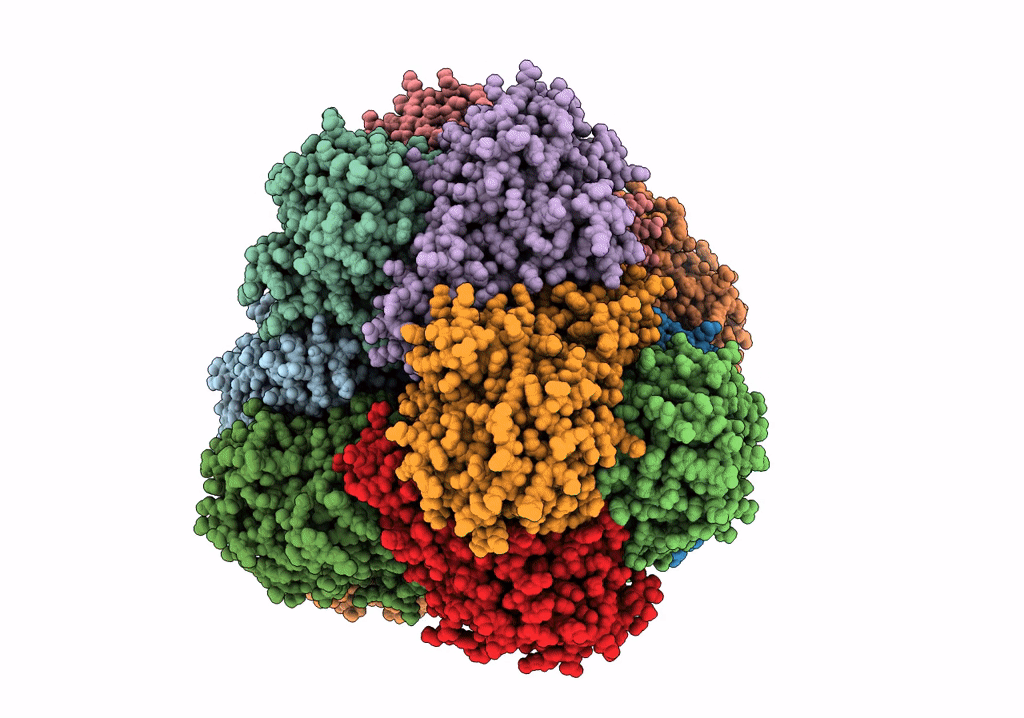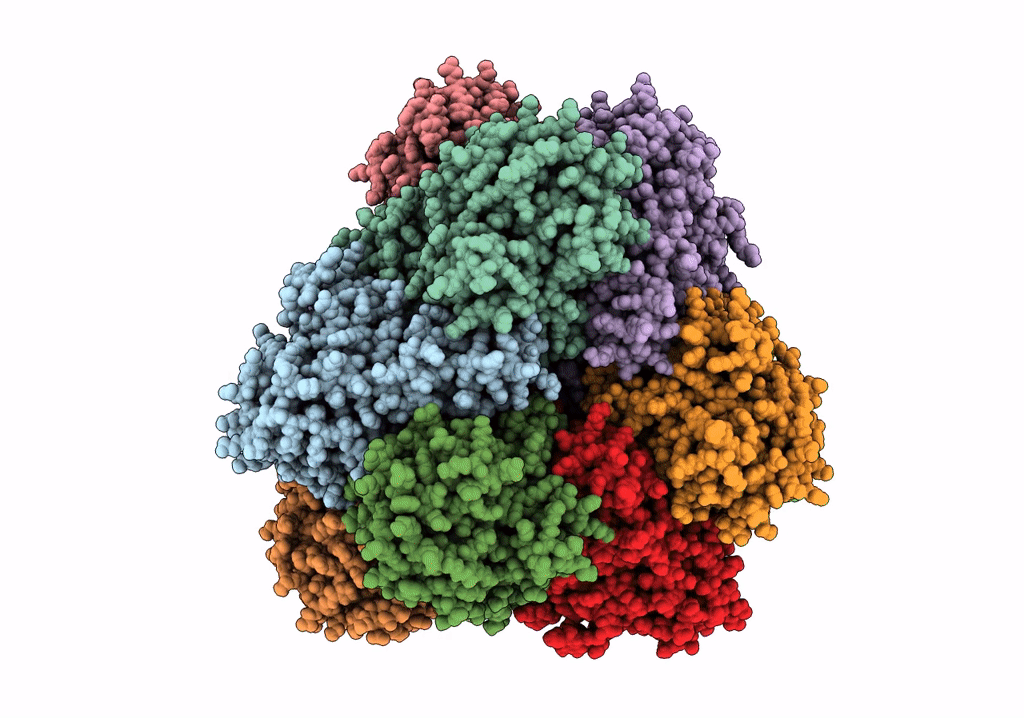
Title:
STRUCTURE DETERMINATION OF THE TETRAHEDRAL AMINOPEPTIDASE TET2 FROM P. HORIKOSHII BY USE OF COMBINED SOLID-STATE NMR, SOLUTION-STATE NMR AND EM DATA 4.1 A, FOLLOWED BY REAL_SPACE_REFINEMENT AT 4.1 A
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 (Taxon ID: 70601)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.10 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


