Deposition Date
2019-03-01
Release Date
2020-01-15
Last Version Date
2024-01-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6QV4
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the Ski2 RNA-helicase Brr2 from Chaetomium thermophilum bound to ATP-gamma-S
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Chaetomium thermophilum (Taxon ID: 209285)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.80 Å
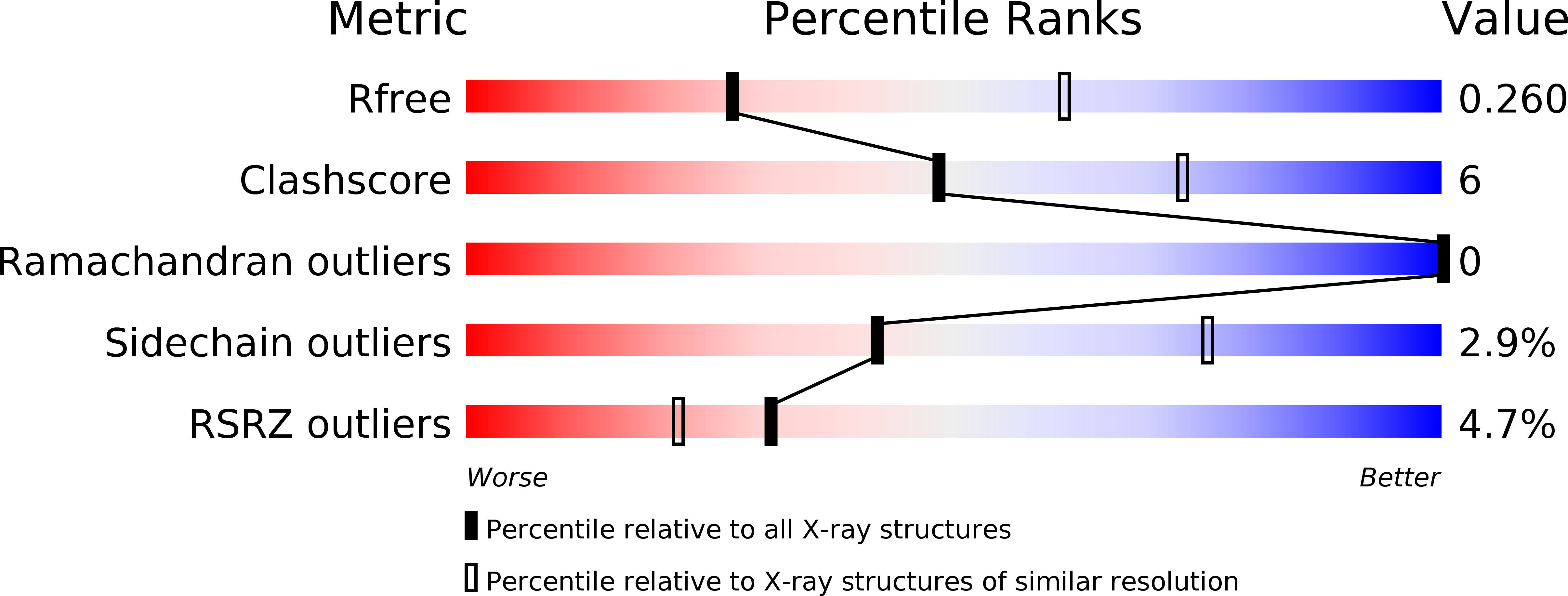
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 31