Deposition Date
2019-06-17
Release Date
2020-03-25
Last Version Date
2023-10-11
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6PCM
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium smegmatis Topoisomerase I with ssDNA bound to both N- and C-terminal domains
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mycobacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (Taxon ID: 246196)
Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (Taxon ID: 1772)
Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (Taxon ID: 1772)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
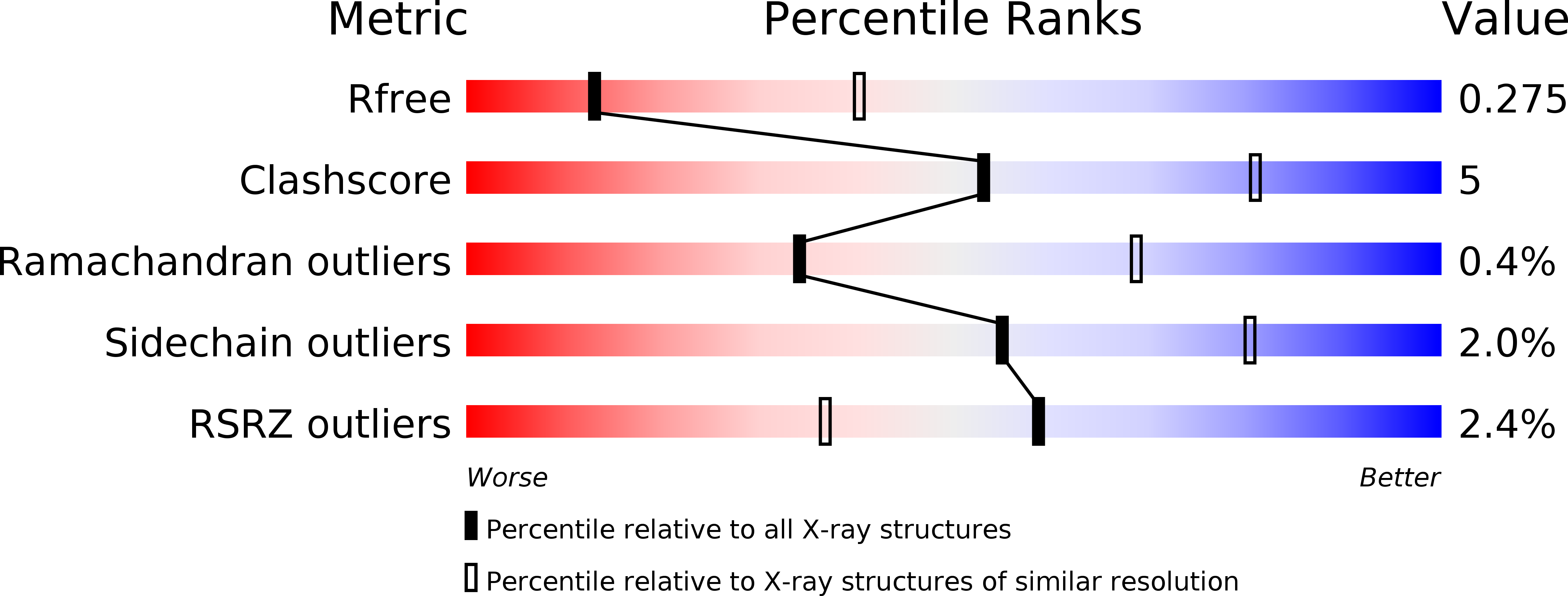
Resolution:
3.11 Å
R-Value Free:
0.27
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 21 21 21