Deposition Date
2019-05-15
Release Date
2019-07-10
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6OZ6
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of MraY bound to 3'-hydroxymureidomycin A
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Aquifex aeolicus (strain VF5) (Taxon ID: 224324)
Aquifex aeolicus (strain VF5) (Taxon ID: 224324)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
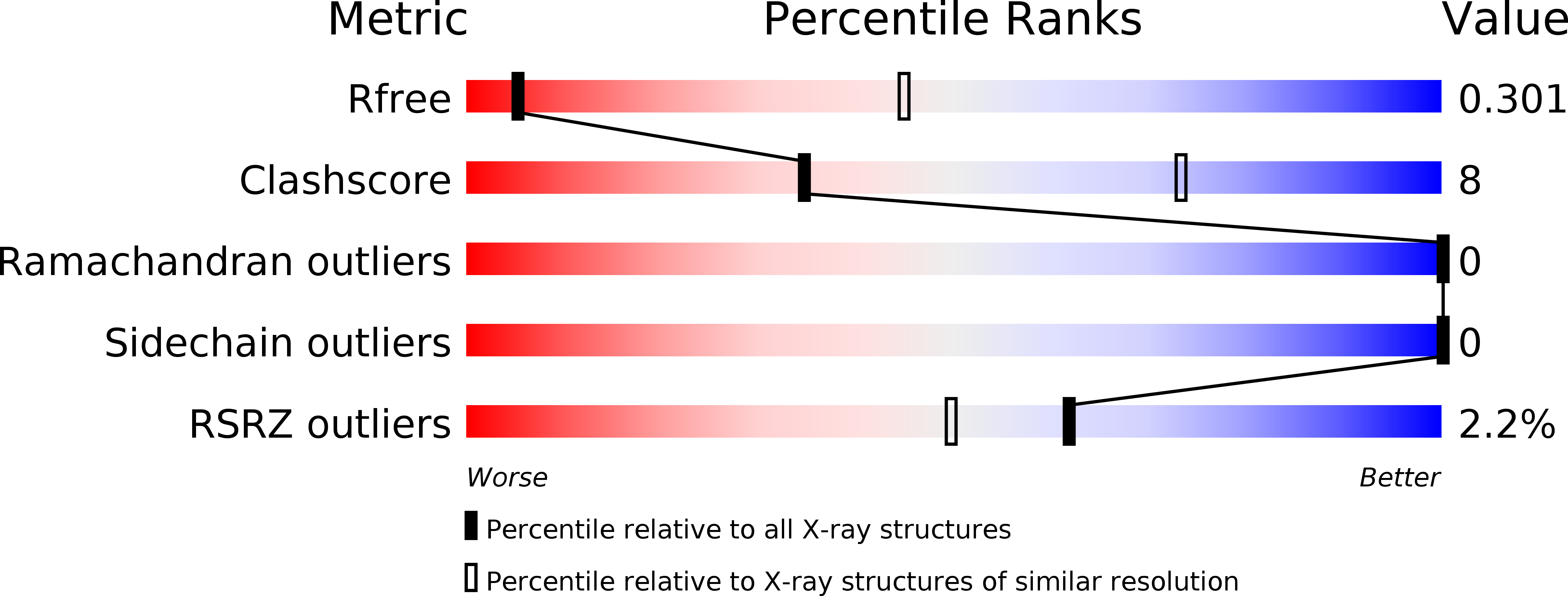
Resolution:
3.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.30
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
P 1 21 1