Deposition Date
2019-03-11
Release Date
2020-04-01
Last Version Date
2023-10-11
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6O8L
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of C9S apo and reduced Sulfide-responsive transcriptional repressor (SqrR) from Rhodobacter capsulatus.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Rhodobacter capsulatus (Taxon ID: 1061)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
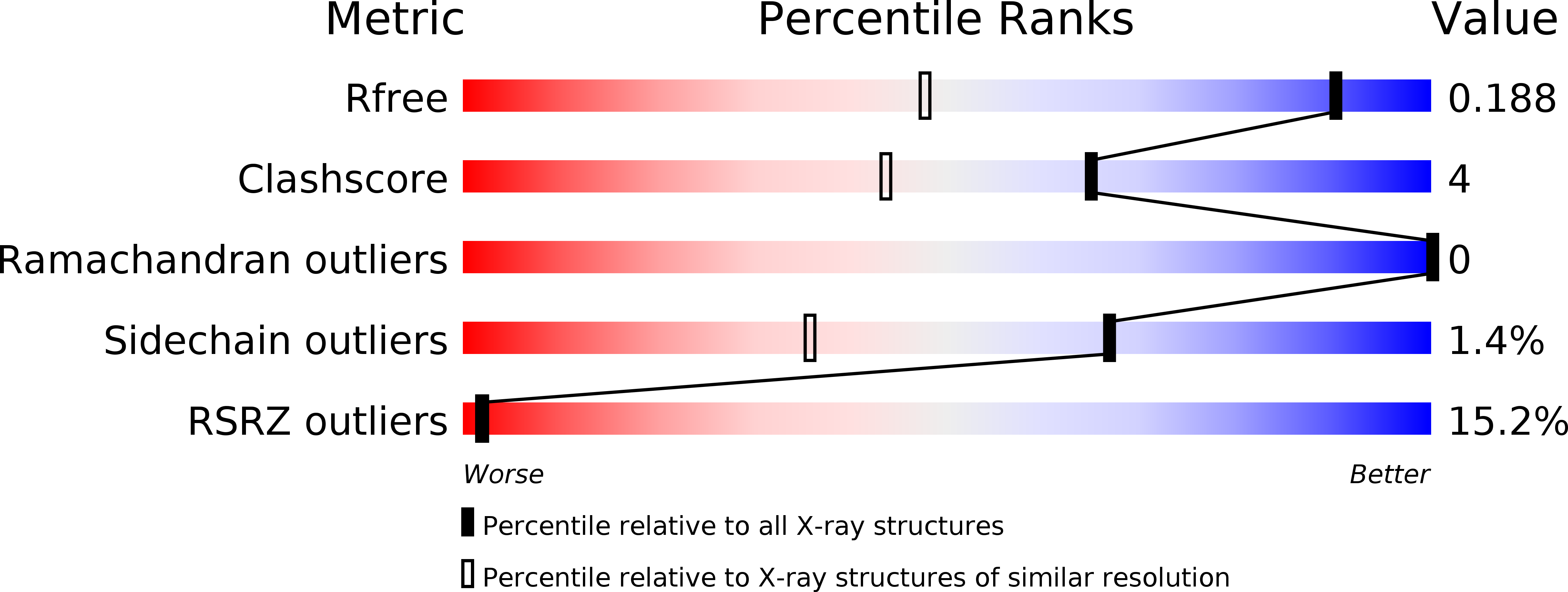
Resolution:
1.36 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.15
Space Group:
P 61 2 2