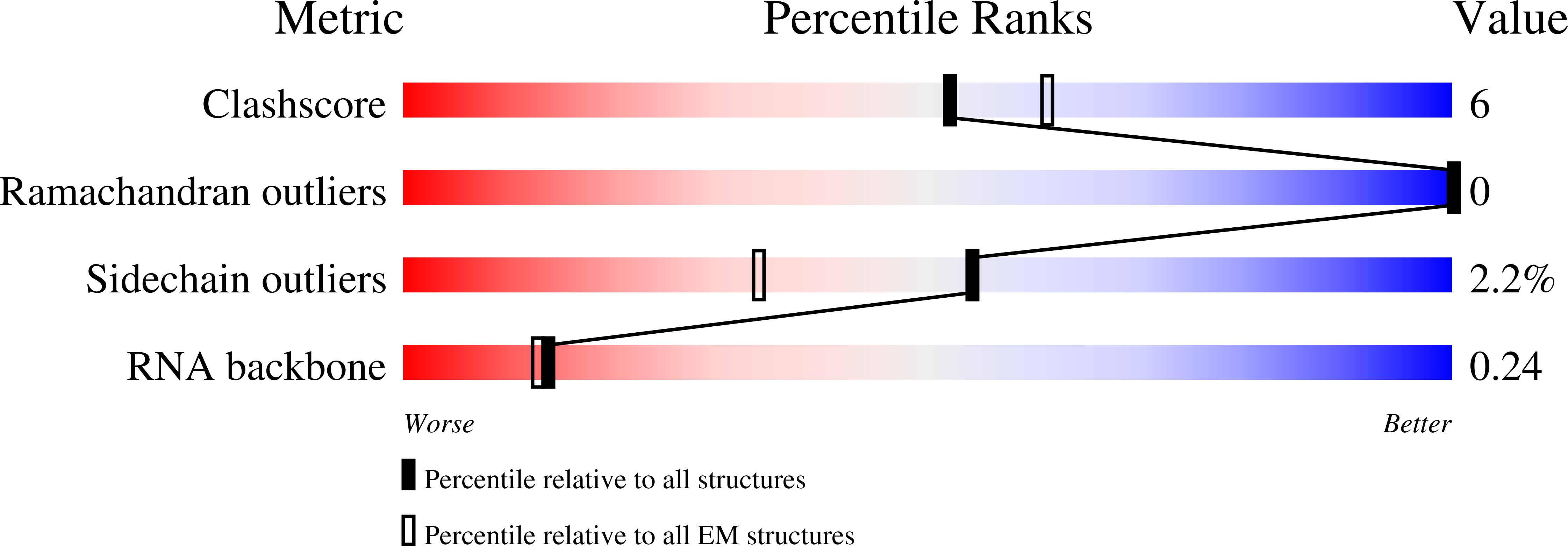Deposition Date
2019-02-20
Release Date
2019-03-13
Last Version Date
2024-03-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6O1M
Keywords:
Title:
Architectural principles for Hfq/Crc-mediated regulation of gene expression. Hfq-Crc-amiE 2:4:2 complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.15 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE