Deposition Date
2018-10-09
Release Date
2019-02-06
Last Version Date
2025-04-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6MPZ
Keywords:
Title:
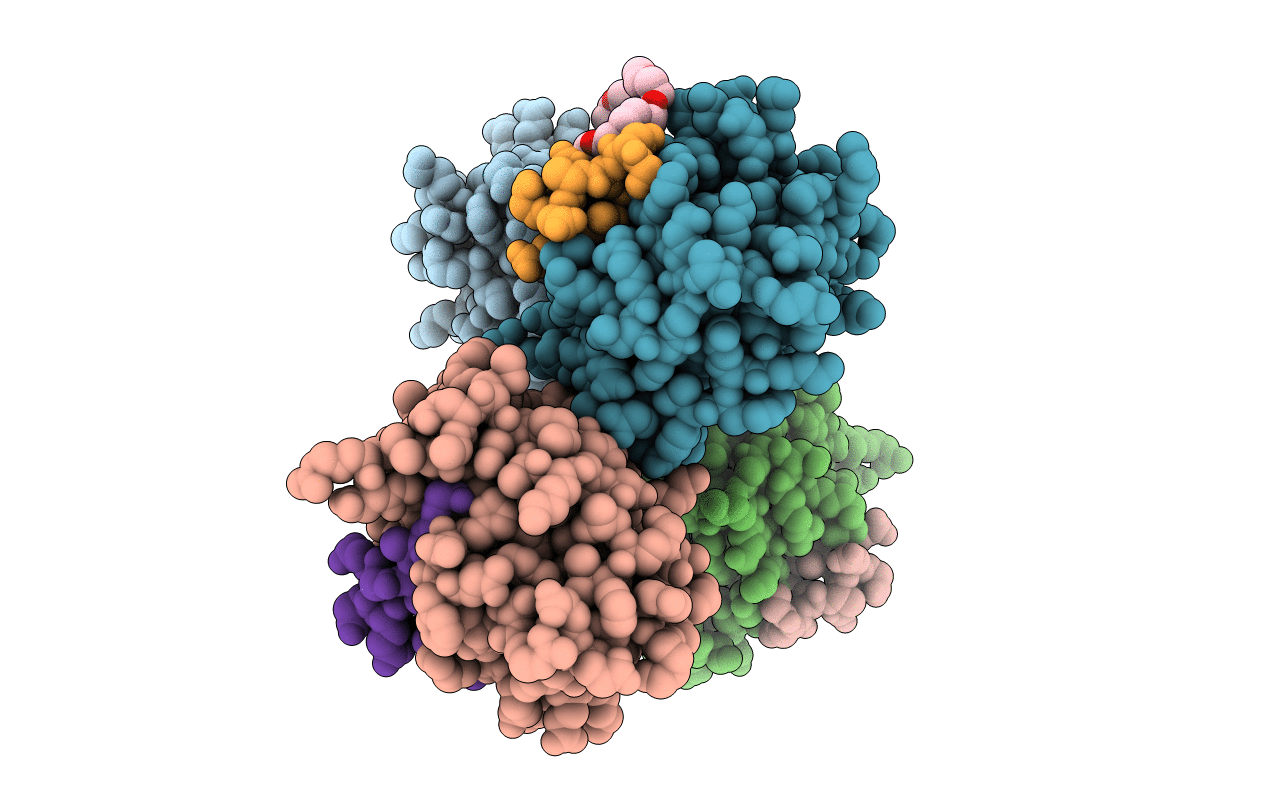
Crystal structure of a double glycine motif protease from AMS/PCAT transporter in complex with the leader peptide
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Lachnospiraceae bacterium C6A11 (Taxon ID: 1410622)
Prochlorococcus marinus str. MIT 9313 (Taxon ID: 74547)
Prochlorococcus marinus str. MIT 9313 (Taxon ID: 74547)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
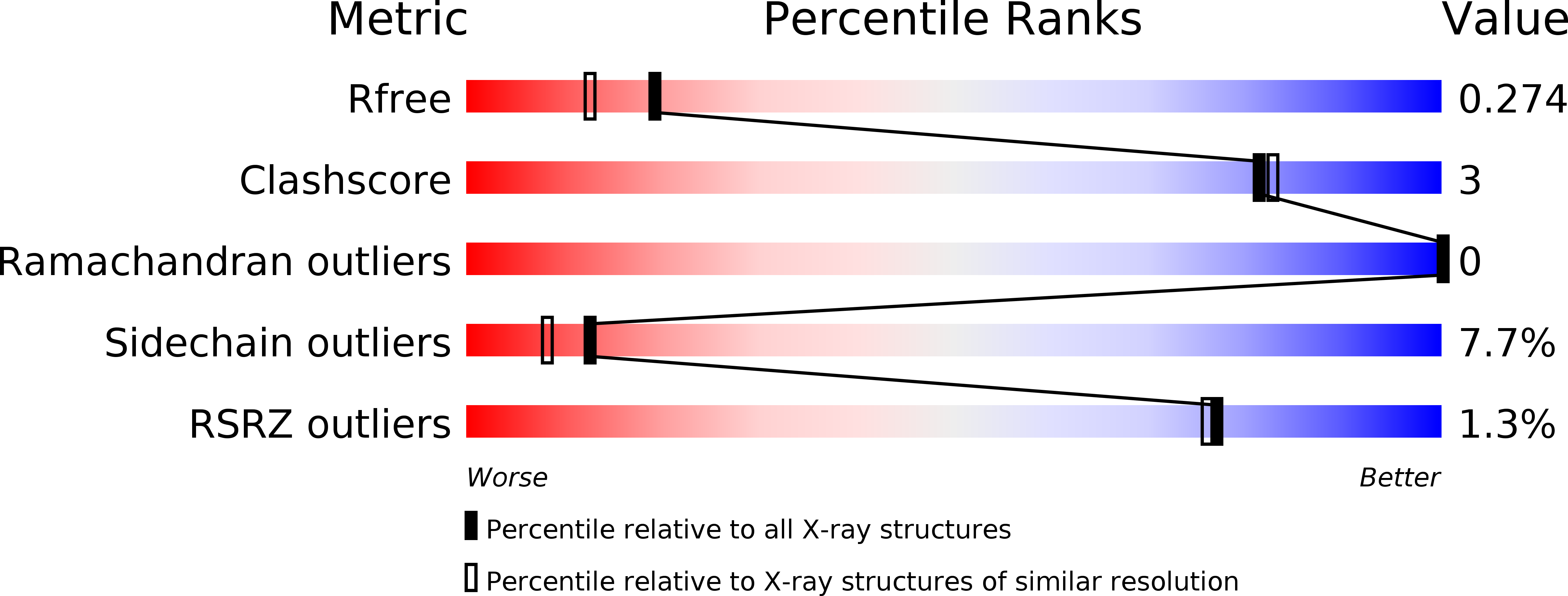
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.23
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
P 1 21 1