Deposition Date
2020-03-14
Release Date
2020-10-14
Last Version Date
2024-03-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6M6C
Keywords:
Title:
CryoEM structure of Thermus thermophilus RNA polymerase elongation complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermus thermophilus (Taxon ID: 274)
Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (Taxon ID: 300852)
Thermus thermophilus (strain HB8 / ATCC 27634 / DSM 579) (Taxon ID: 300852)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
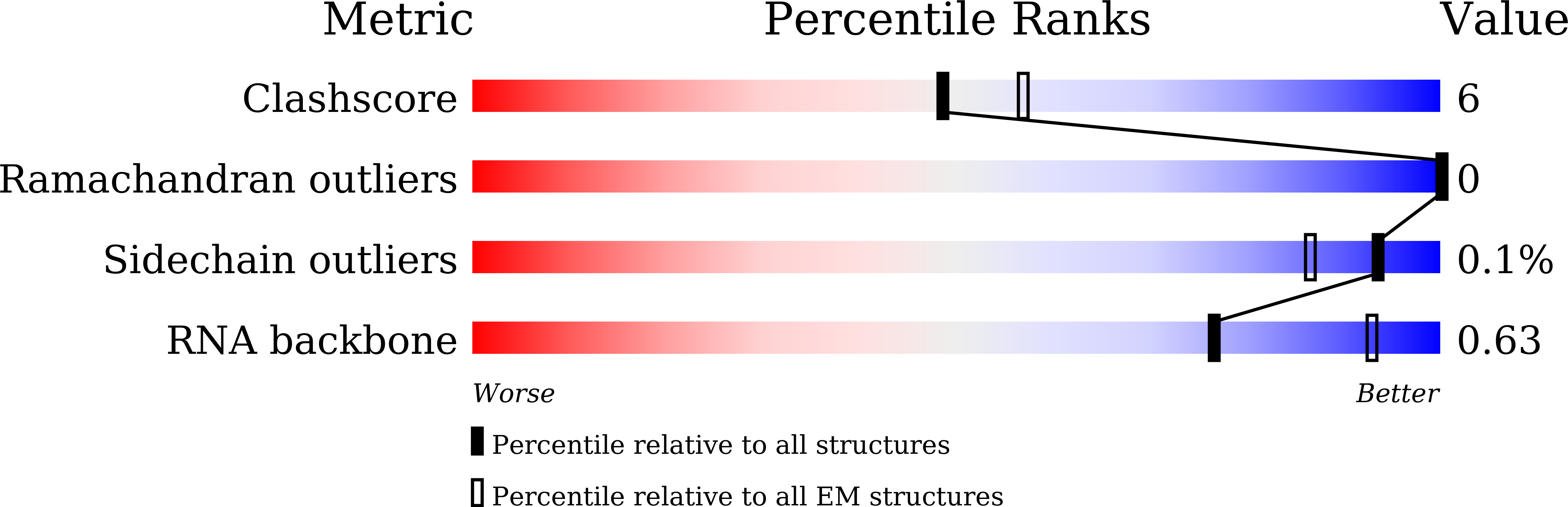
Resolution:
3.10 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE