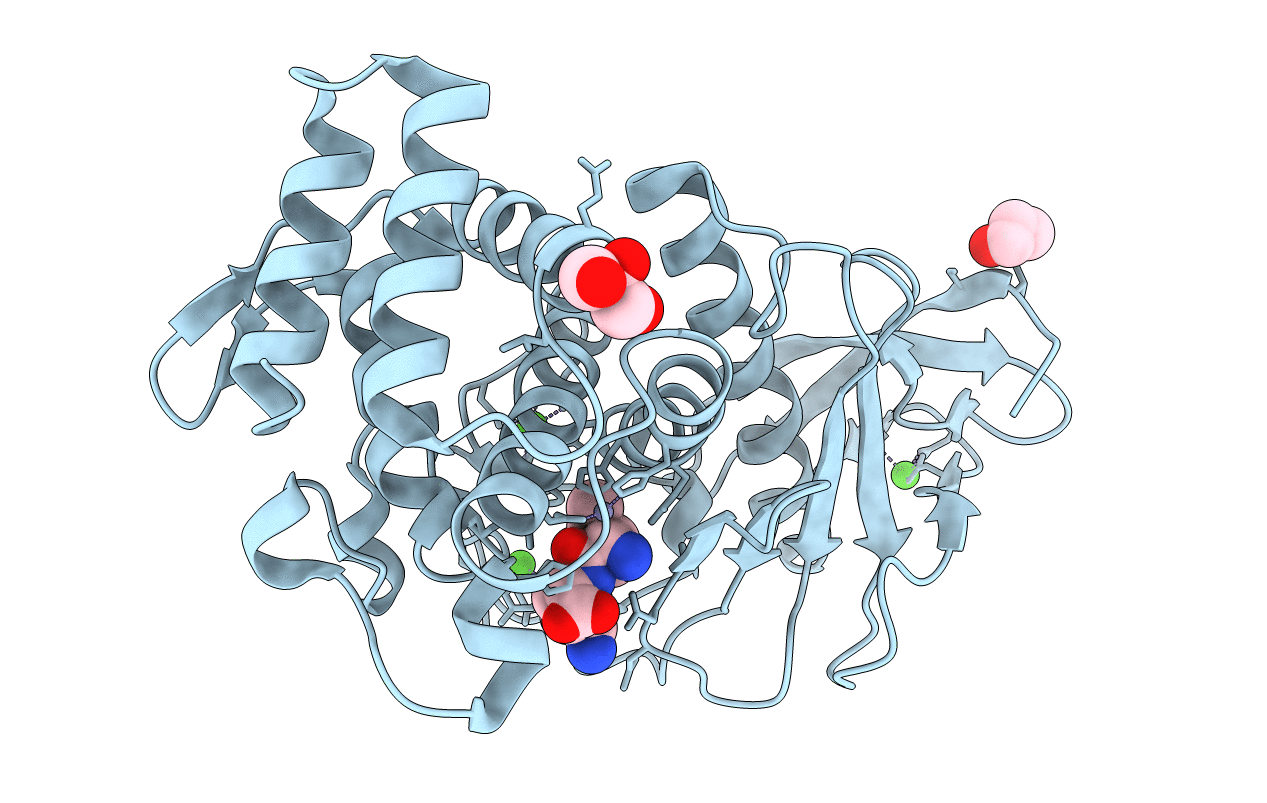Abstact
Metalloproteases and their inhibitors are important in numerous fundamental biochemical phenomena and medical applications. The heterocyclic organic compound, 1,10-phenanthroline, forms a complex with transition metal ions and is a Zn2+-chelating metalloprotease inhibitor; however, the mechanism of 1,10-phenanthroline-based chelation inhibition has not been fully elucidated. This study aimed to understand the structural basis of zinc metalloproteinase inhibition by 1,10-phenanthroline. Herein, the crystal structure of thermolysin was determined in the absence and presence of 1,10-phenanthroline at 1.5 and 1.8 Å, respectively. In native thermolysin, Zn2+ at the active site is tetrahedrally coordinated by His142, His146, Glu166, and water molecule and contains three Ca2+ ions, which are involved in thermostability. In the crystal structure of 1,10-phenanthroline-treated thermolysin crystal, seven 1,10-phenanthroline molecules were observed on the surface of thermolysin. These molecules are stabilized by π- π stacking interactions with aromatic amino acids (Phe63, Tyr66, Tyr110, His216, and Try251) or between the 1,10-phenanthrolines. Moreover, interactions with Ser5 and Arg101 were also observed. In this structure, Zn2+ at the active site was completely chelated, but no large conformational changes were observed in Zn2+ coordination with amino acid residues. Ca2+ at the Ca3 site exposed to the solvent was chelated by 1,10-phenanthroline, resulting in a conformational change in the side chain of Asp56 and Gln61. Based on the surface structure, for 1,10-phenanthroline to chelate a metal, it is important that the metal is exposed on the protein surface and that there is no steric hindrance impairing 1,10-phenanthroline access by the amino acids around the metal.