Deposition Date
2020-02-13
Release Date
2020-10-21
Last Version Date
2025-09-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6LY5
Keywords:
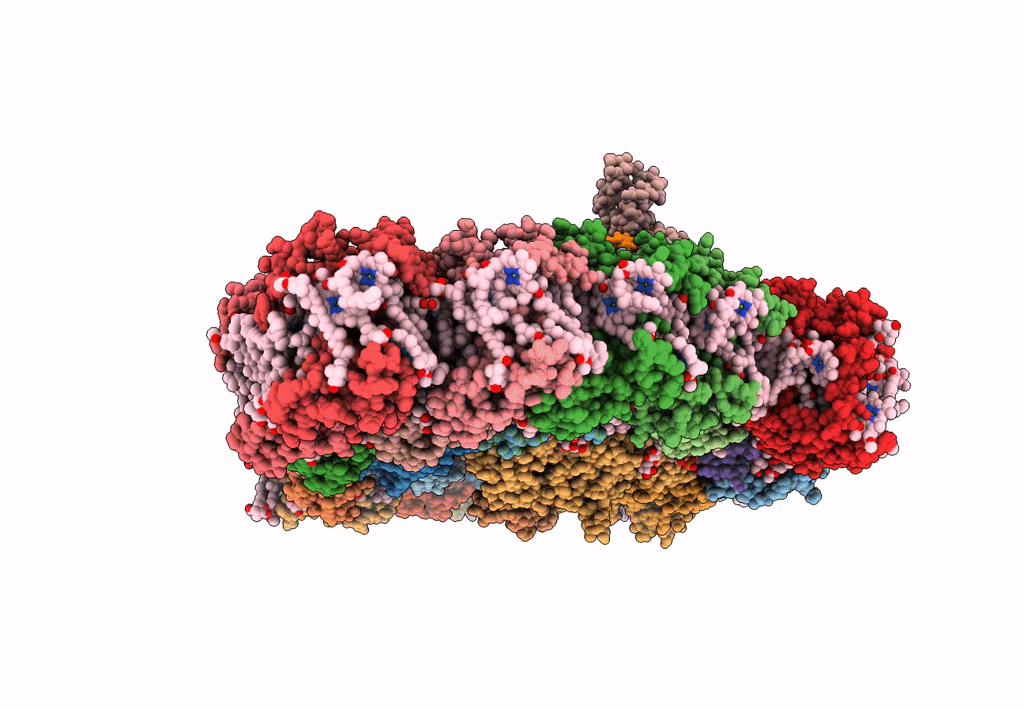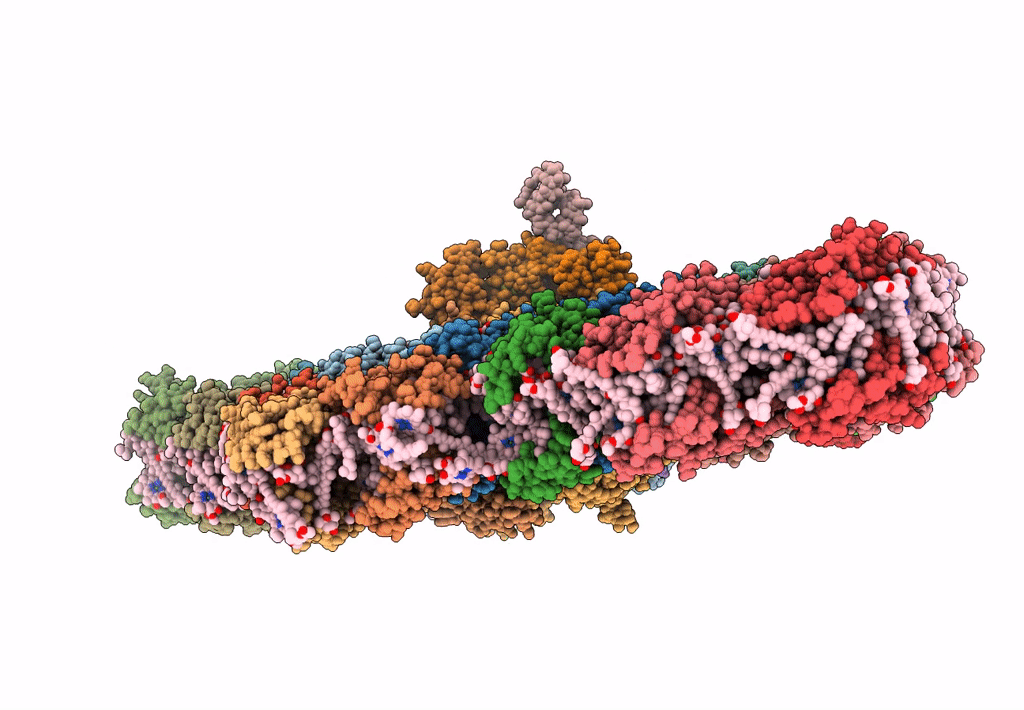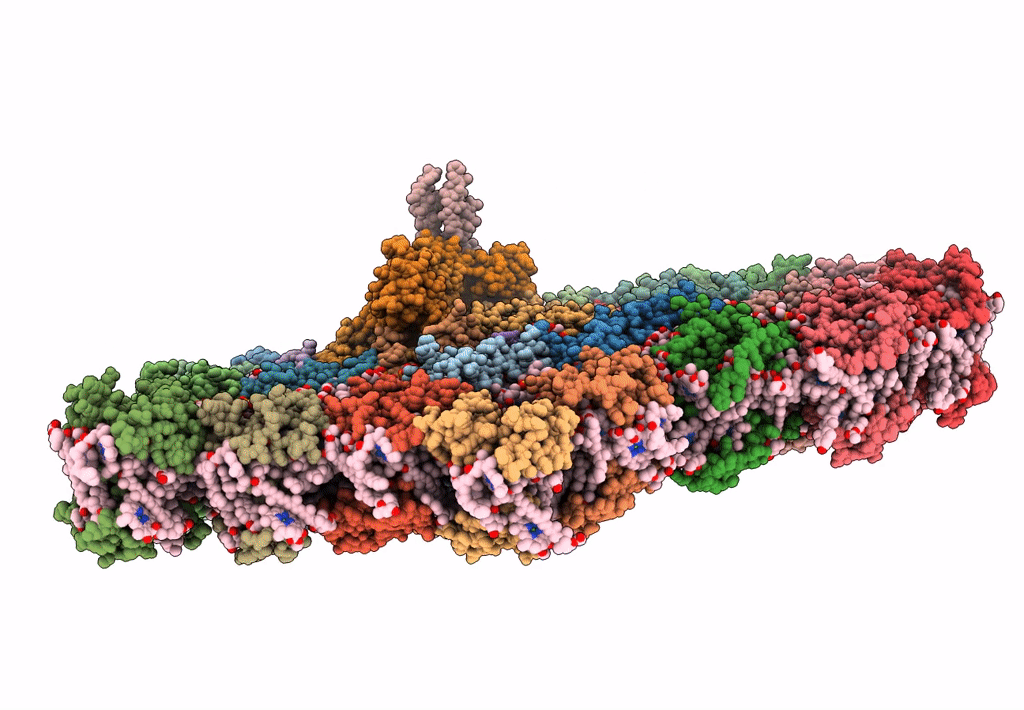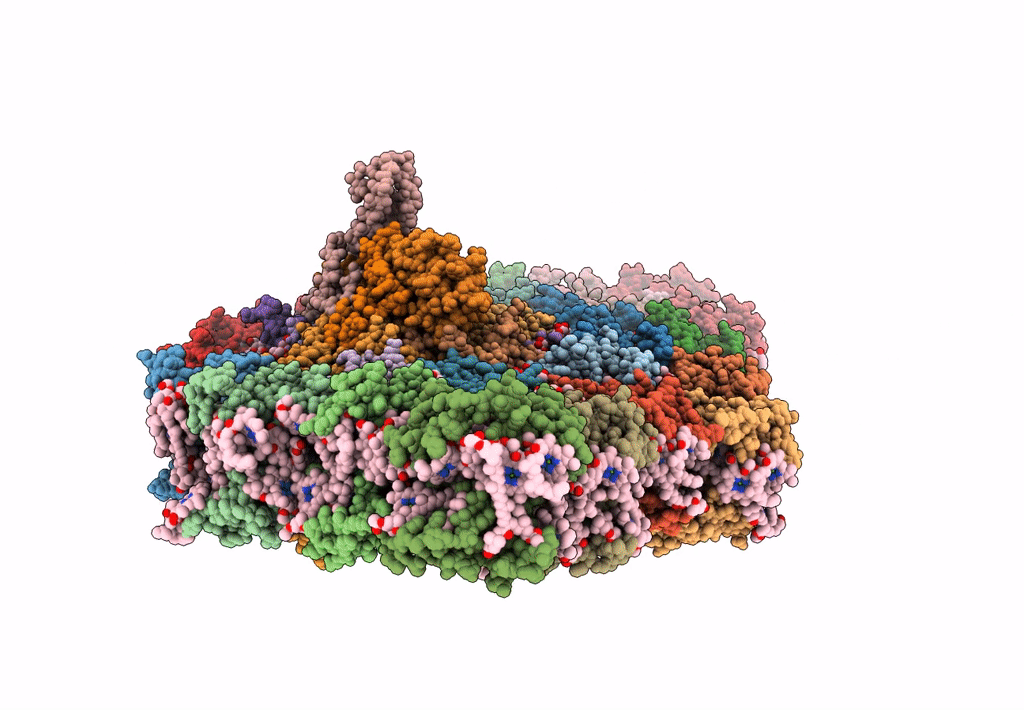
Title:
Organization and energy transfer in a huge diatom PSI-FCPI supercomplex
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Chaetoceros gracilis (Taxon ID: 184592)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.38 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


