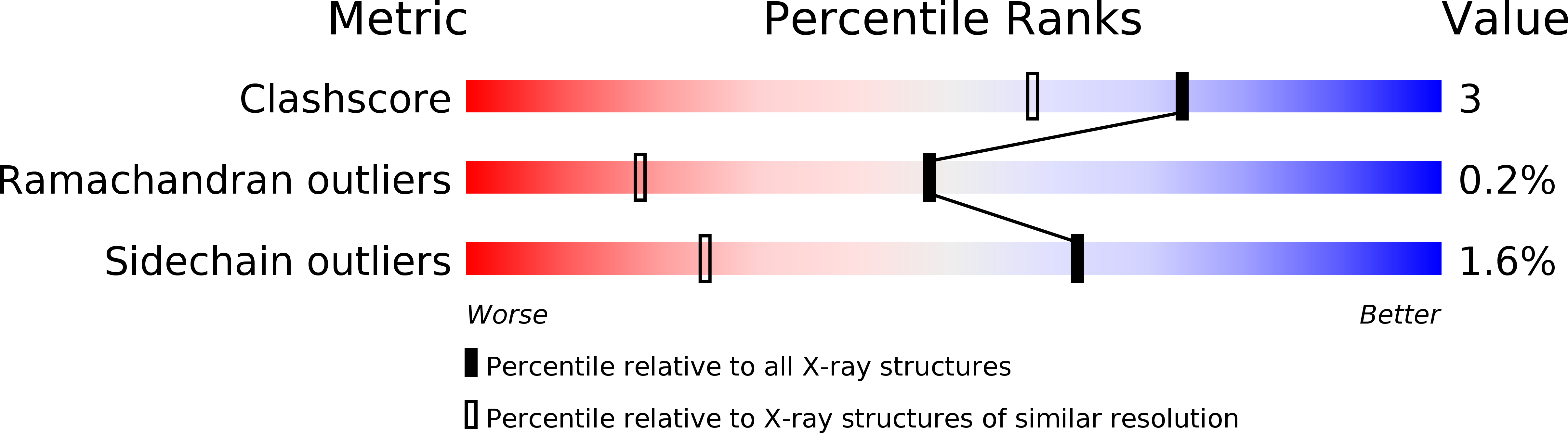
Deposition Date
2019-11-08
Release Date
2020-04-29
Last Version Date
2023-11-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6L9C
Keywords:
Title:
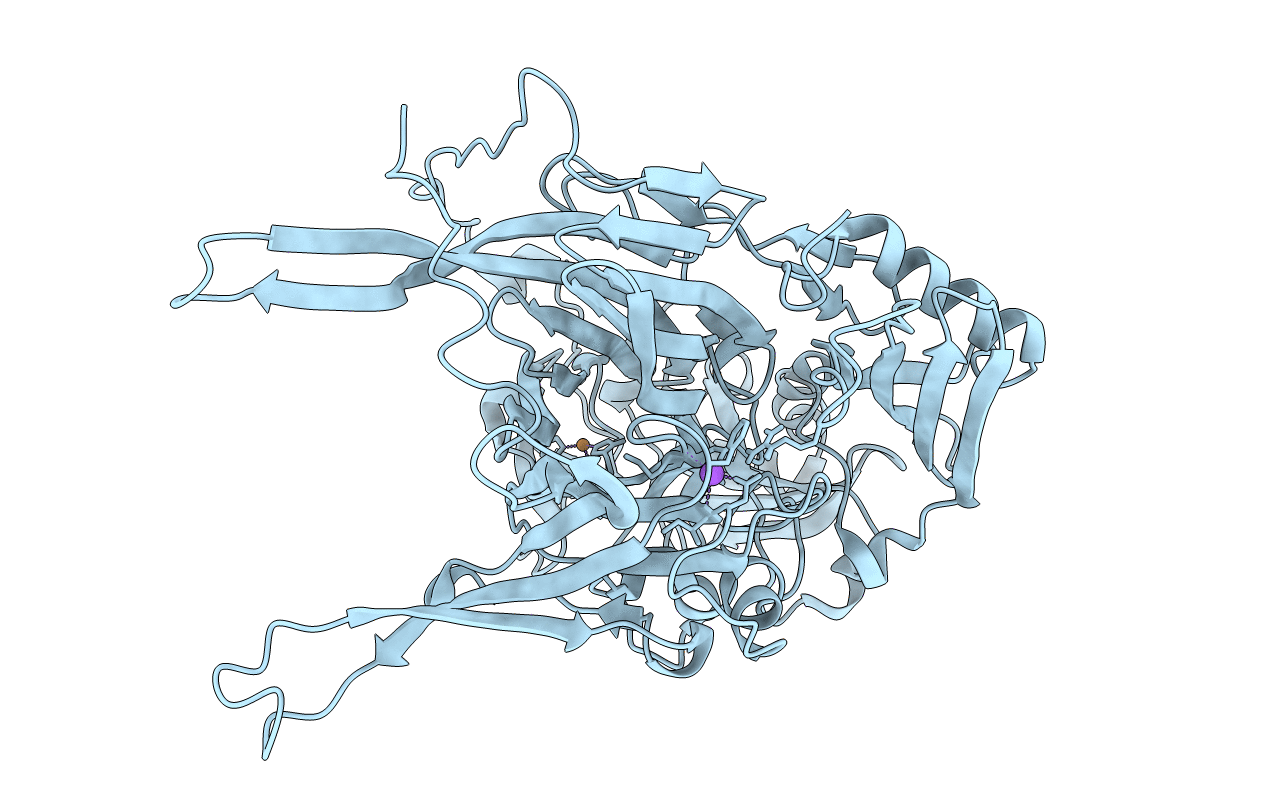
Neutron structure of copper amine oxidase from Arthrobacter glibiformis at pD 7.4
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Arthrobacter globiformis (Taxon ID: 1665)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
R-Value Free:
['0.18
R-Value Work:
['0.16
R-Value Observed:
['0.16
Space Group:
C 1 2 1