Deposition Date
2019-10-26
Release Date
2020-09-02
Last Version Date
2025-09-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6L63
Keywords:
Title:
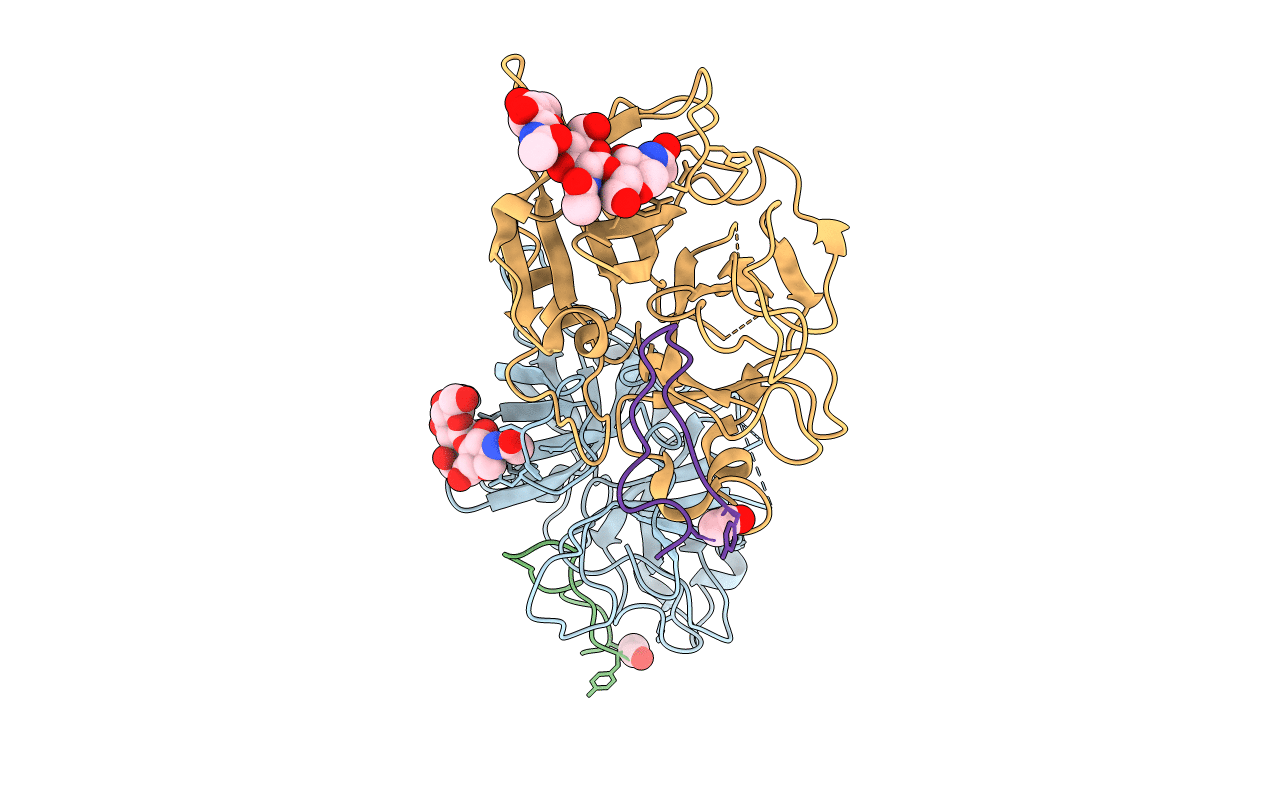
Human Coagulation Factor XIIa (FXIIa) bound with the macrocyclic peptide F3 containing two (1S,2S)-2-ACHC residues
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
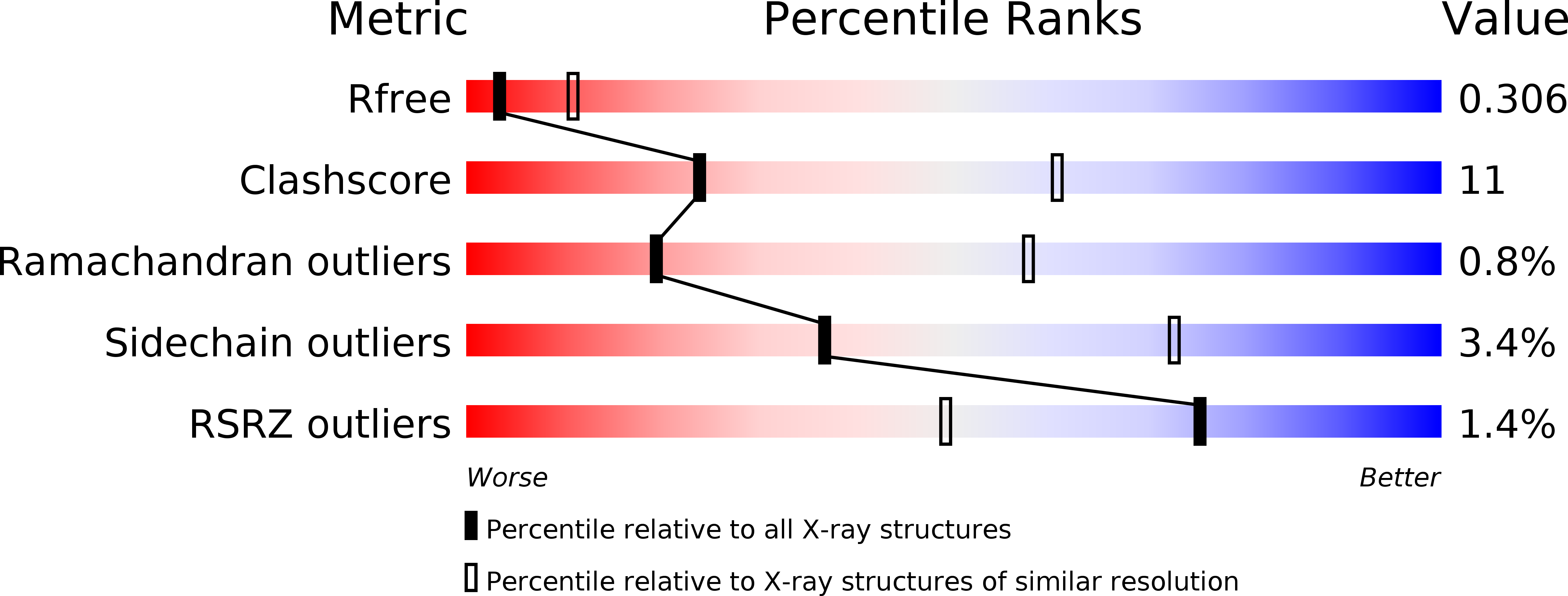
Resolution:
3.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.30
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.26
Space Group:
P 2 21 21