Deposition Date
2019-07-02
Release Date
2020-03-04
Last Version Date
2023-11-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6KDJ
Keywords:
Title:
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with Q151M/Y115F/F116Y:DNA:lamivudine 5'-triphosphate ternary complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (Taxon ID: 11676)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
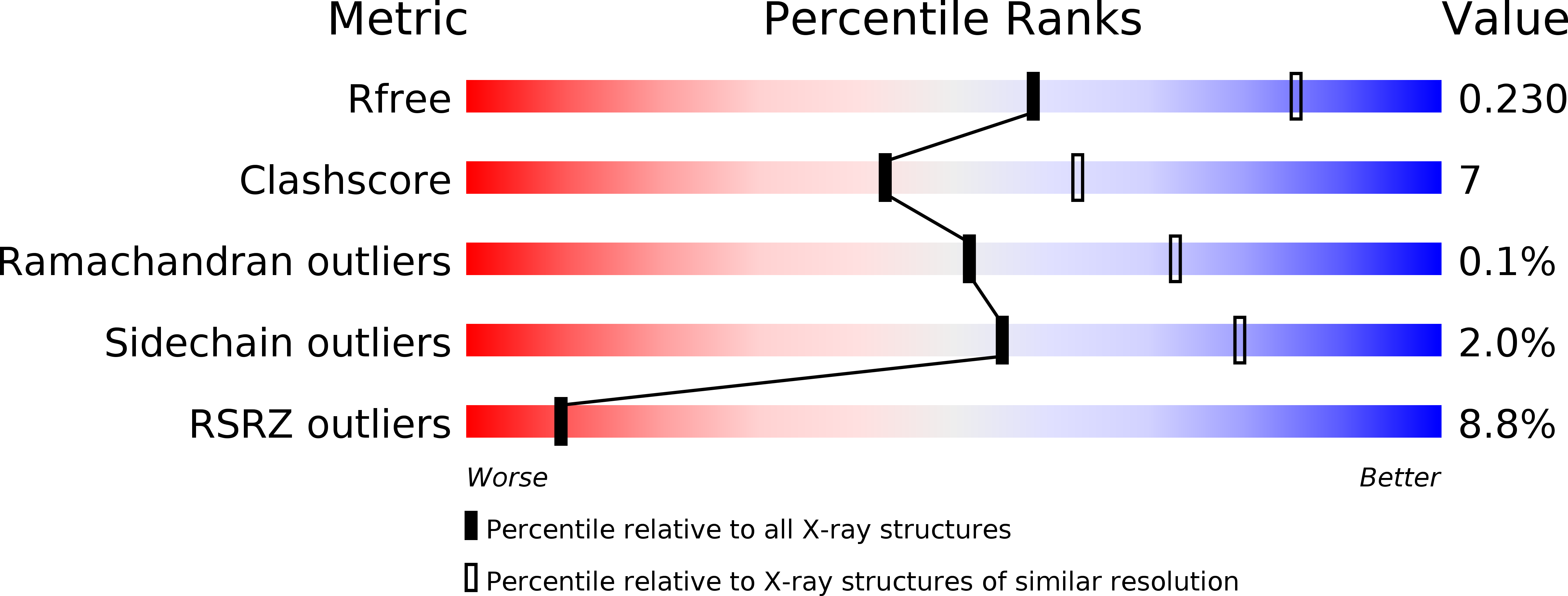
Resolution:
2.51 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
H 3