Abstact
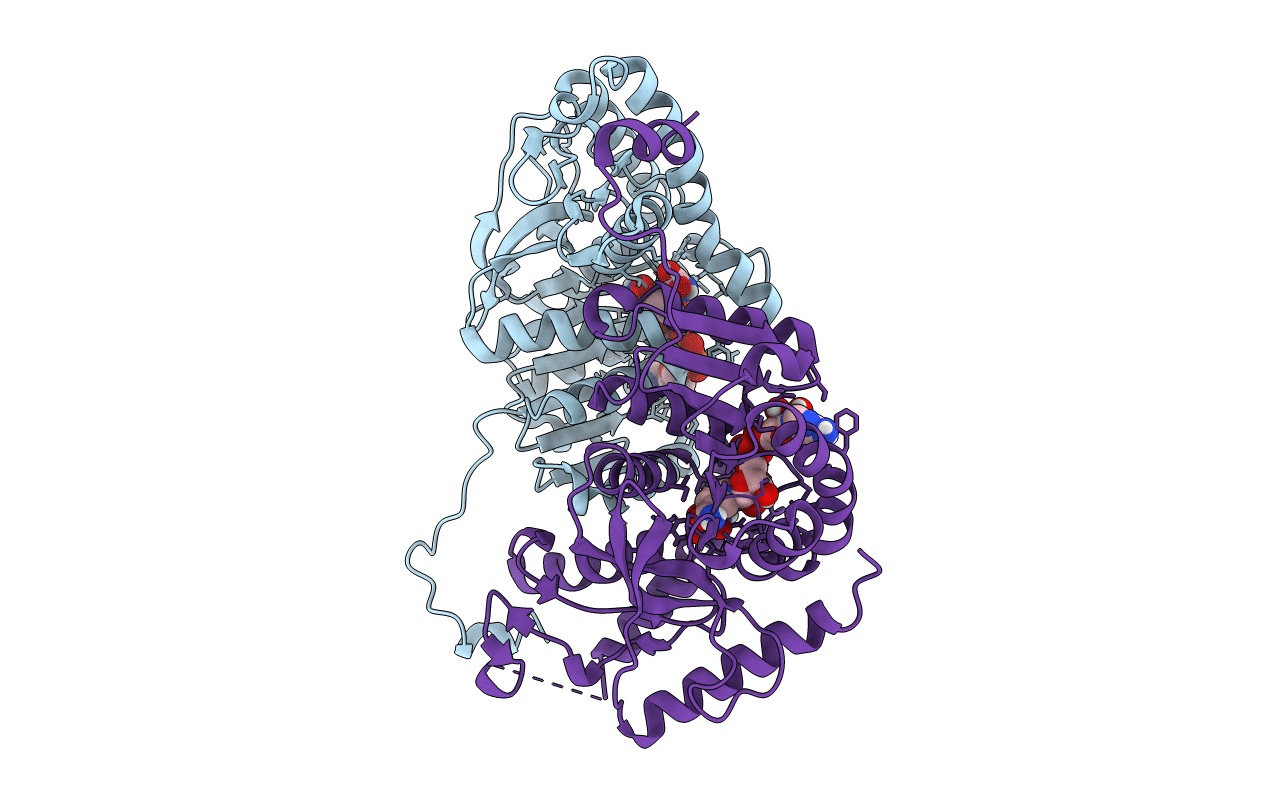
The tick- and transfusion-transmitted human pathogen Babesia microti infects host erythrocytes to cause the pathologic symptoms associated with human babesiosis, an emerging disease with worldwide distribution and potentially fatal clinical outcome. Drugs currently recommended for the treatment of babesiosis are associated with a high failure rate and significant adverse events, highlighting the urgent need for more-effective and safer babesiosis therapies. Unlike other apicomplexan parasites, B. microti lacks a canonical lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) but instead expresses a unique enzyme, B. microti LDH (BmLDH), acquired through evolution by horizontal transfer from a mammalian host. Here, we report the crystal structures of BmLDH in apo state and ternary complex (enzyme-NADH-oxamate) solved at 2.79 and 1.89 Å. Analysis of these structures reveals that upon binding to the coenzyme and substrate, the active pocket of BmLDH undergoes a major conformational change from an opened and disordered to a closed and stabilized state. Biochemical assays using wild-type and mutant B. microti and human LDHs identified Arg99 as a critical residue for the catalytic activity of BmLDH but not its human counterpart. Interestingly, mutation of Arg99 to Ala had no impact on the overall structure and affinity of BmLDH to NADH but dramatically altered the closure of the enzyme's active pocket. Together, these structural and biochemical data highlight significant differences between B. microti and human LDH enzymes and suggest that BmLDH could be a suitable target for the development of selective antibabesial inhibitors.-Yu, L., Shen, Z., Liu, Q., Zhan, X., Luo, X., An, X., Sun, Y., Li, M., Wang, S., Nie, Z., Ao, Y., Zhao, Y., Peng, G., Ben Mamoun, C., He, L., Zhao, J. Crystal structures of Babesia microti lactate dehydrogenase BmLDH reveal a critical role for Arg99 in catalysis.