Deposition Date
2019-02-21
Release Date
2019-04-24
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6JIJ
Keywords:
Title:
The Crystal Structure of Main Protease from Mouse Hepatitis Virus A59 in Complex with an inhibitor
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Murine coronavirus (strain A59) (Taxon ID: 11142)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
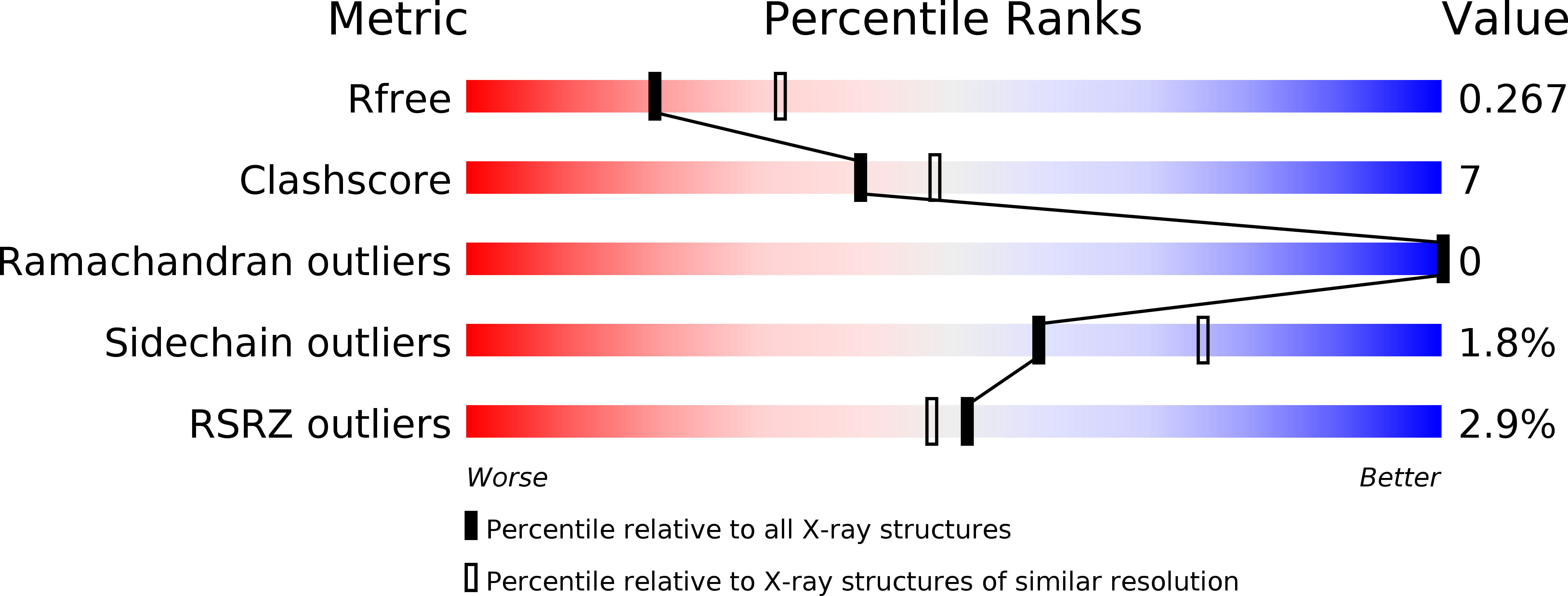
Resolution:
2.65 Å
R-Value Free:
0.27
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
C 1 2 1