Deposition Date
2019-01-22
Release Date
2019-07-17
Last Version Date
2024-03-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6J9E
Keywords:
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of Xanthomonos oryzae transcription elongation complex with NusA and the bacteriophage protein P7
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (strain PXO99A) (Taxon ID: 360094)
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Taxon ID: 64187)
Xanthomonas virus Xp10 (Taxon ID: 232237)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Taxon ID: 64187)
Xanthomonas virus Xp10 (Taxon ID: 232237)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
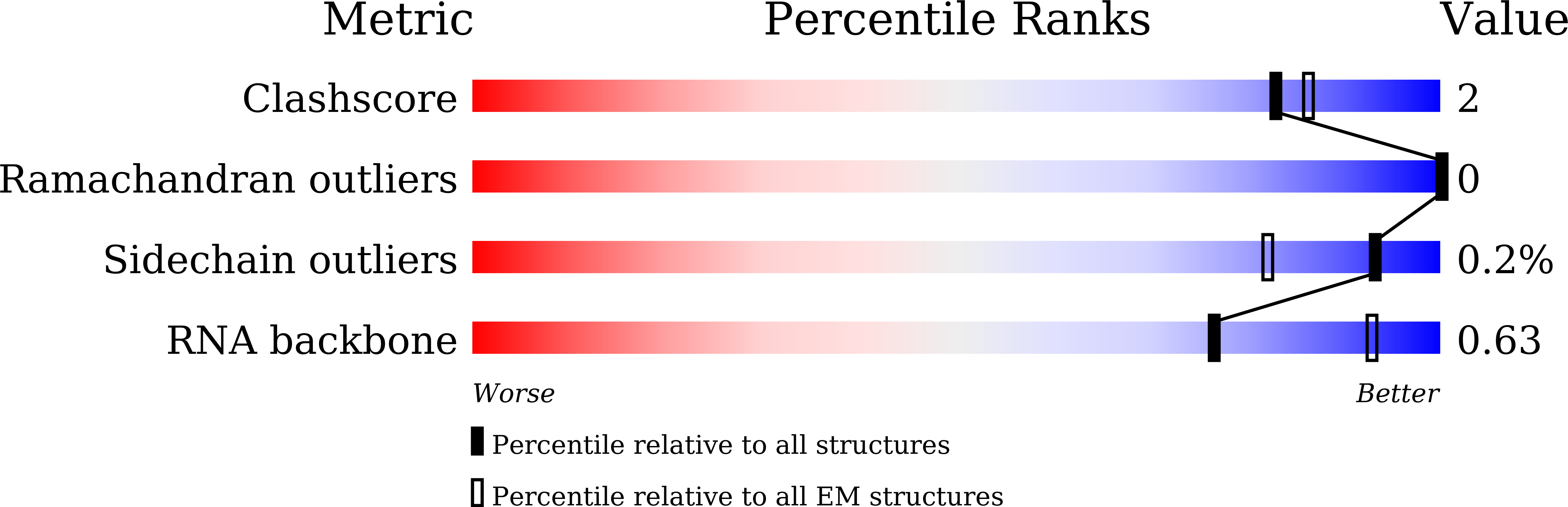
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.41 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE