Deposition Date
2018-09-27
Release Date
2019-06-05
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6HRN
Keywords:
Title:
C-Phycocyanin from heterocyst forming filamentous cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. WR13
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Nostoc sp. (Taxon ID: 1180)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
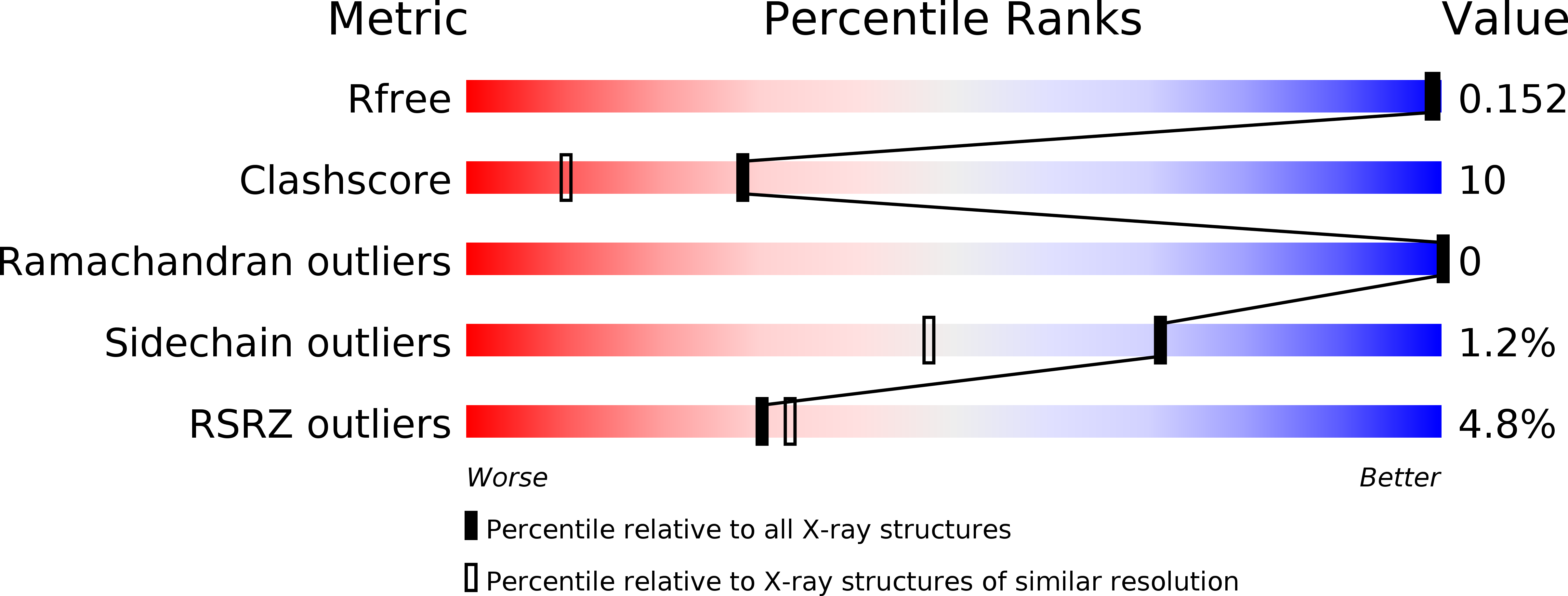
Resolution:
1.51 Å
R-Value Free:
0.15
R-Value Work:
0.11
R-Value Observed:
0.11
Space Group:
P 63


