Deposition Date
2018-09-26
Release Date
2019-02-13
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6HR8
Keywords:
Title:
HMG-CoA reductase from Methanothermococcus thermolithotrophicus in complex with NADPH at 2.9 A resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
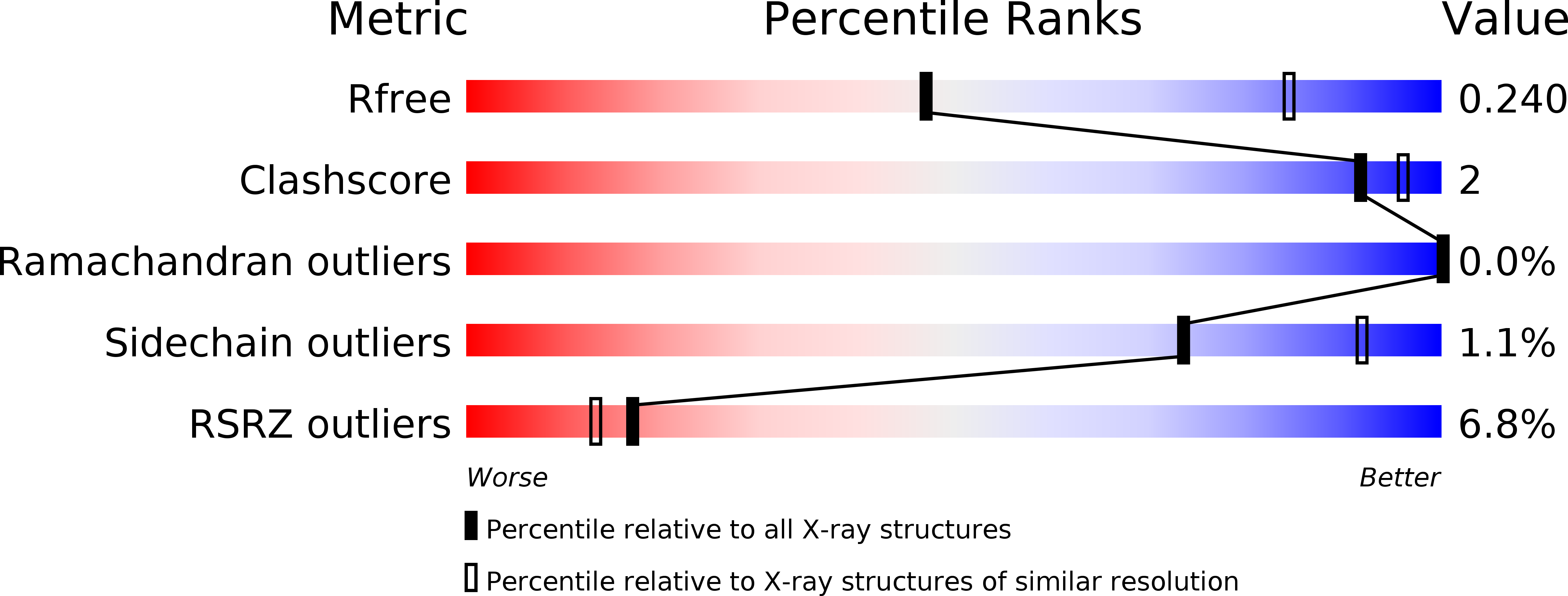
Resolution:
2.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 4 21 2