Deposition Date
2018-04-23
Release Date
2018-08-29
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
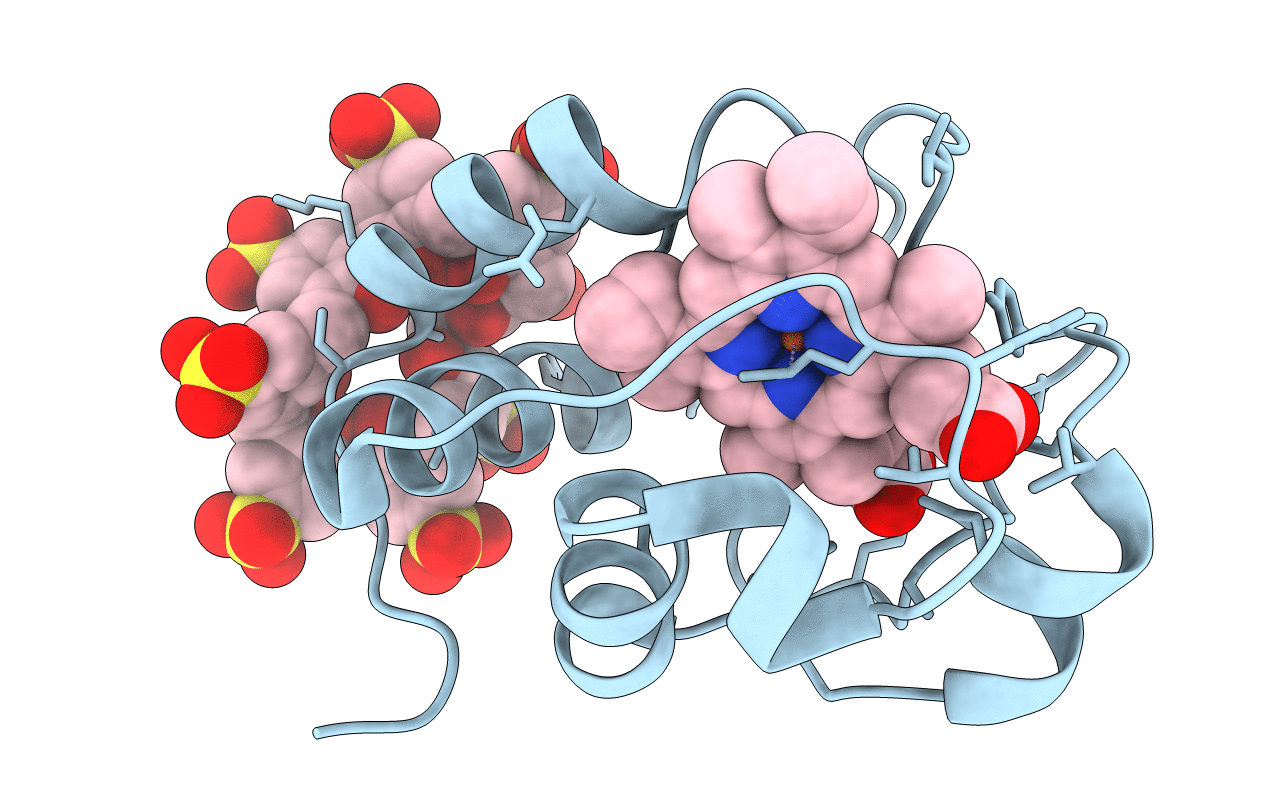
PDB ID:
6GD7
Keywords:
Title:
Cytochrome c in complex with Sulfonato-calix[8]arene, H3 form with PEG
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.55 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.15
Space Group:
H 3


