Deposition Date
2018-04-17
Release Date
2019-01-09
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6GCI
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of the bongkrekic acid-inhibited mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermothelomyces thermophila (strain ATCC 42464 / BCRC 31852 / DSM 1799) (Taxon ID: 573729)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
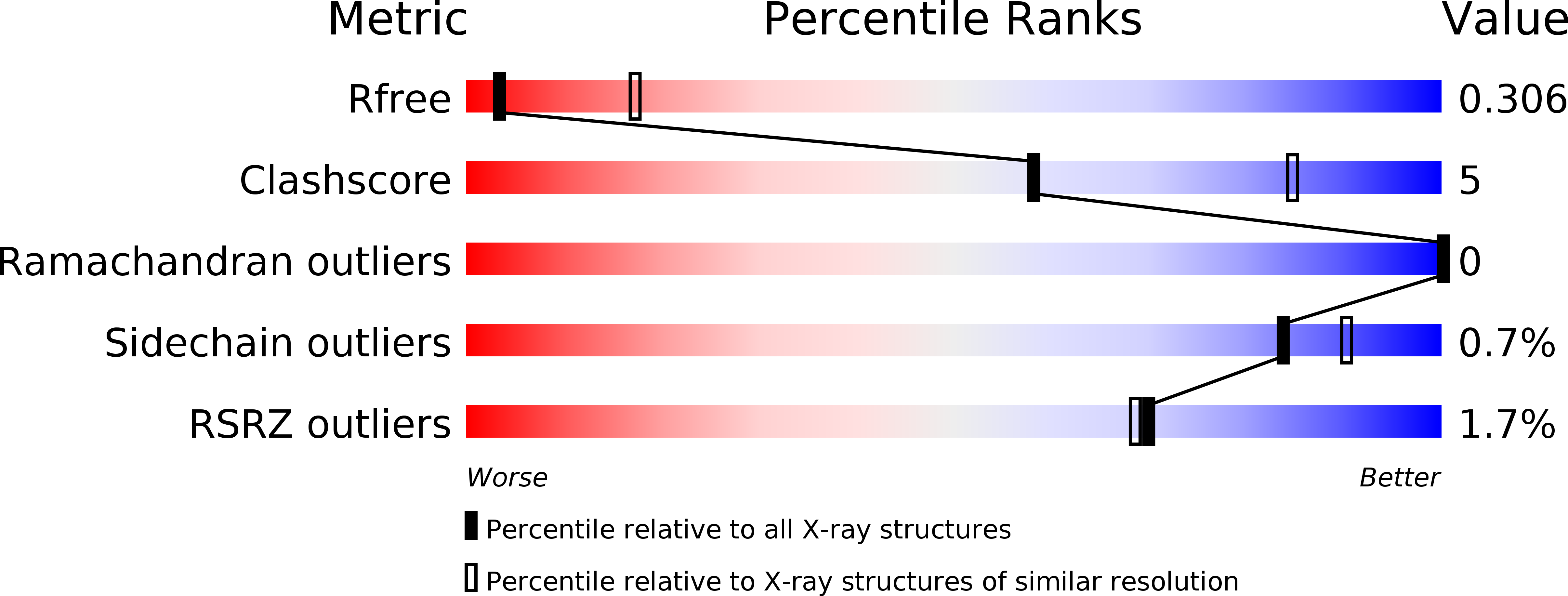
Resolution:
3.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.25
R-Value Observed:
0.25
Space Group:
P 32 2 1