Deposition Date
2018-04-06
Release Date
2018-06-27
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6G7J
Keywords:
Title:
Retinal isomerization in bacteriorhodopsin revealed by a femtosecond X-ray laser: 457-646 fs state structure
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
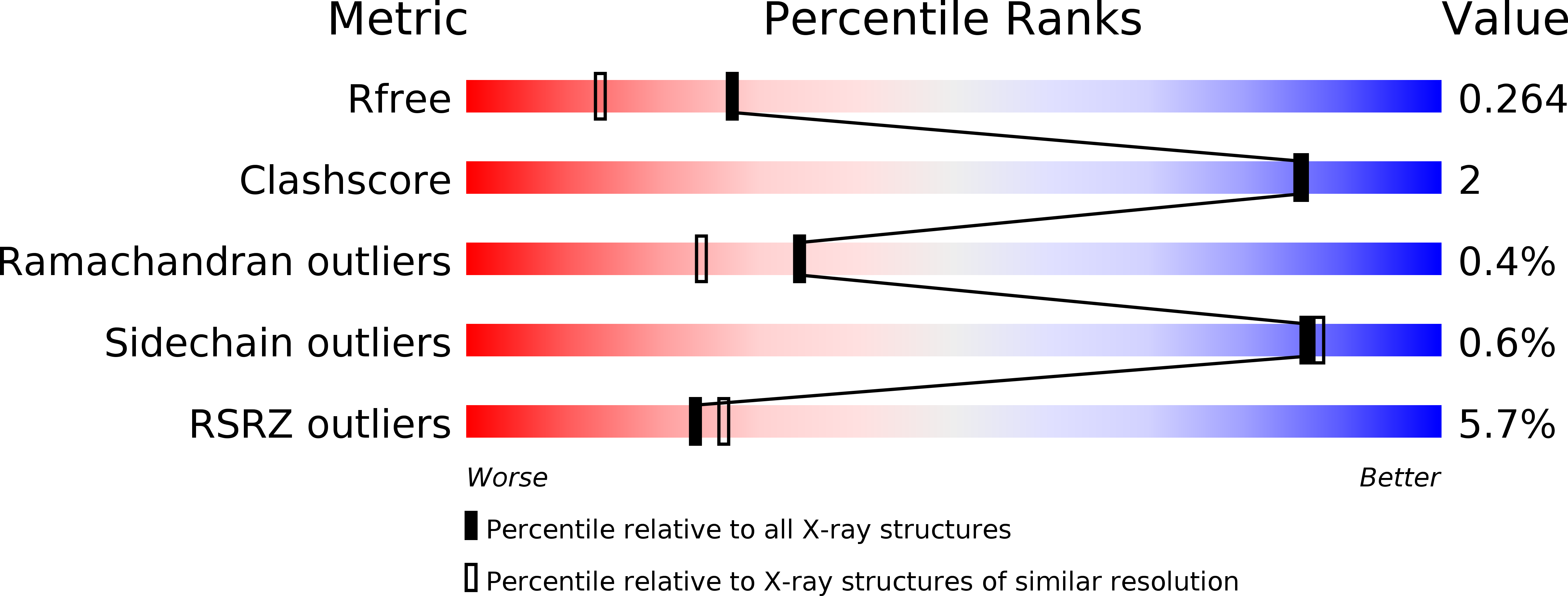
Resolution:
1.90 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 63