Deposition Date
2017-12-18
Release Date
2018-07-18
Last Version Date
2024-01-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6FB5
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of a Tailored I-CreI Homing Endonuclease Protein (3115 variant) in complex with an altered version of its target DNA (Haemoglobin beta subunit gene) at 5NNN region in the presence of Magnesium
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Taxon ID: 3055)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
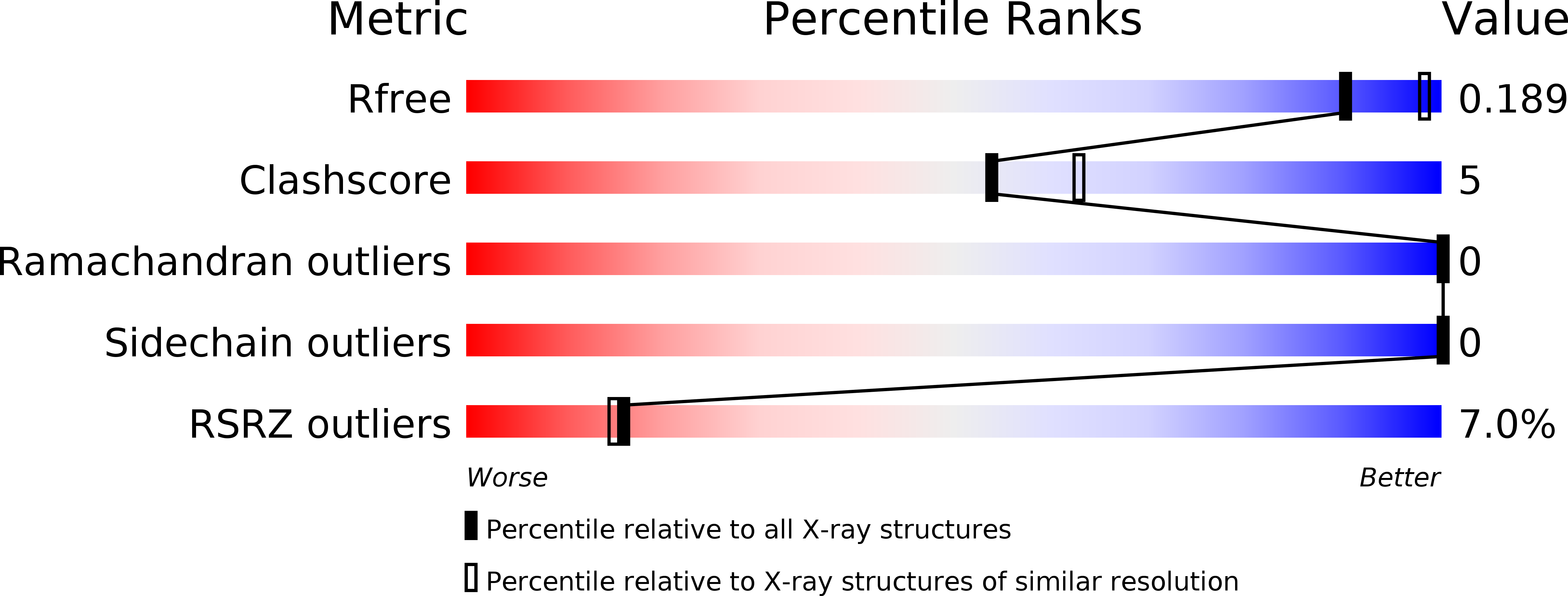
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 1 21 1