Deposition Date
2017-12-15
Release Date
2018-01-24
Last Version Date
2025-10-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6FAH
Keywords:
Title:
Molecular basis of the flavin-based electron-bifurcating caffeyl-CoA reductase reaction
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
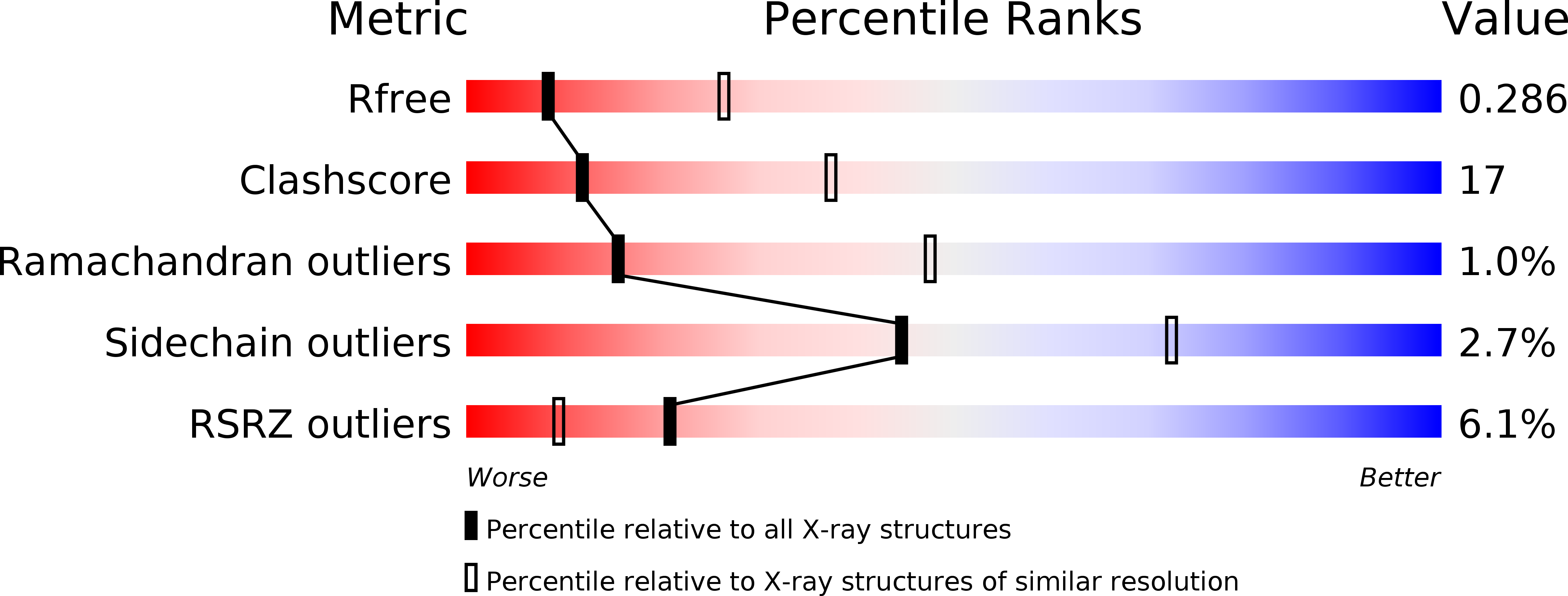
Resolution:
3.13 Å
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.23
R-Value Observed:
0.23
Space Group:
C 1 2 1