Deposition Date
2017-12-12
Release Date
2018-03-14
Last Version Date
2024-01-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6F88
Keywords:
Title:
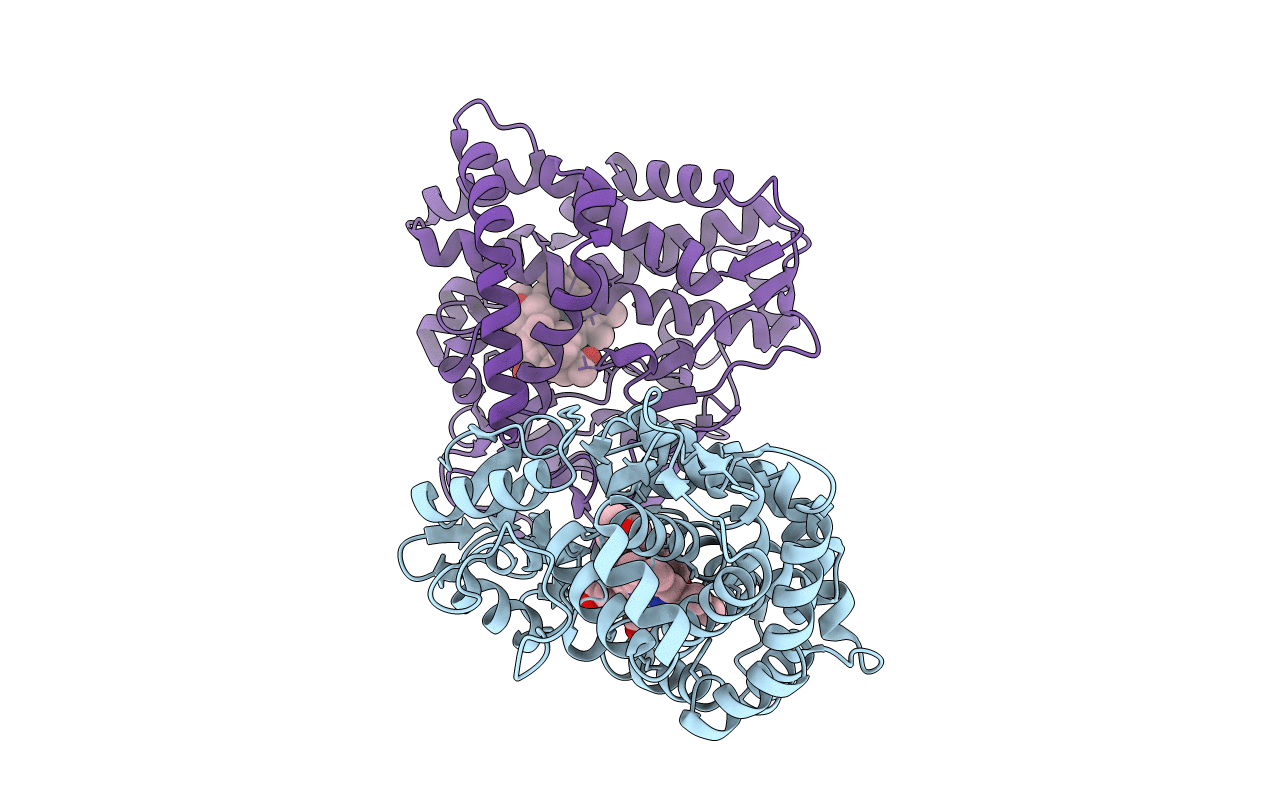
Crystal structure of cytochrome P450 CYP260A1 (S276N) bound with progesterone
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Sorangium cellulosum (strain So ce56) (Taxon ID: 448385)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
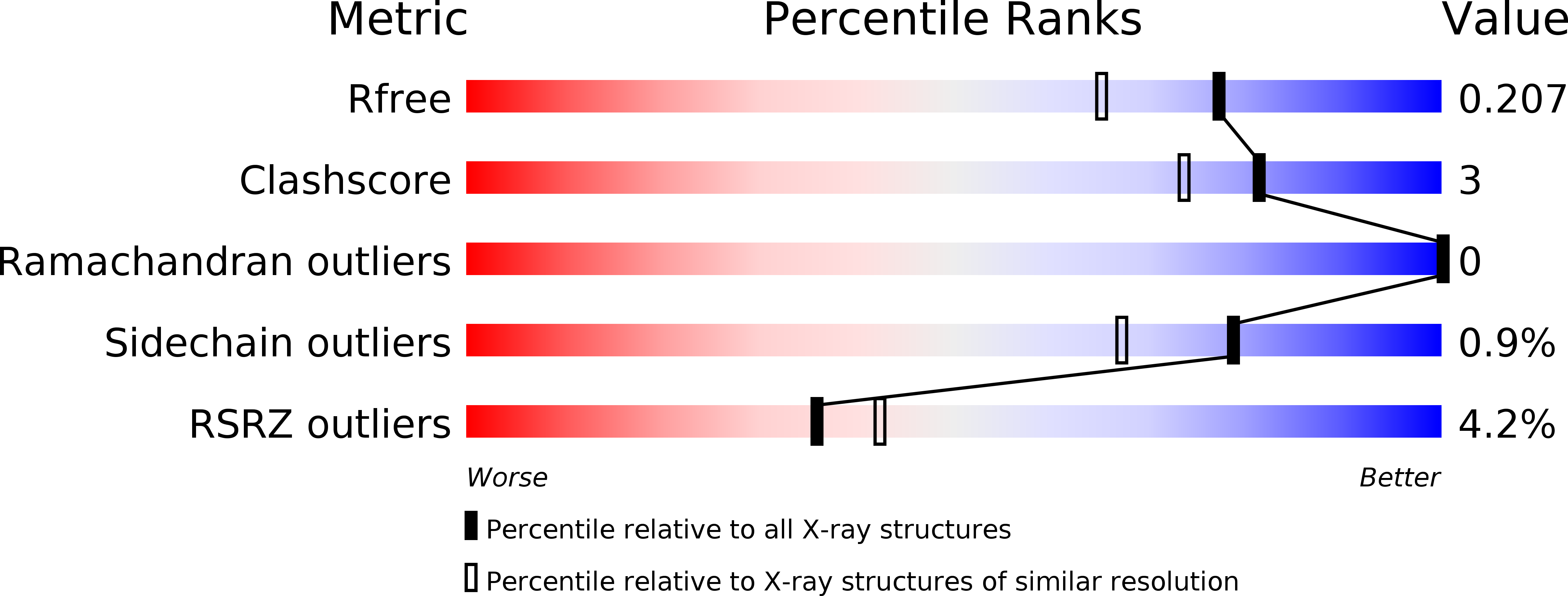
Resolution:
1.75 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
C 1 2 1