Deposition Date
2017-12-07
Release Date
2018-02-14
Last Version Date
2024-01-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6F7A
Keywords:
Title:
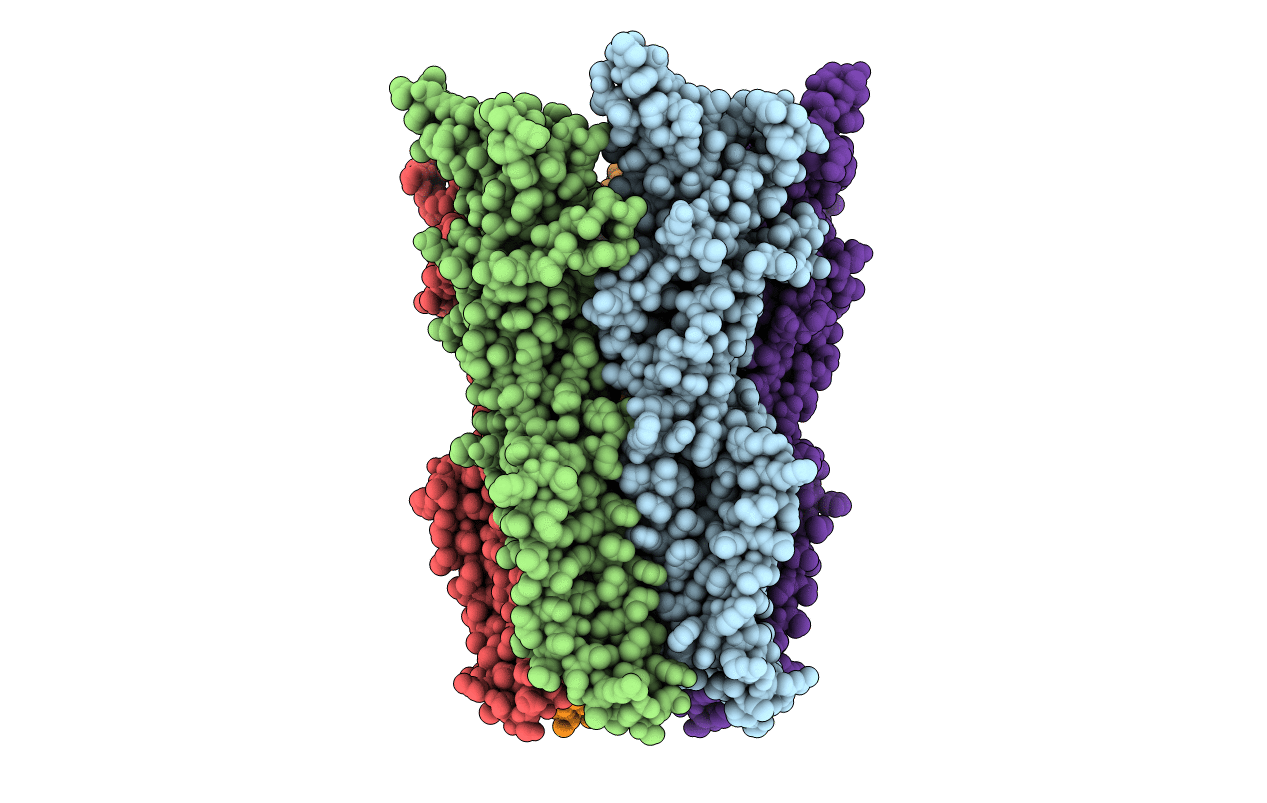
Gloeobacter Ligand-gated Ion Channel (GLIC) closed state crystallized in an ultra-swollen lipidic mesophase
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Gloeobacter violaceus (strain PCC 7421) (Taxon ID: 251221)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
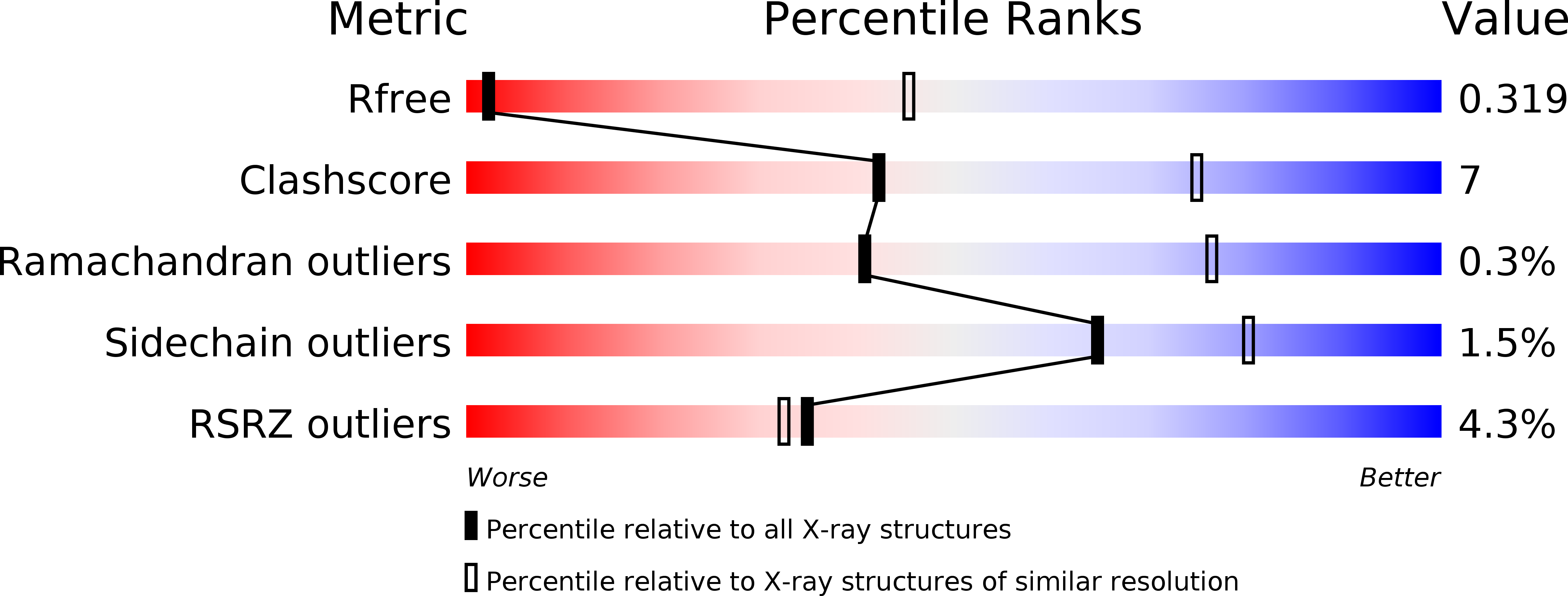
Resolution:
6.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.31
R-Value Work:
0.28
R-Value Observed:
0.28
Space Group:
C 2 2 21