Deposition Date
2017-10-13
Release Date
2018-10-24
Last Version Date
2024-05-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6EQO
Keywords:
Title:
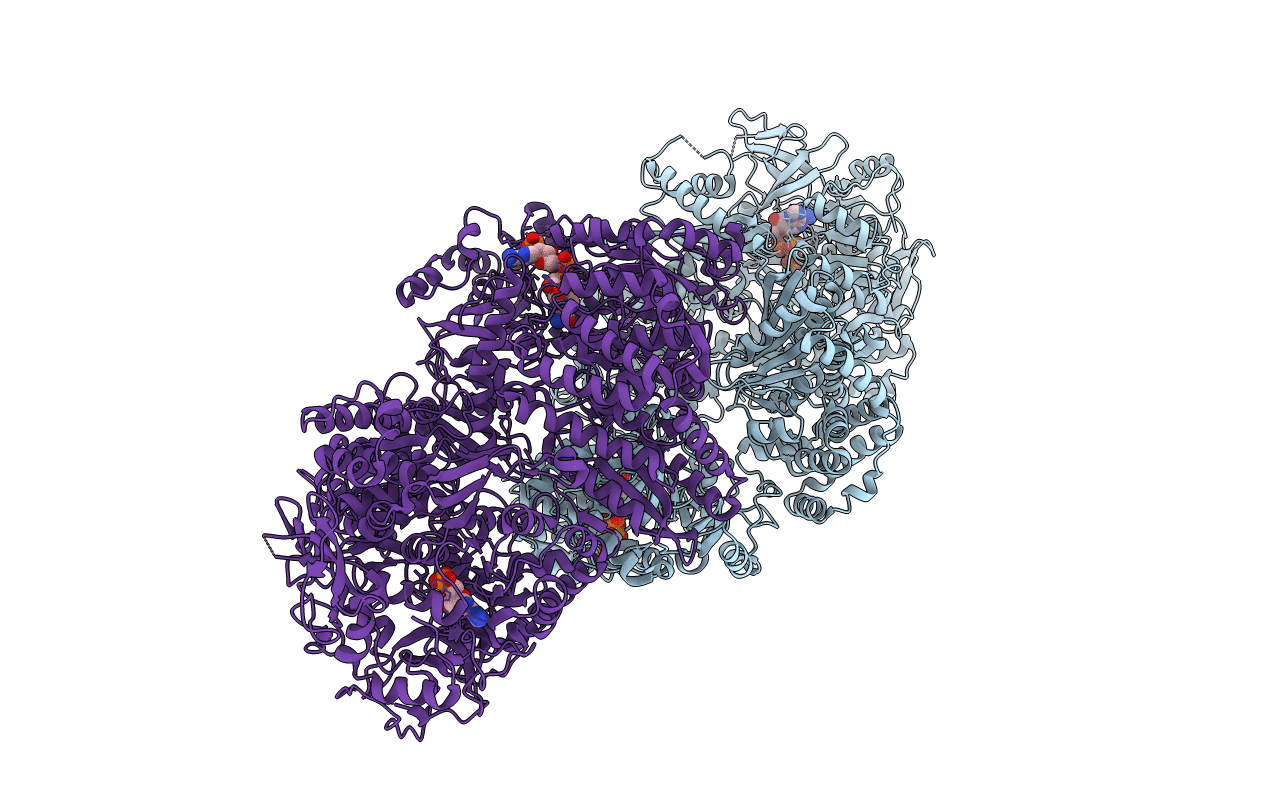
Tri-functional propionyl-CoA synthase of Erythrobacter sp. NAP1 with bound NADP+ and phosphomethylphosphonic acid adenylate ester
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Erythrobacter sp. NAP1 (Taxon ID: 237727)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
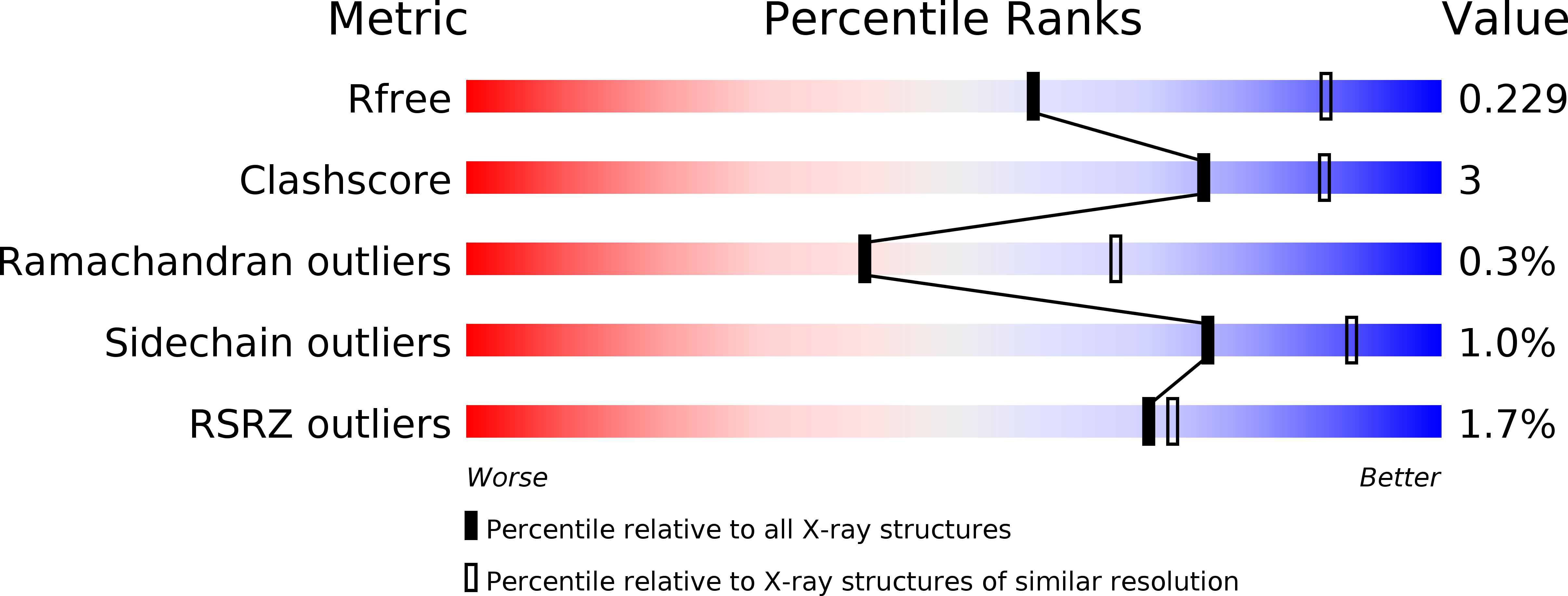
Resolution:
2.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
C 1 2 1