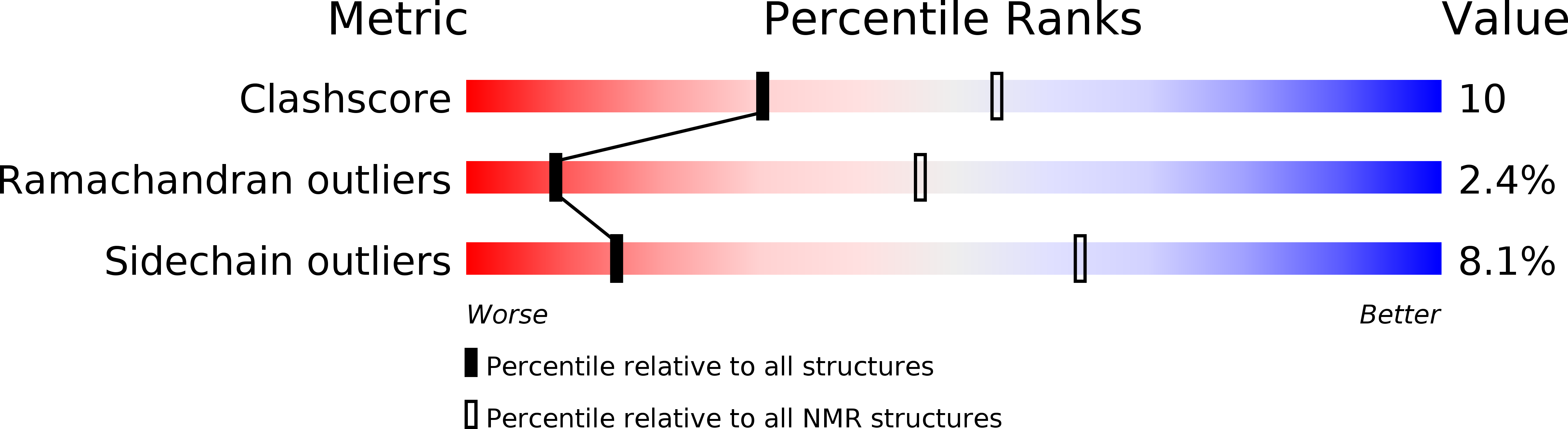
Deposition Date
2018-07-13
Release Date
2019-04-17
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6E3C
Keywords:
Title:
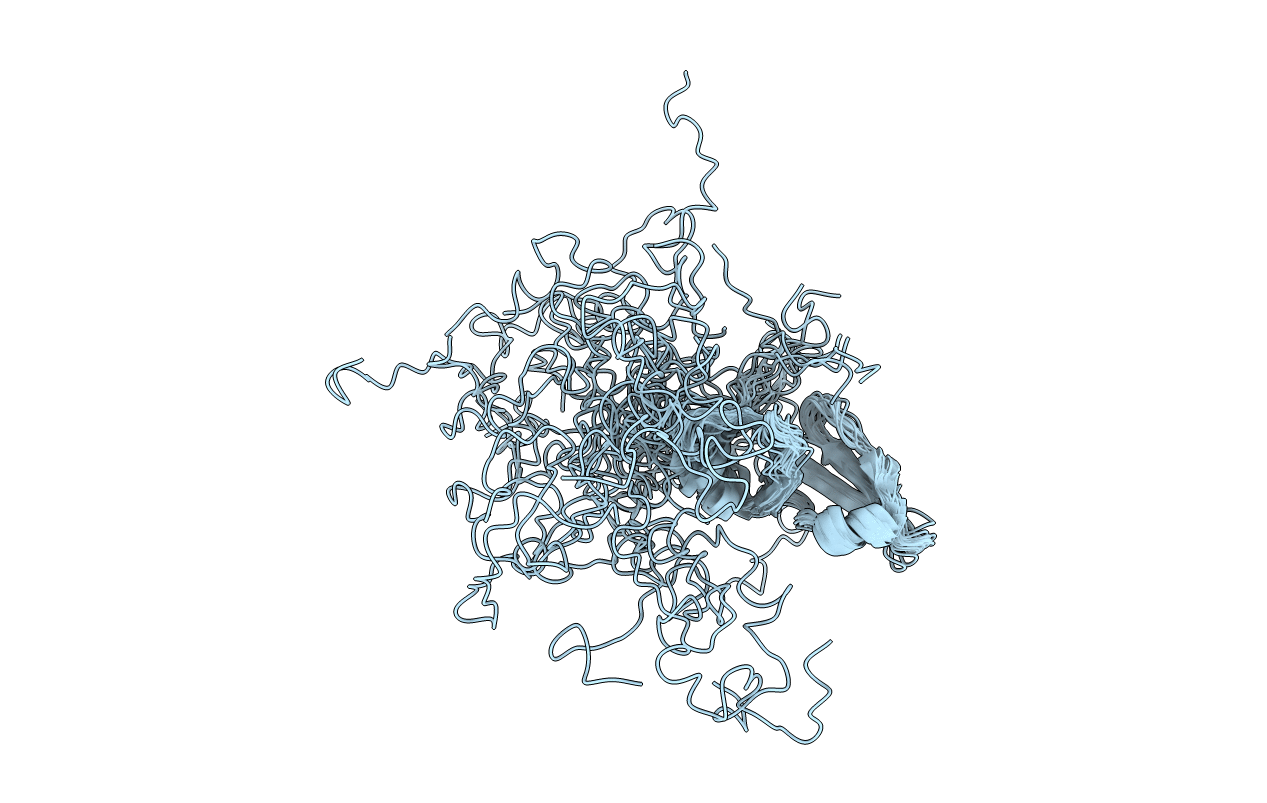
NMR Solution Structure of the Monomeric Form of the Phage L Decoration Protein
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Enterobacteria phage L (Taxon ID: 45441)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
250
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the least restraint violations