Deposition Date
2018-07-09
Release Date
2019-05-22
Last Version Date
2024-03-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6E13
Keywords:
Title:
Pseudomonas putida PqqB with a non-physiological zinc at the active site binds the substrate mimic, 5-cysteinyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (5-Cys-DOPA), non-specifically but supports the proposed function of the enzyme in pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthesis.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
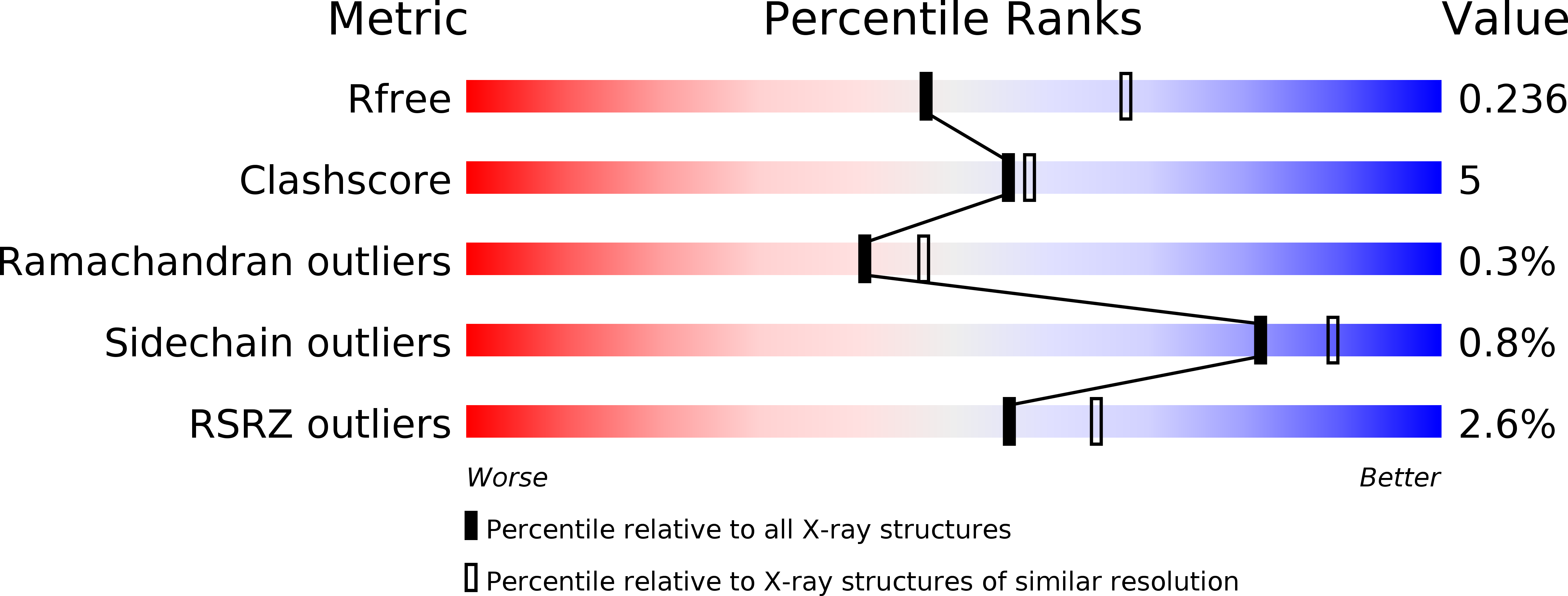
Resolution:
2.35 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 43 21 2