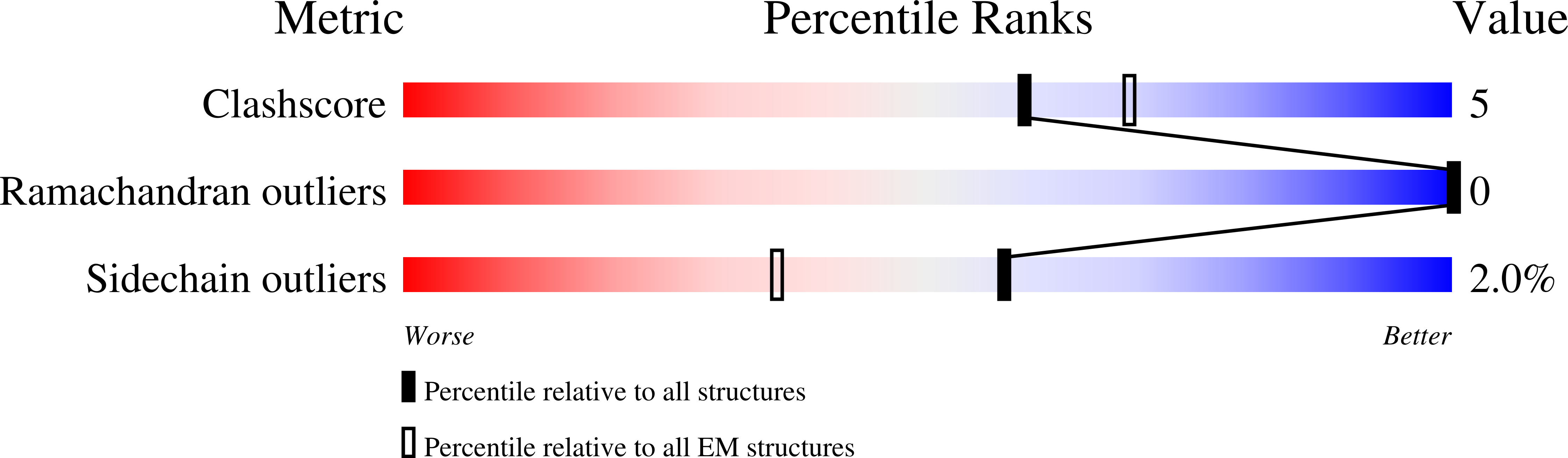
Deposition Date
2018-05-24
Release Date
2019-04-24
Last Version Date
2024-03-13
Entry Detail
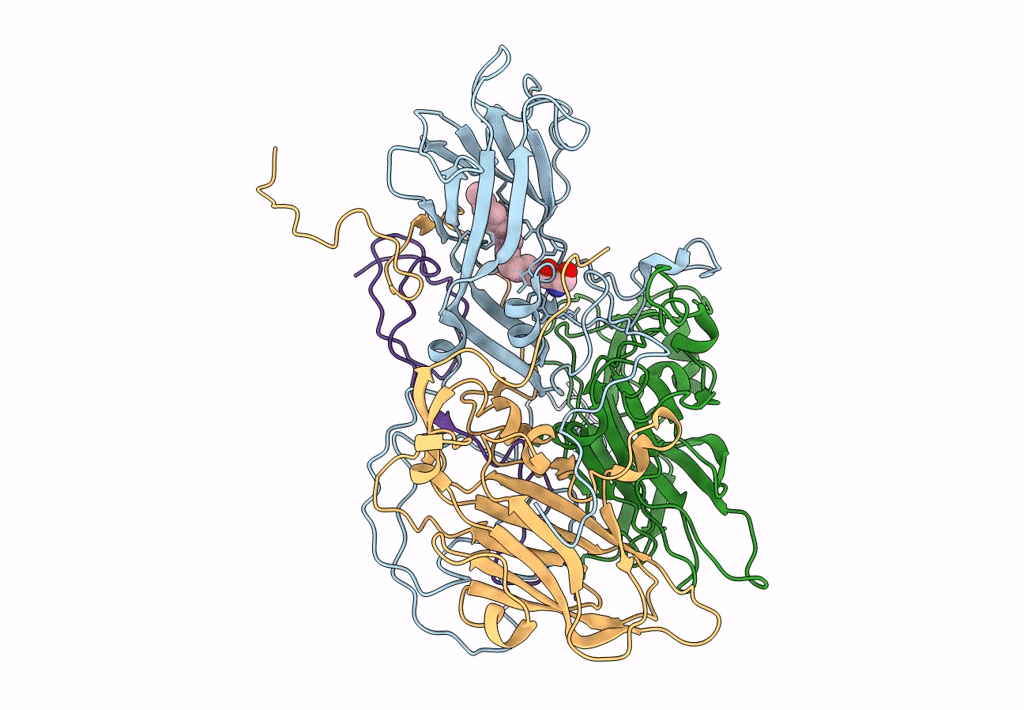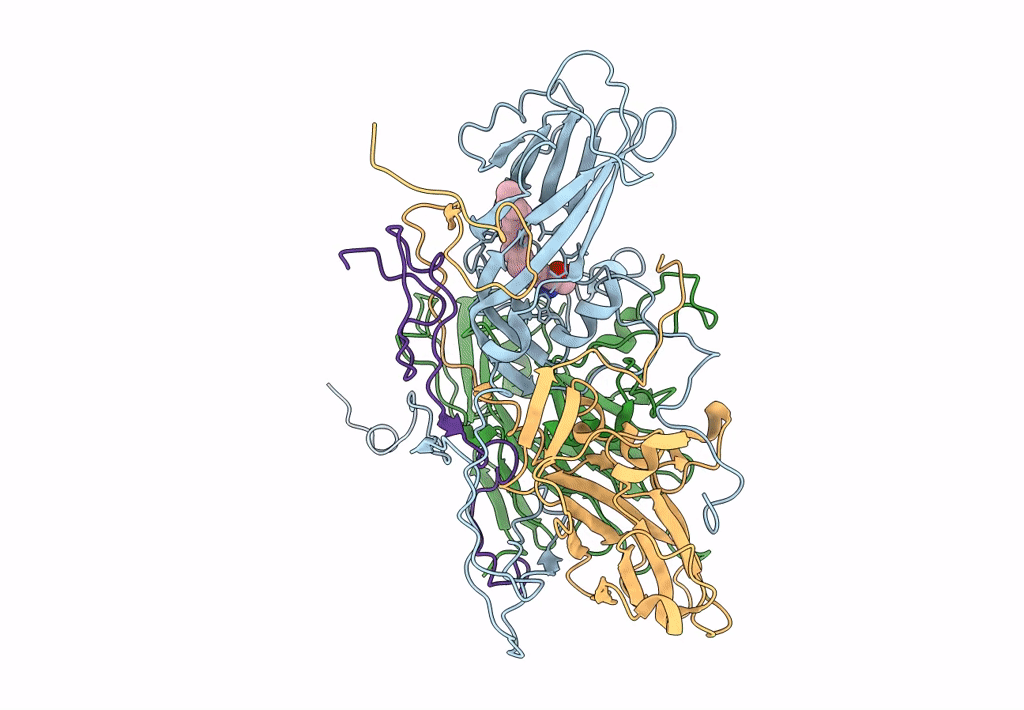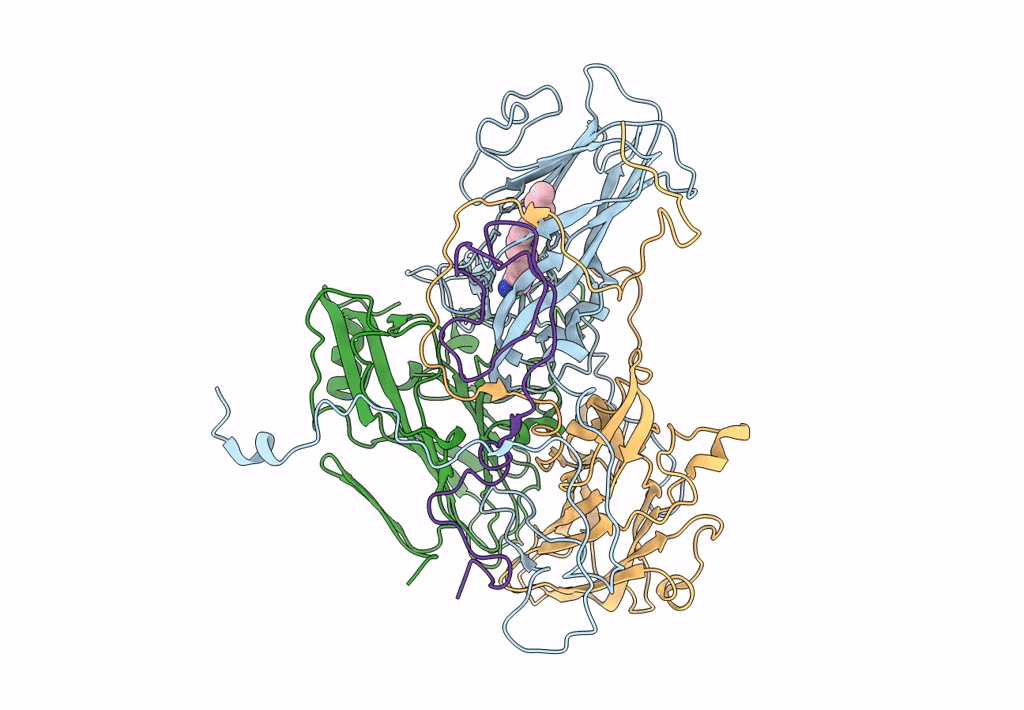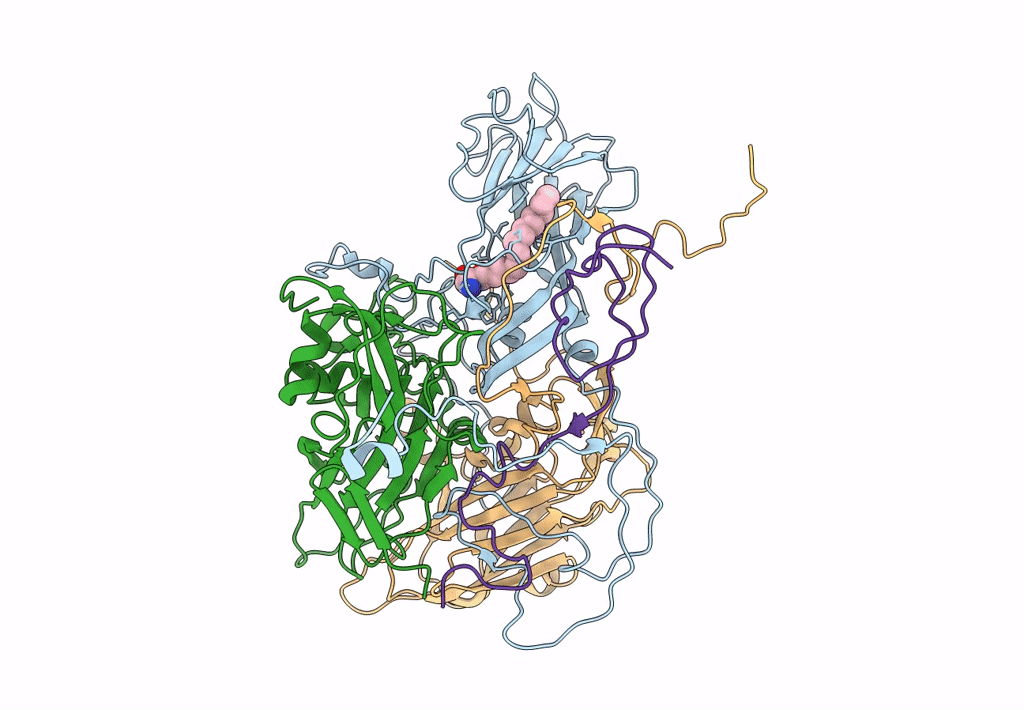
PDB ID:
6DIZ
Keywords:
Title:
EV-A71 strain 11316 complexed with tryptophan dendrimer MADAL_0385
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Enterovirus A71 (Taxon ID: 39054)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.59 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE