Deposition Date
2018-03-16
Release Date
2018-06-27
Last Version Date
2023-10-04
Entry Detail
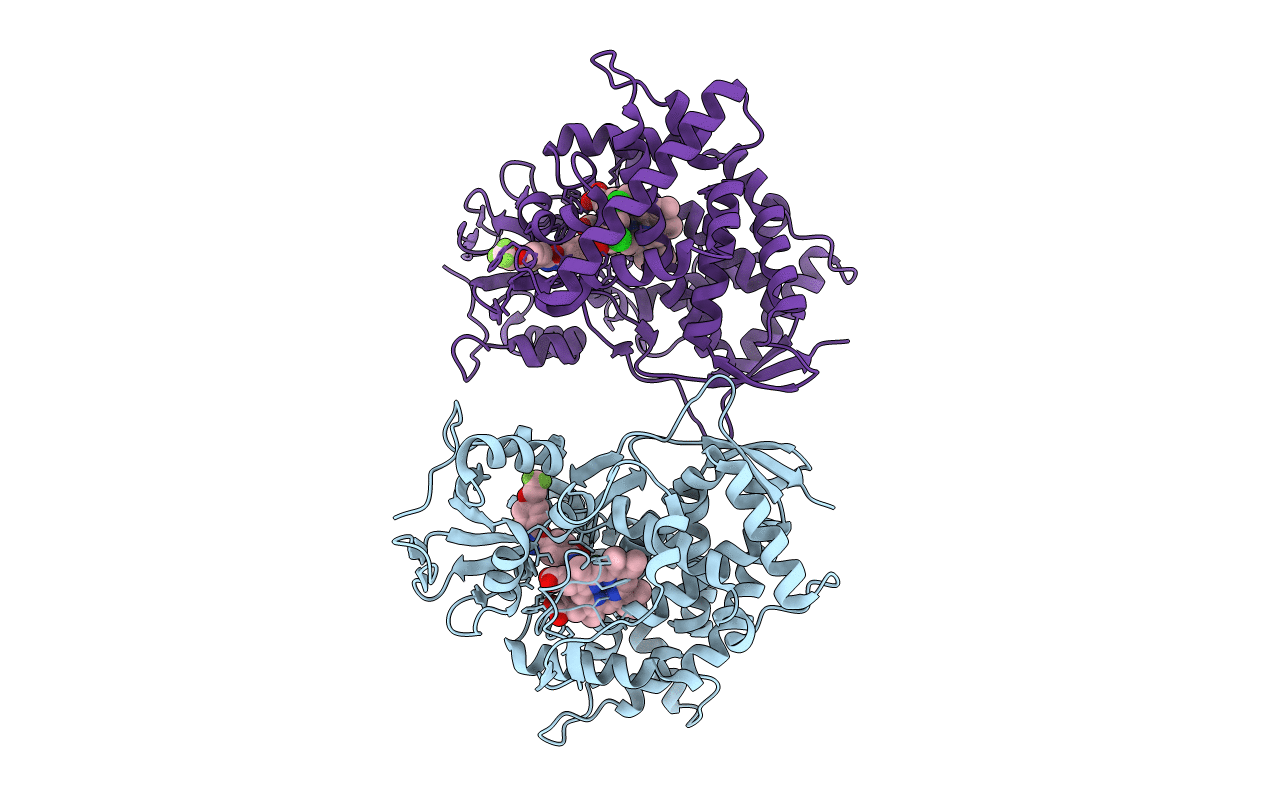
PDB ID:
6CR2
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of sterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51B) from Aspergillus fumigatus in complex with the VNI derivative N-(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethyl)-4-(5-(2-fluoro-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzamide
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Aspergillus fumigatus (Taxon ID: 330879)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.38 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 31


