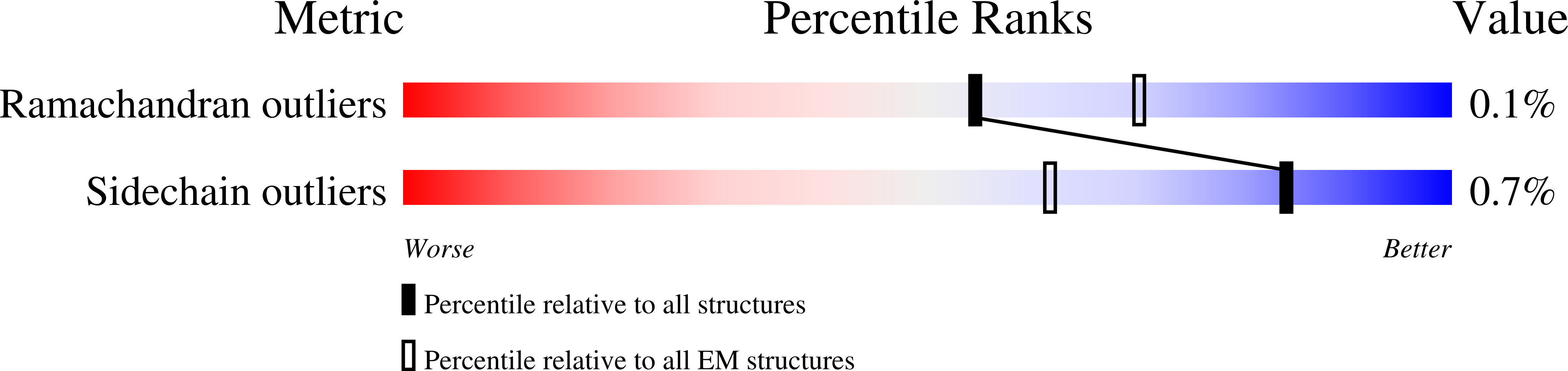
Deposition Date
2018-02-08
Release Date
2018-05-16
Last Version Date
2024-12-25
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6CDI
Keywords:
Title:
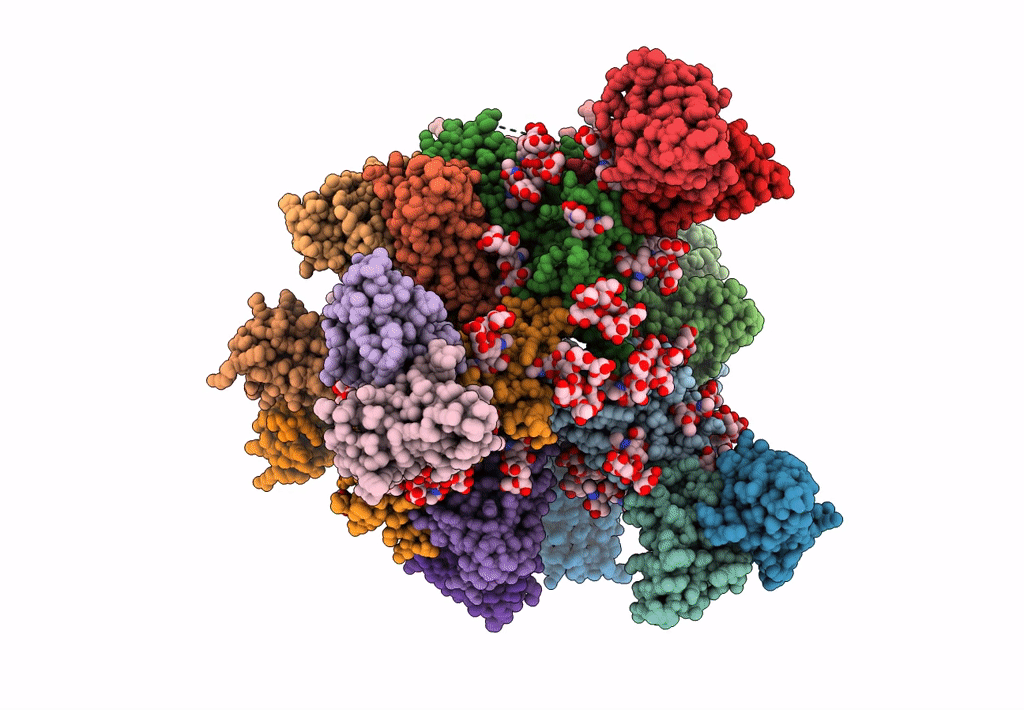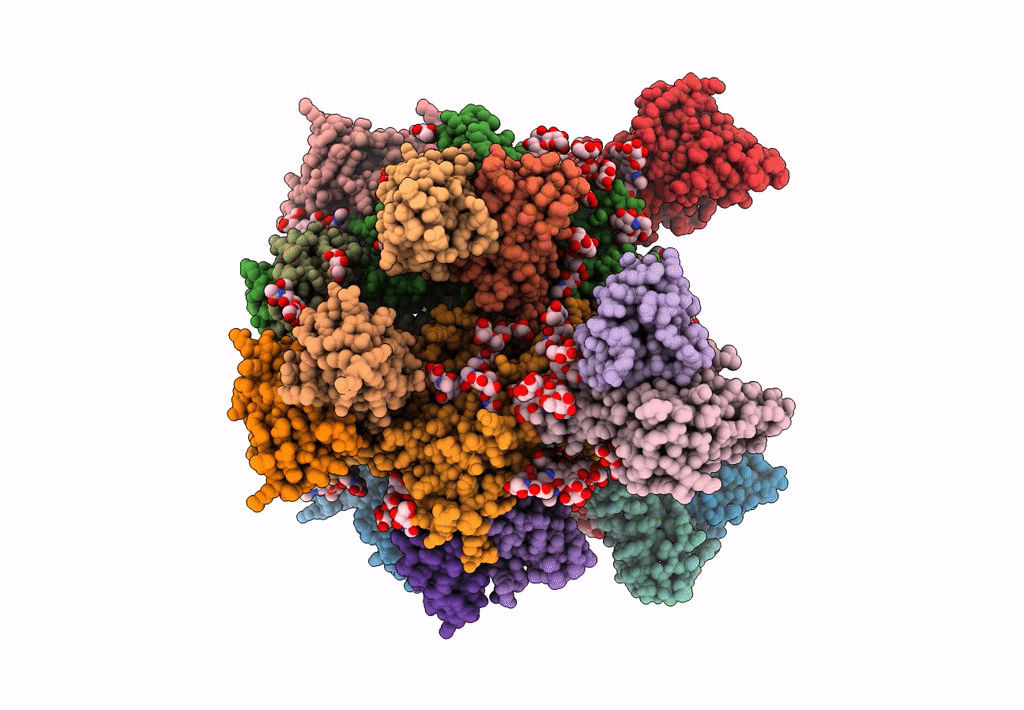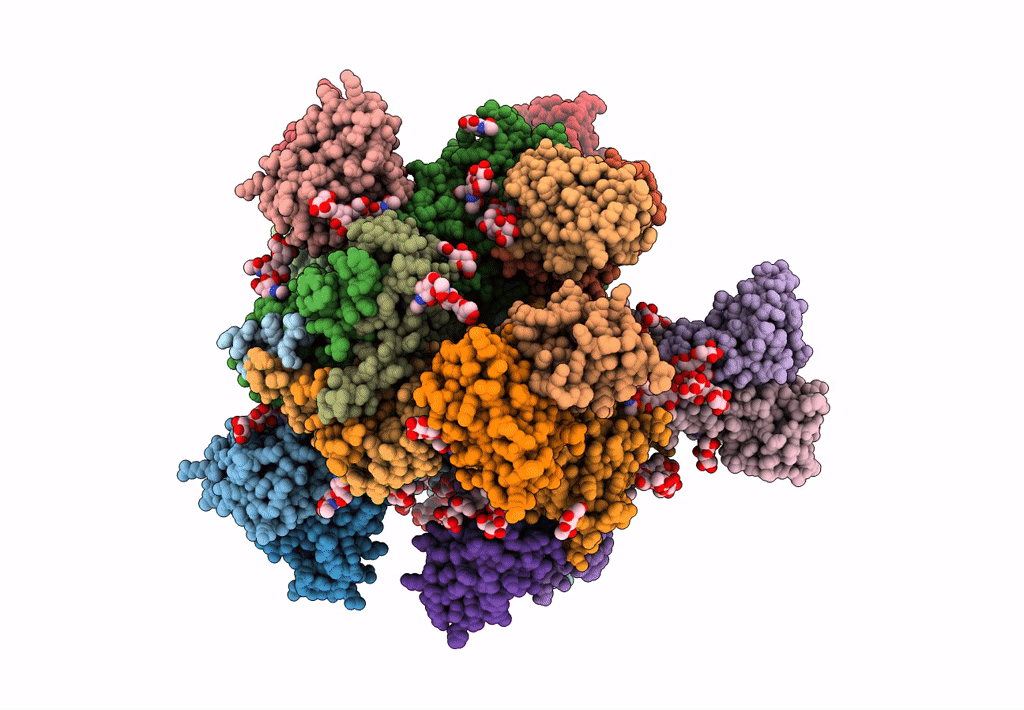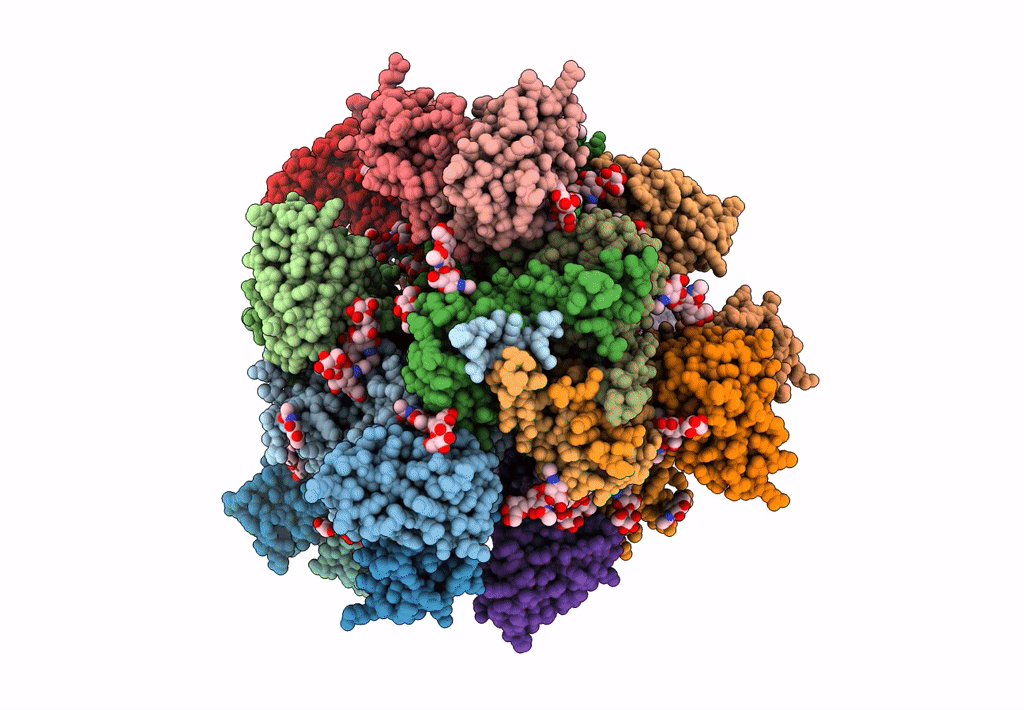
Cryo-EM structure at 3.6 A resolution of vaccine-elicited antibody vFP16.02 in complex with HIV-1 Env BG505 DS-SOSIP, and antibodies VRC03 and PGT122
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (Taxon ID: 11676)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE