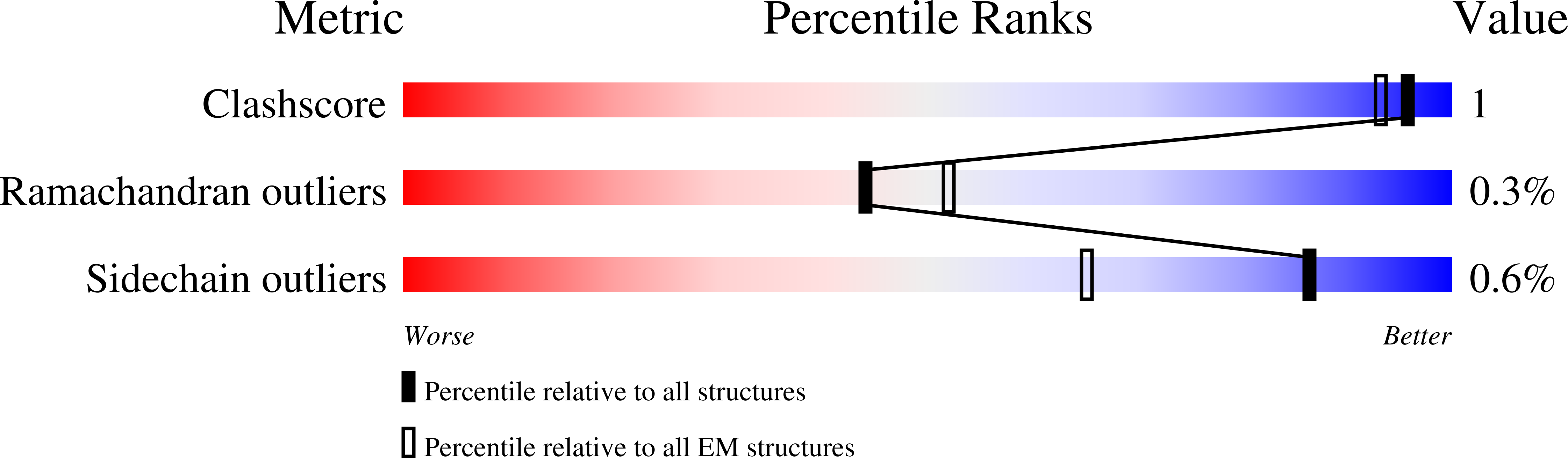
Deposition Date
2018-01-16
Release Date
2018-05-02
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6C5V
Keywords:
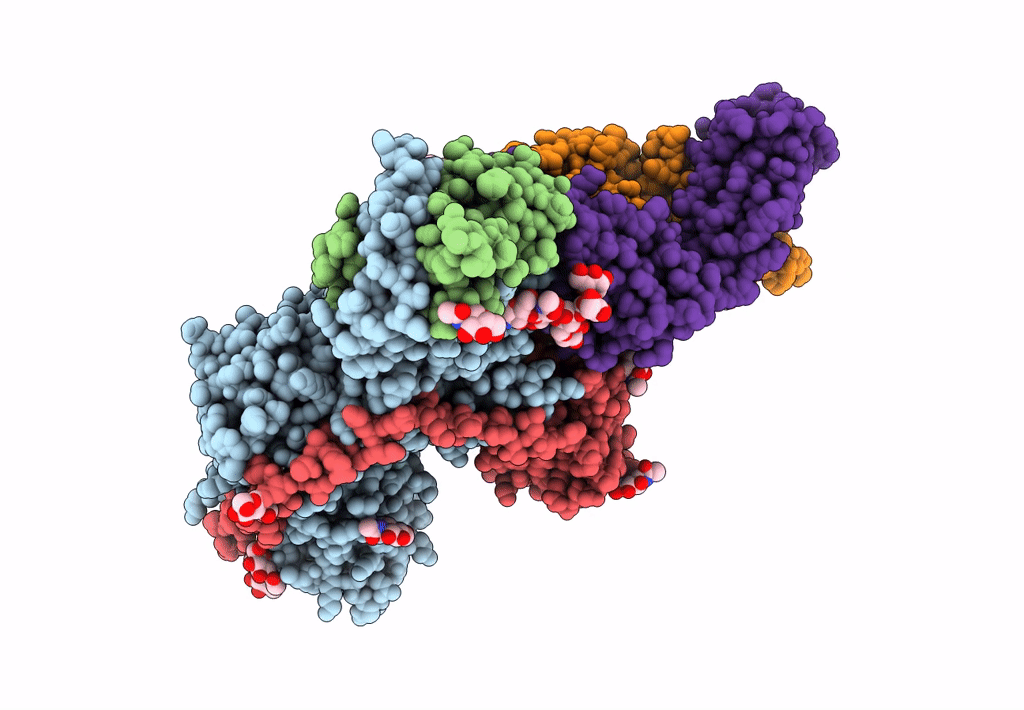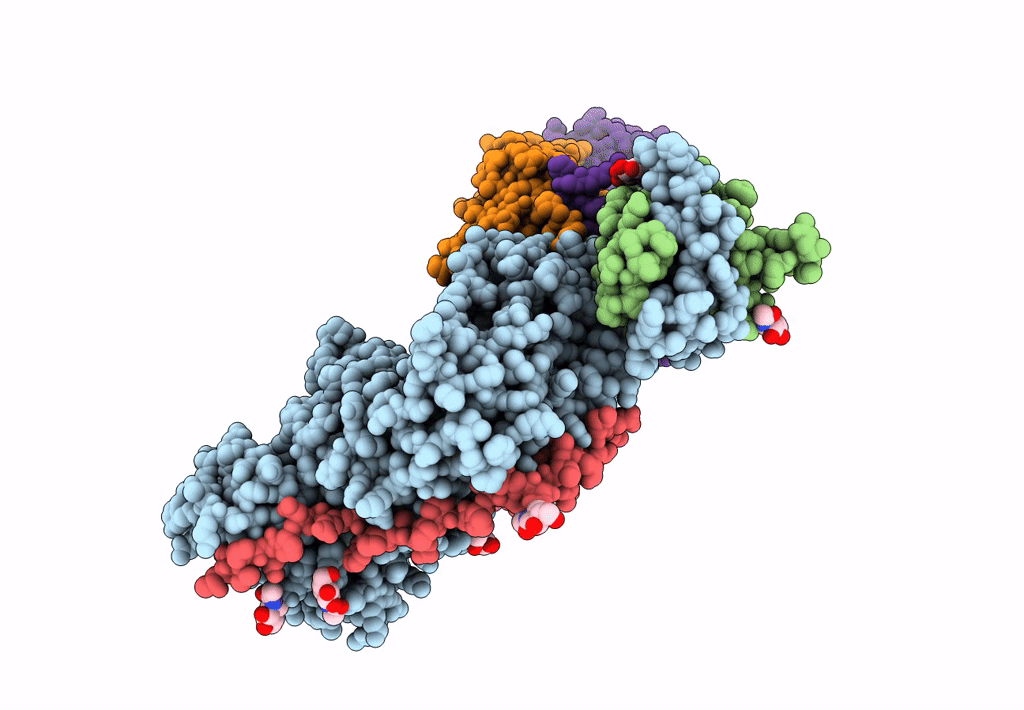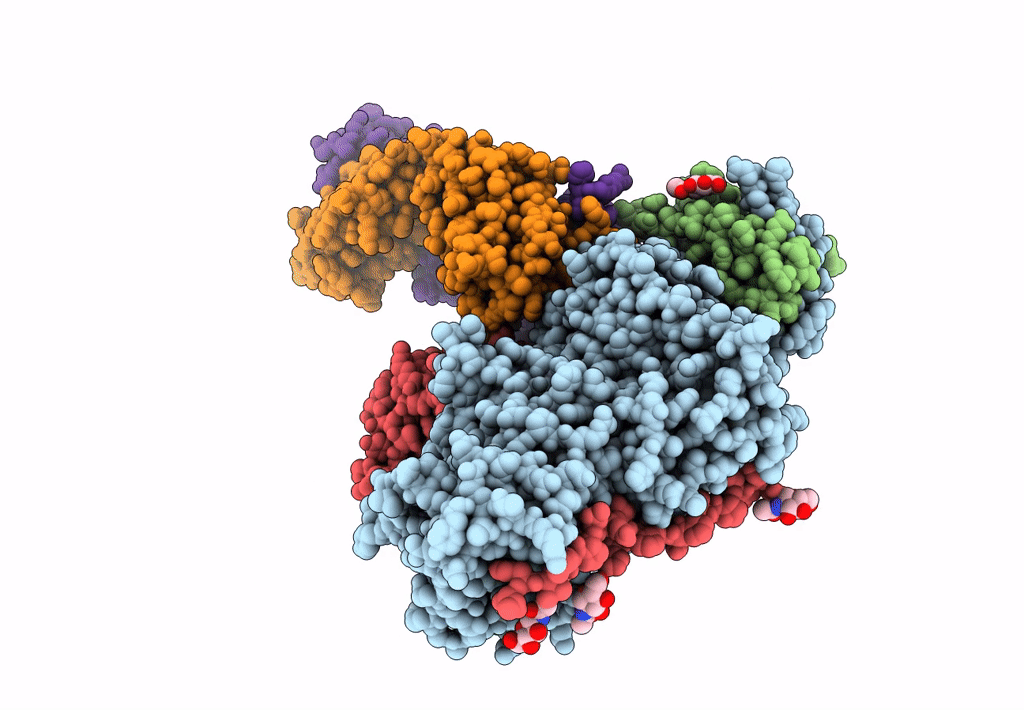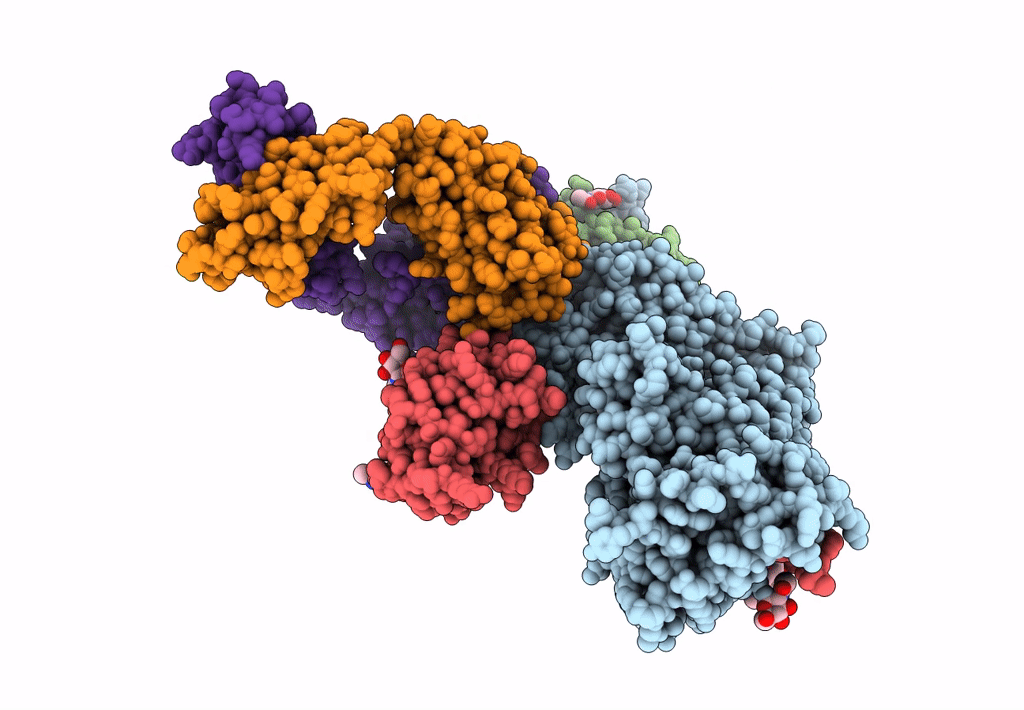
Title:
An anti-gH/gL antibody that neutralizes dual-tropic infection defines a site of vulnerability on Epstein-Barr virus
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Human herpesvirus 4 (Taxon ID: 10376)
Human herpesvirus 4 (Taxon ID: 82830)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Human herpesvirus 4 (Taxon ID: 82830)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.80 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE