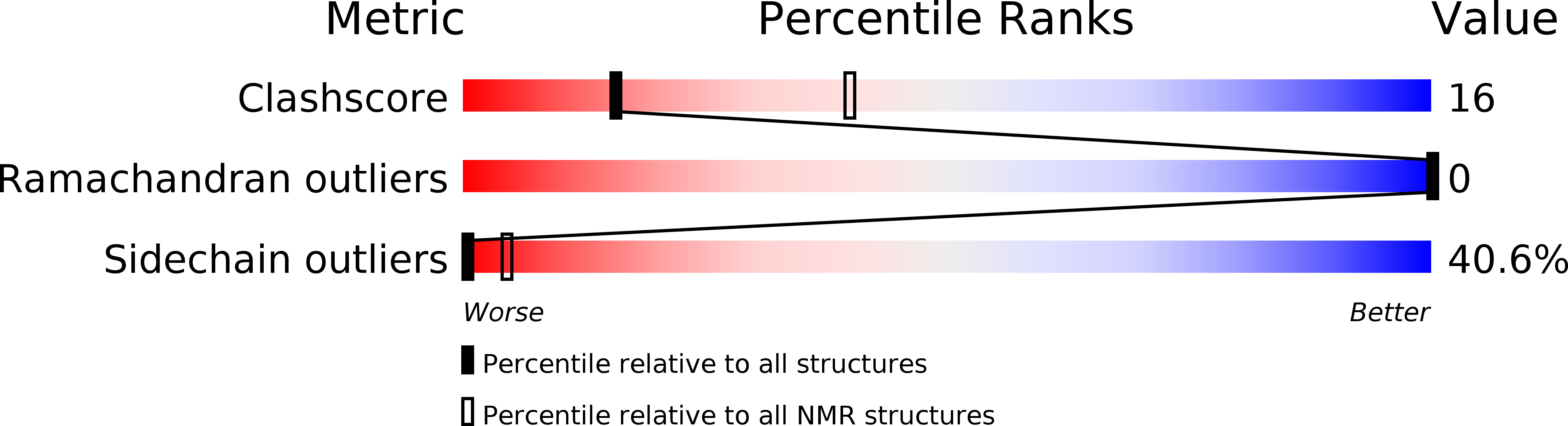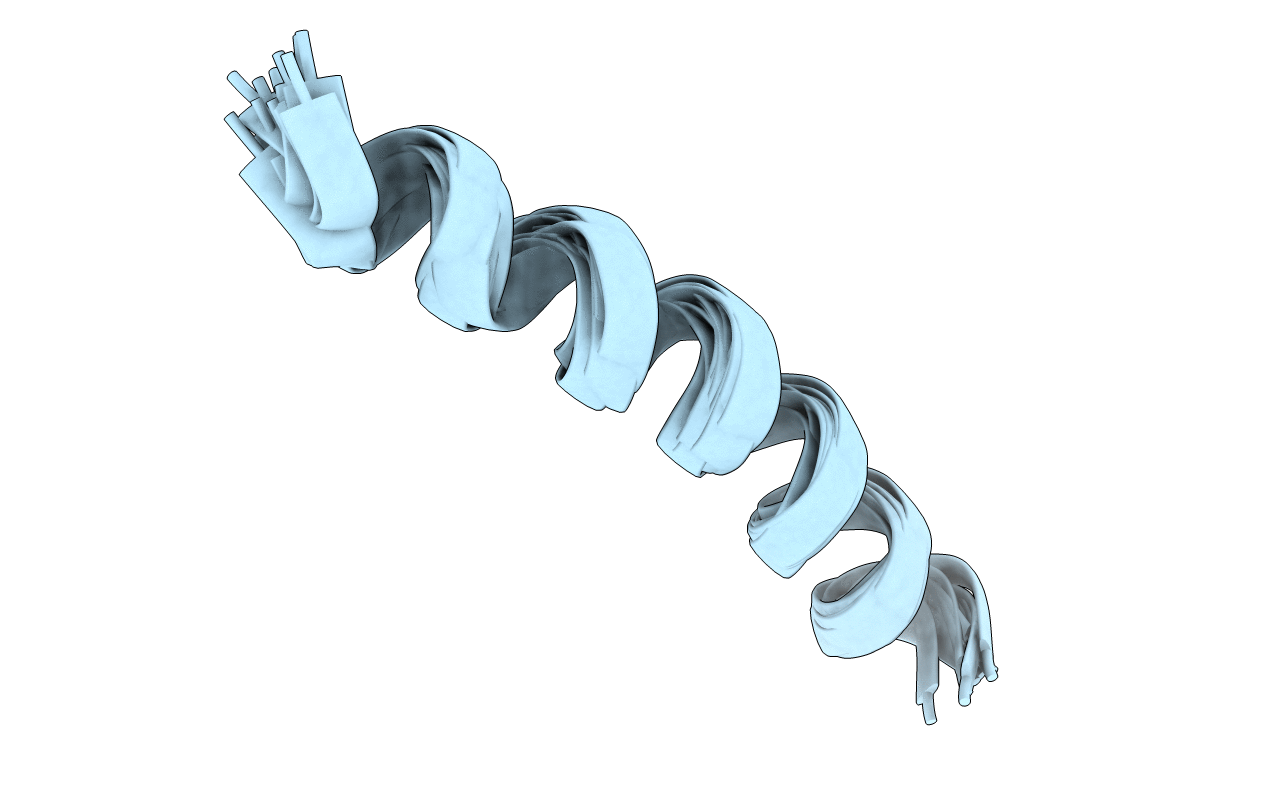
Deposition Date
2018-01-11
Release Date
2018-02-07
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6C41
Keywords:
Title:
The clavanin peptide in the presence of TFE (2,2,2-trifluoroethanol), presented a amphipathic alpha-helices from Phe-2 to Val-22 residues
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Styela clava (Taxon ID: 7725)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
200
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy