Deposition Date
2017-09-25
Release Date
2017-10-18
Last Version Date
2025-05-21
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6B45
Keywords:
Title:
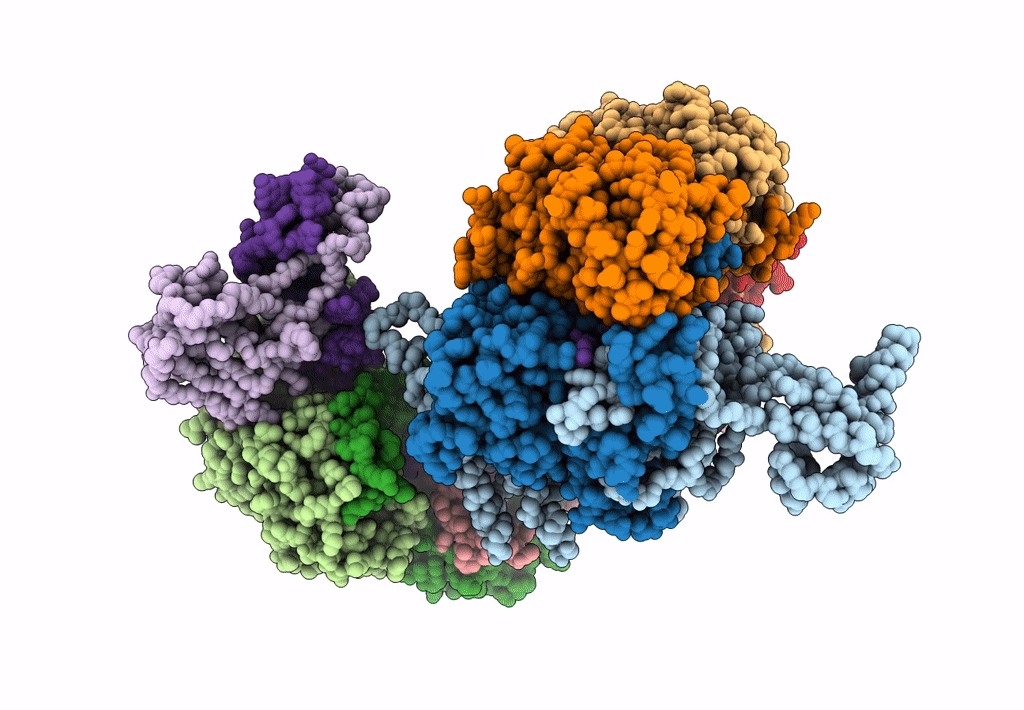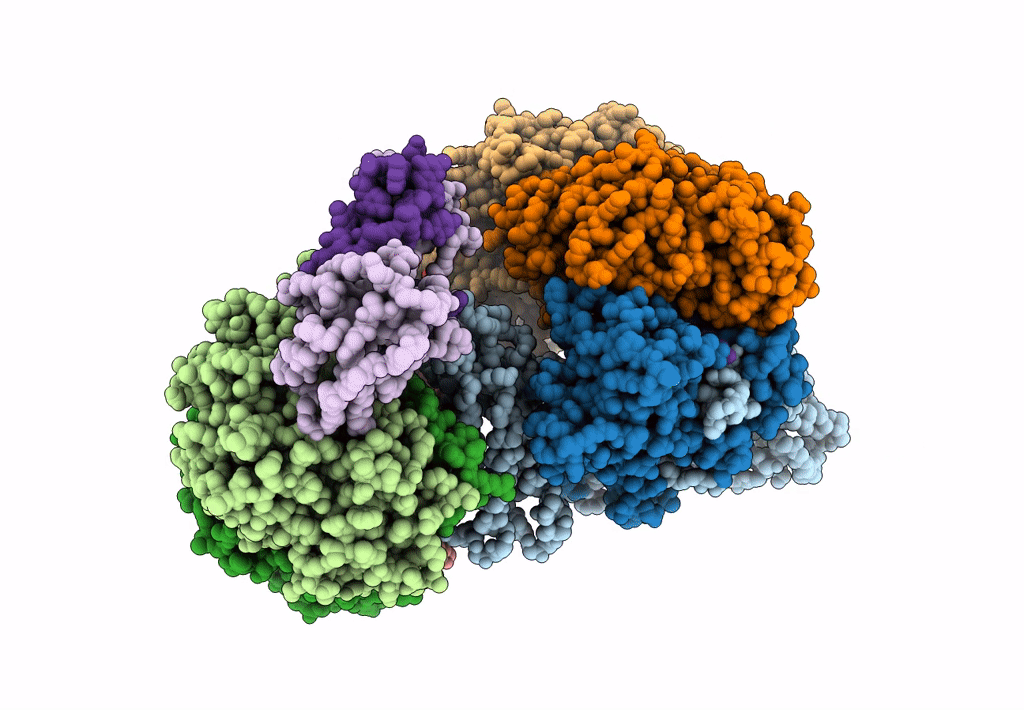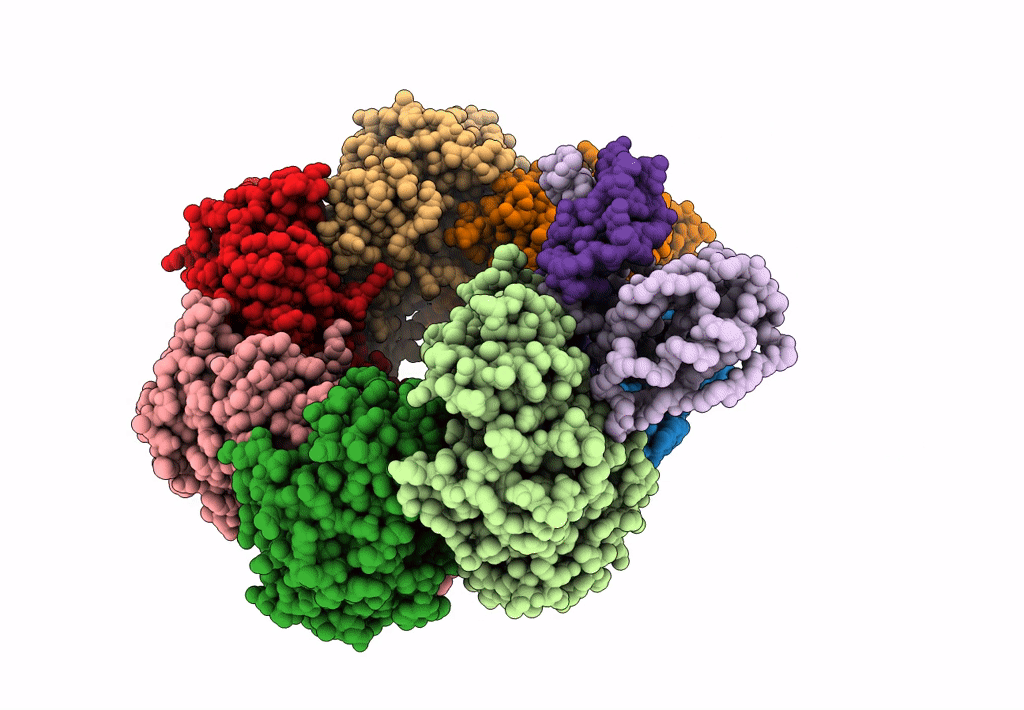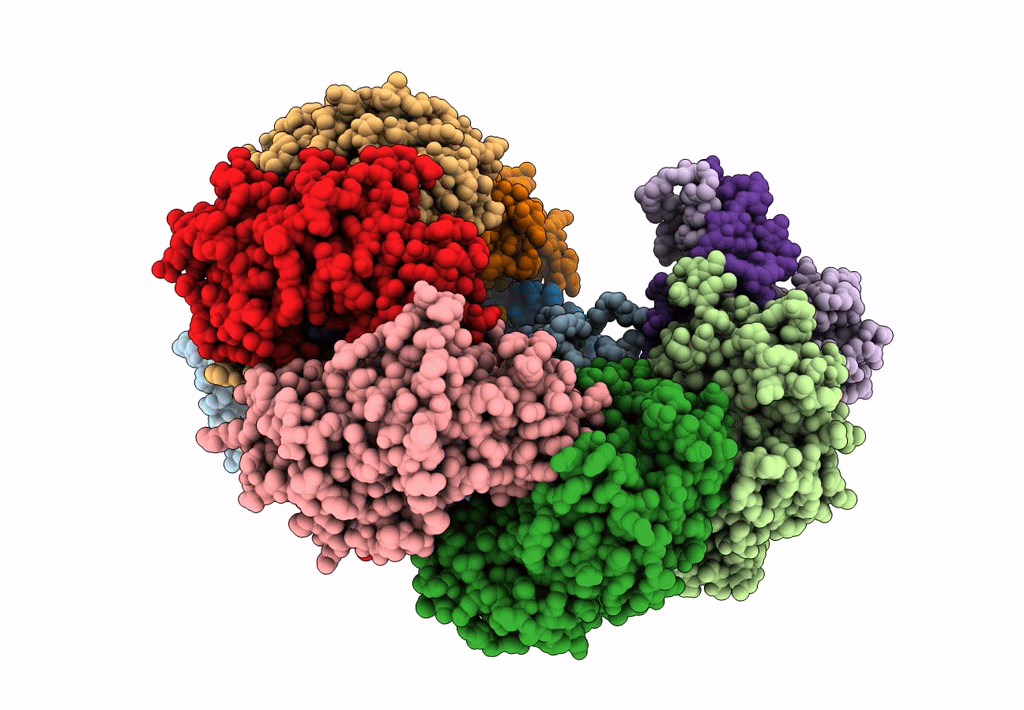
Cryo-EM structure of Type I-F CRISPR crRNA-guided Csy surveillance complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain UCBPP-PA14) (Taxon ID: 208963)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Taxon ID: 287)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Taxon ID: 287)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.50 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


