Deposition Date
2017-09-11
Release Date
2018-02-21
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6AZO
Keywords:
Title:
Structural and biochemical characterization of a non-canonical biuret hydrolase (BiuH) from the cyanuric acid catabolism pathway of Rhizobium leguminasorum bv. viciae 3841
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
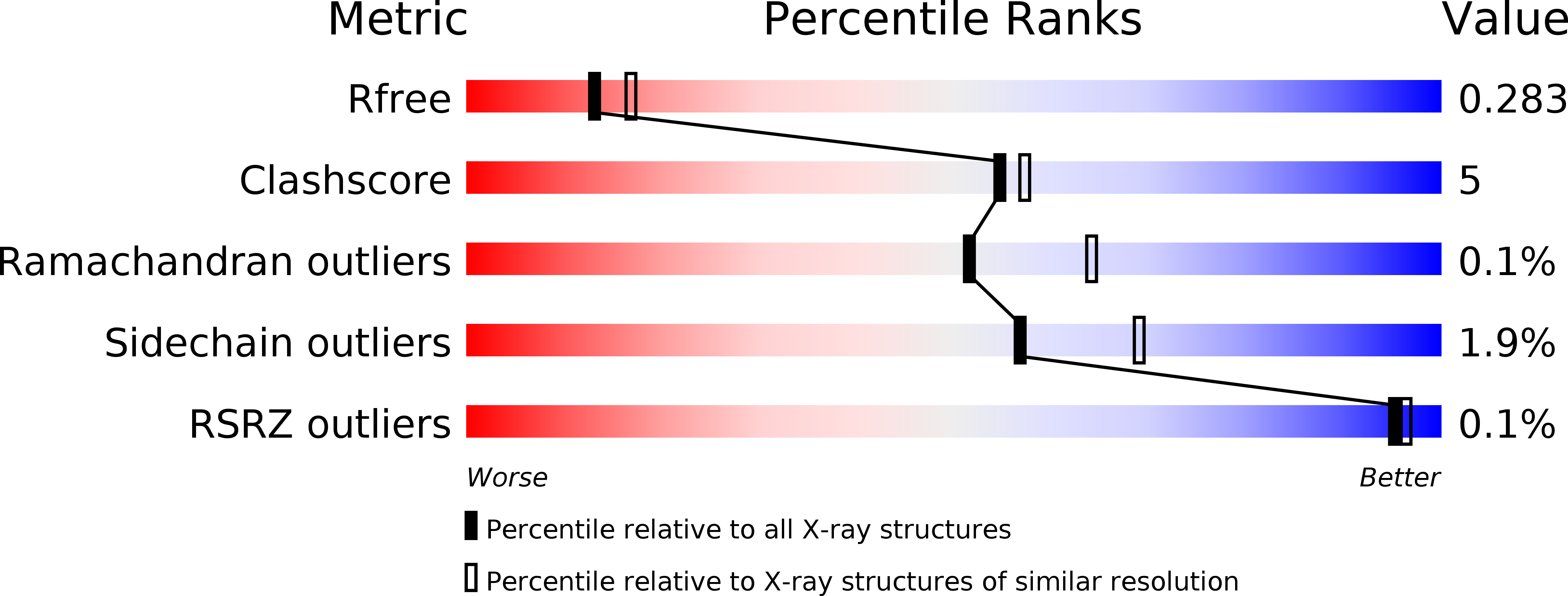
Resolution:
2.46 Å
R-Value Free:
0.27
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
C 1 2 1