Deposition Date
2017-08-24
Release Date
2018-01-31
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6ASF
Keywords:
Title:
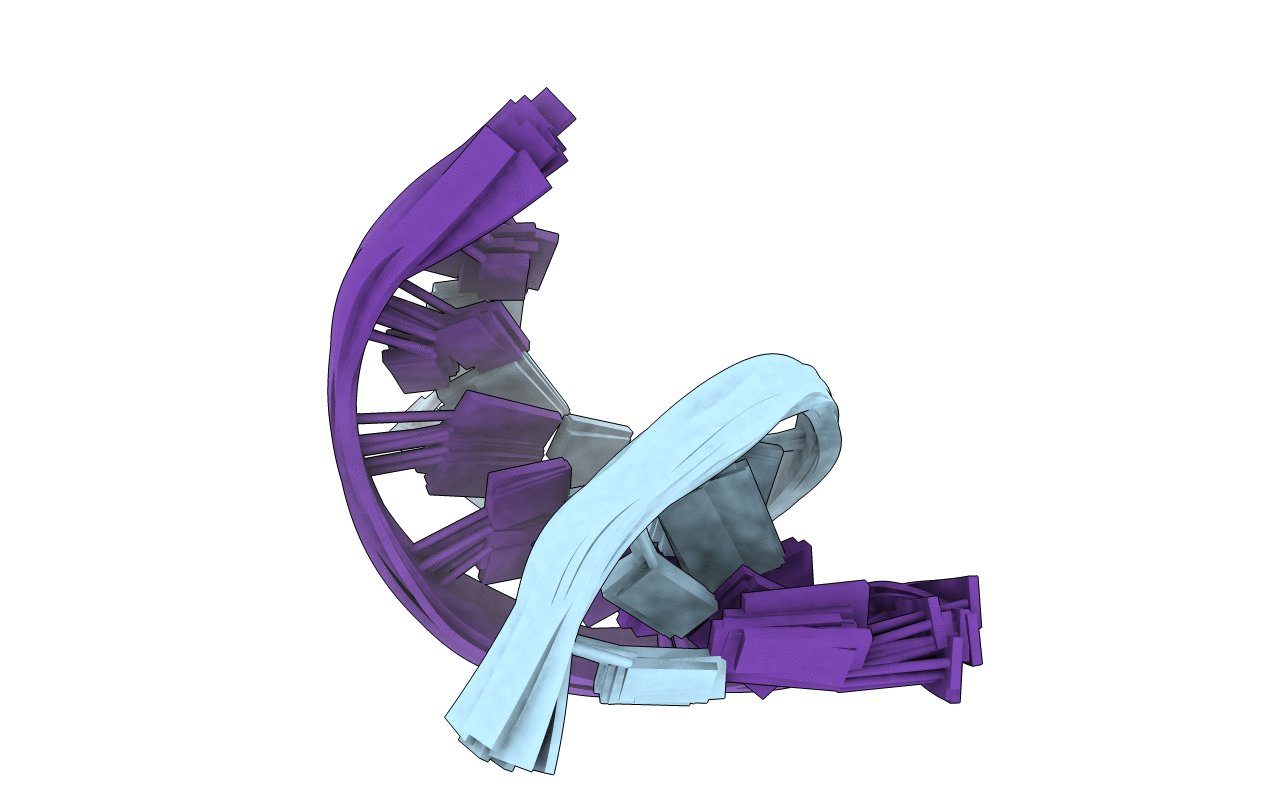
NMR and Restrained Molecular Dynamics Determination of the Structure of an Aza-Benzimidazole Derivative Complex with the DNA Minor Groove of an -AAGATA- Sequence
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
11
Conformers Submitted:
11
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted