Deposition Date
2018-07-13
Release Date
2019-03-20
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Enterobacteria phage RB59 (Taxon ID: 697290)
Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) (Taxon ID: 284812)
Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) (Taxon ID: 284812)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
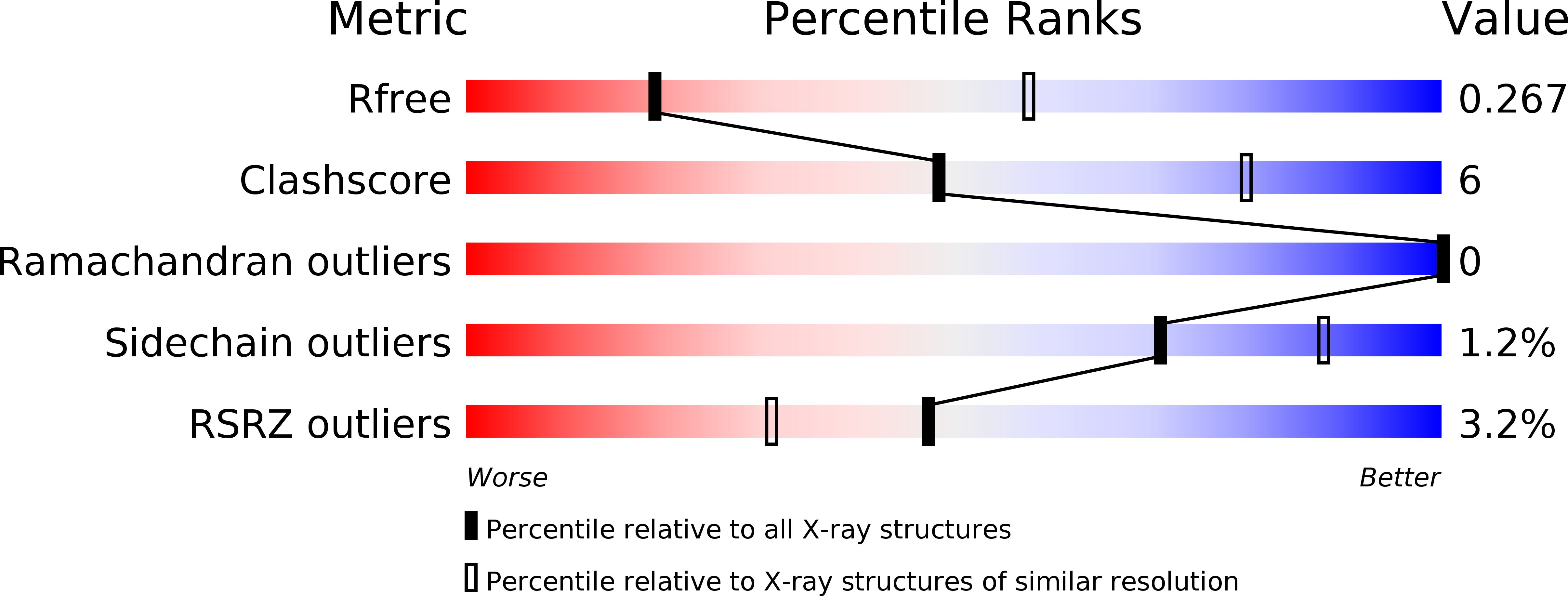
Resolution:
3.21 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
P 1 21 1