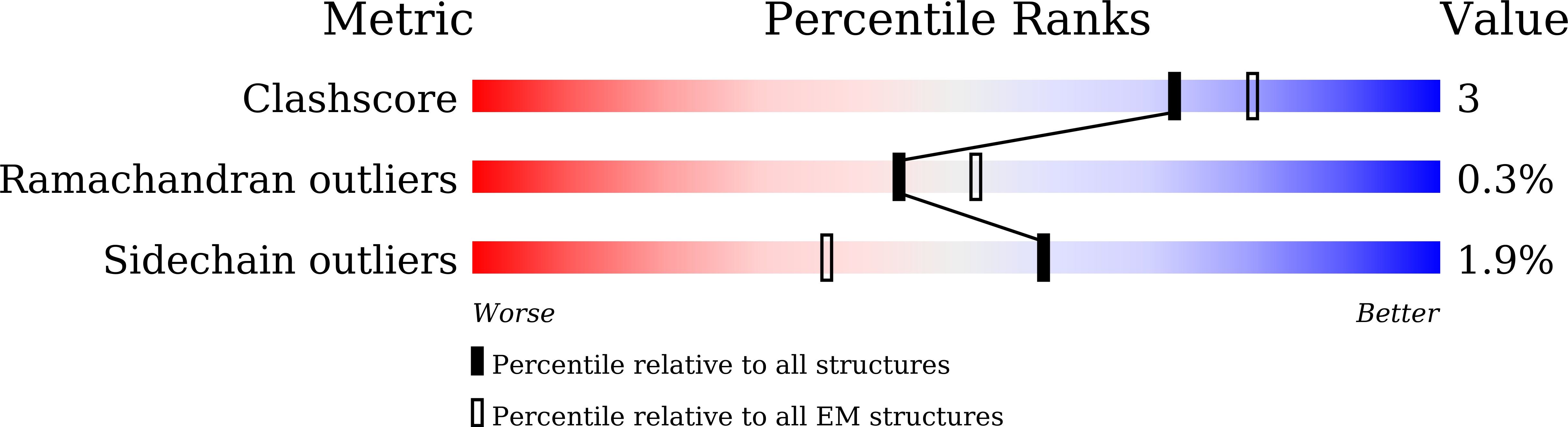Deposition Date
2018-07-11
Release Date
2018-08-08
Last Version Date
2024-10-30
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6A90
Keywords:
Title:
Complex of voltage-gated sodium channel NavPaS from American cockroach Periplaneta americana and Dc1a
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Periplaneta americana (Taxon ID: 6978)
Diguetia canities (Taxon ID: 38407)
Diguetia canities (Taxon ID: 38407)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.80 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE