Deposition Date
2018-06-29
Release Date
2019-01-23
Last Version Date
2023-11-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6A6Q
Keywords:
Title:
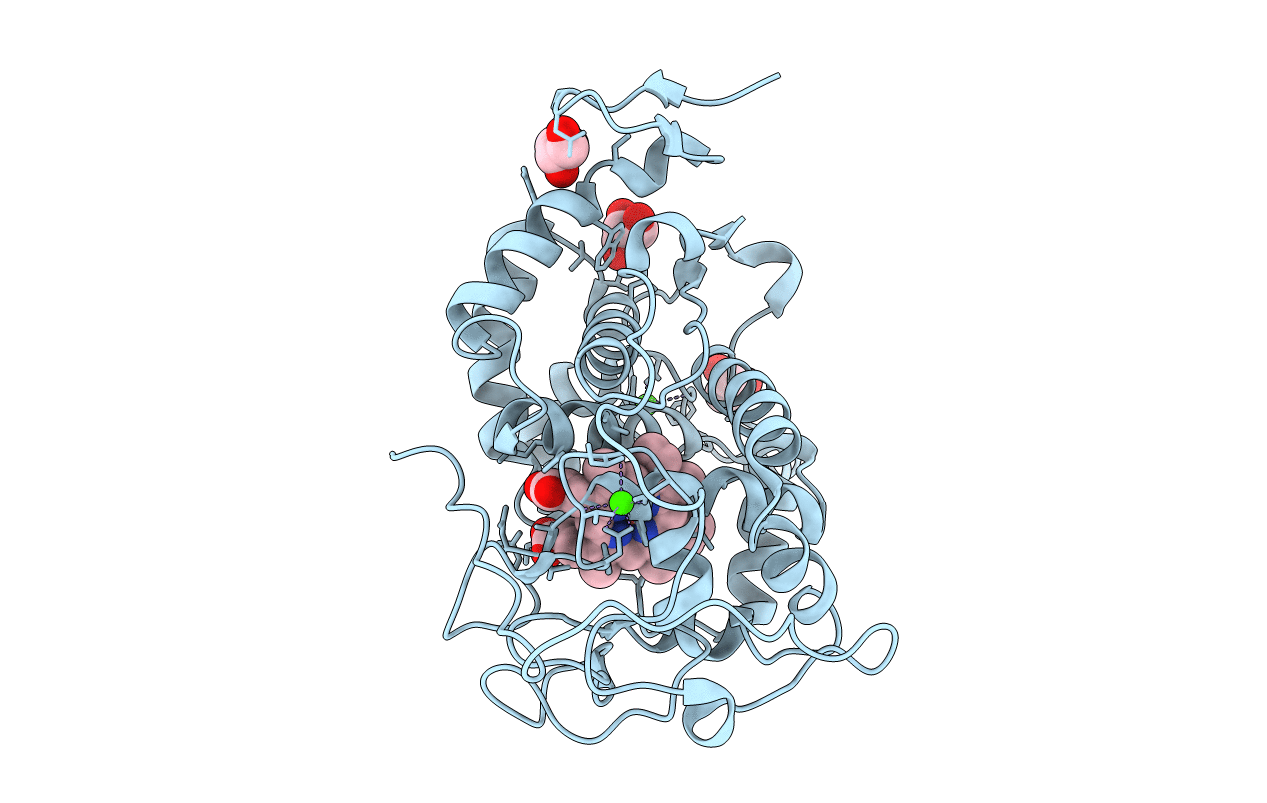
Crystal structure of a lignin peroxidase isozyme H8 variant that is stable at very acidic pH
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Phanerochaete chrysosporium RP-78 (Taxon ID: 273507)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
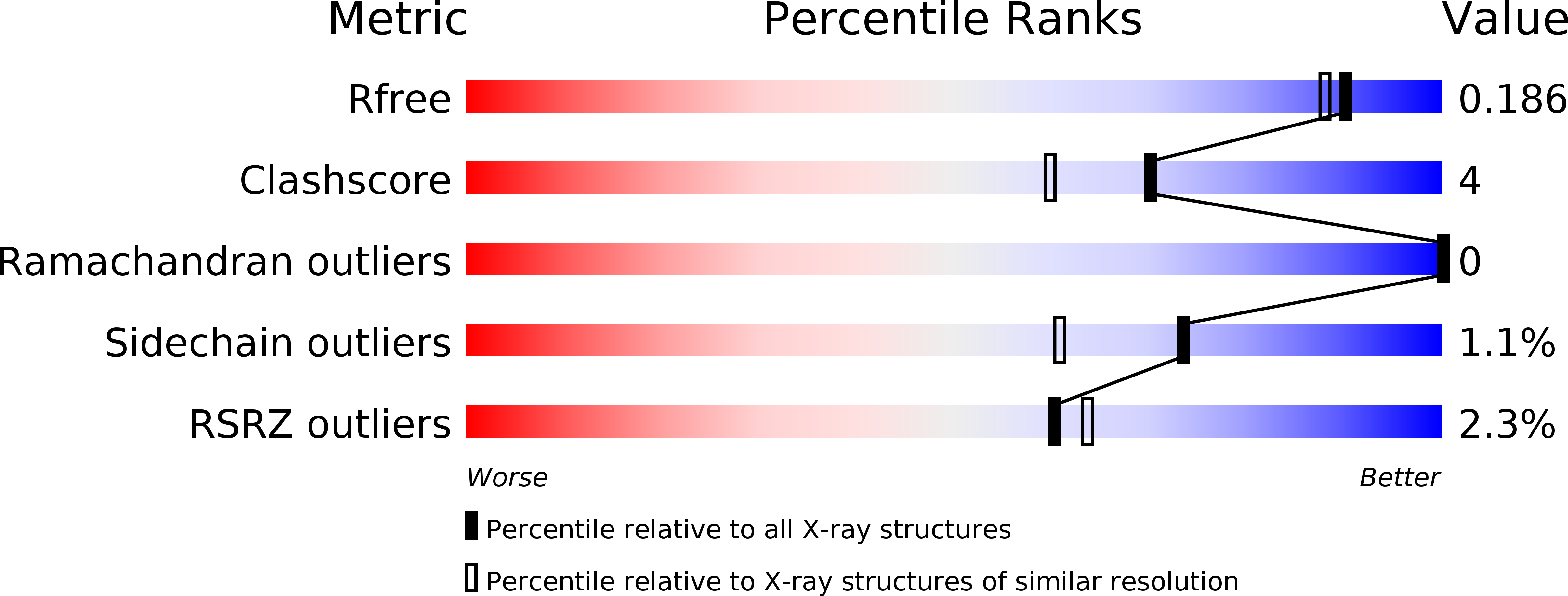
Resolution:
1.67 Å
R-Value Free:
0.17
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.14
Space Group:
P 1 21 1