Deposition Date
2017-06-28
Release Date
2017-10-04
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5XVP
Keywords:
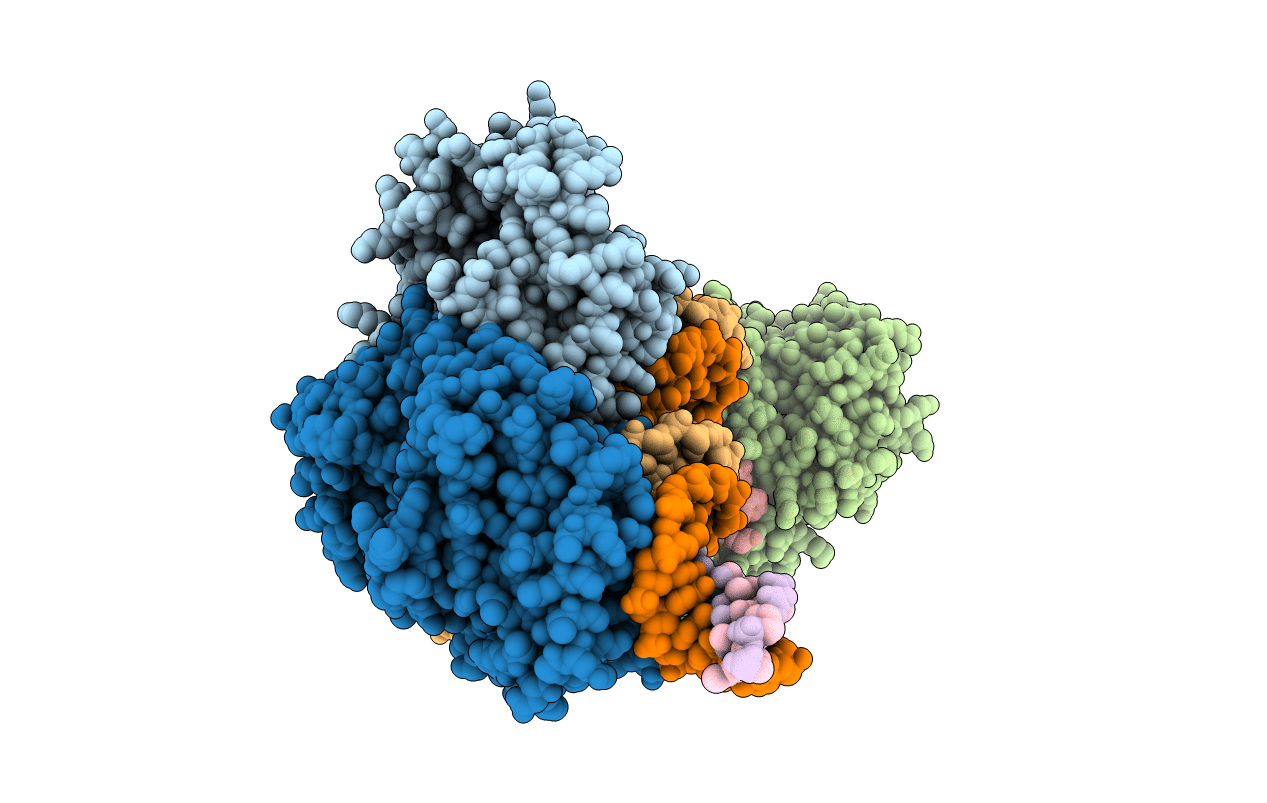
Title:
E. fae Cas1-Cas2/prespacer/target ternary complex revealing the fully integrated states
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Enterococcus faecalis TX0027 (Taxon ID: 749498)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
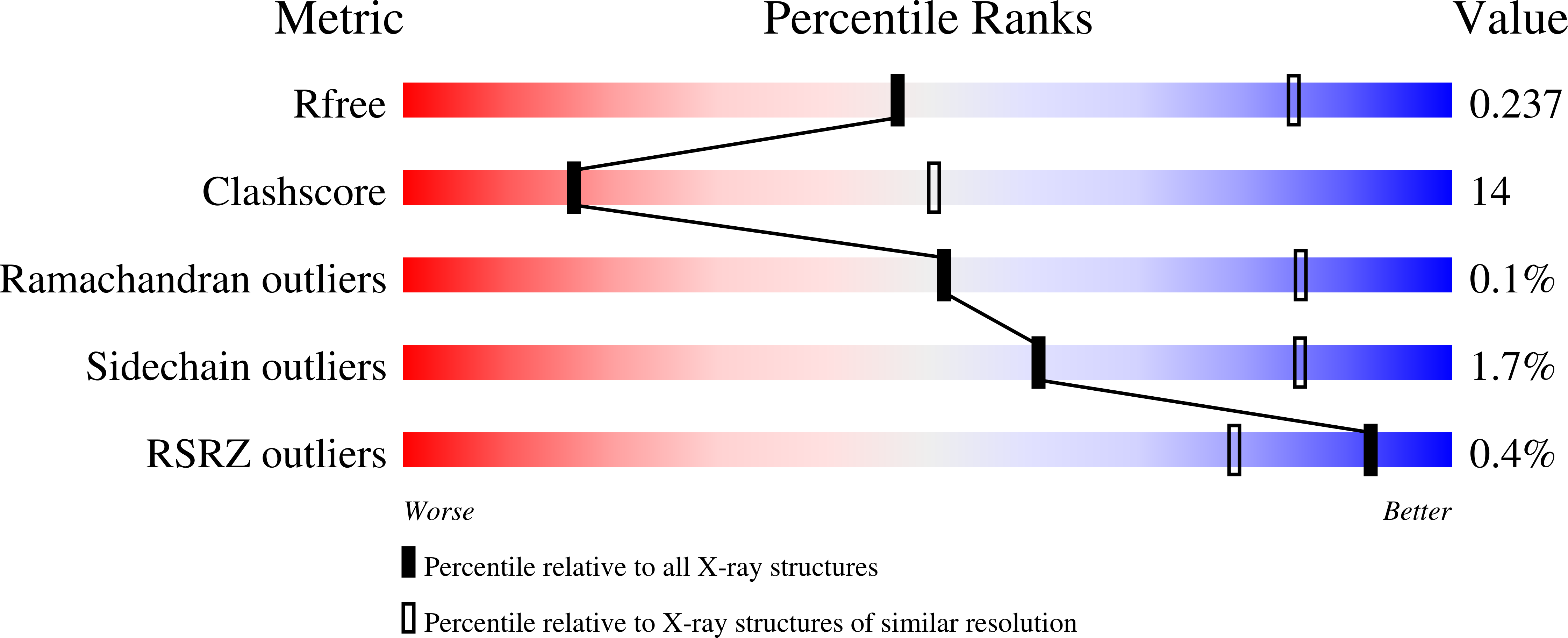
Resolution:
3.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
I 2 2 2