Deposition Date
2017-06-07
Release Date
2018-05-16
Last Version Date
2023-11-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5XQU
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of Notched-fin eelpout type III antifreeze protein A20I mutant (NFE6, AFP), P212121 form
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Zoarces elongatus (Taxon ID: 291231)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
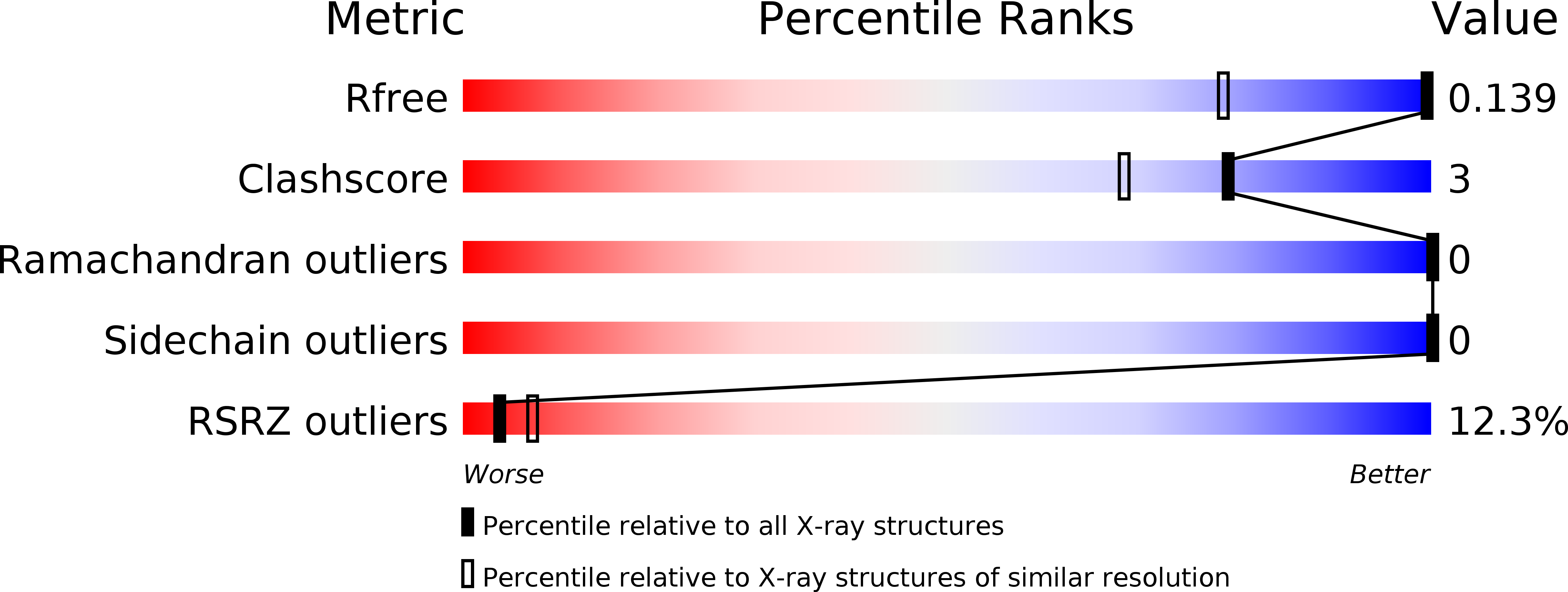
Resolution:
1.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.13
R-Value Work:
0.12
R-Value Observed:
0.12
Space Group:
P 21 21 21