Deposition Date
2017-01-31
Release Date
2017-03-29
Last Version Date
2024-03-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5X2G
Keywords:
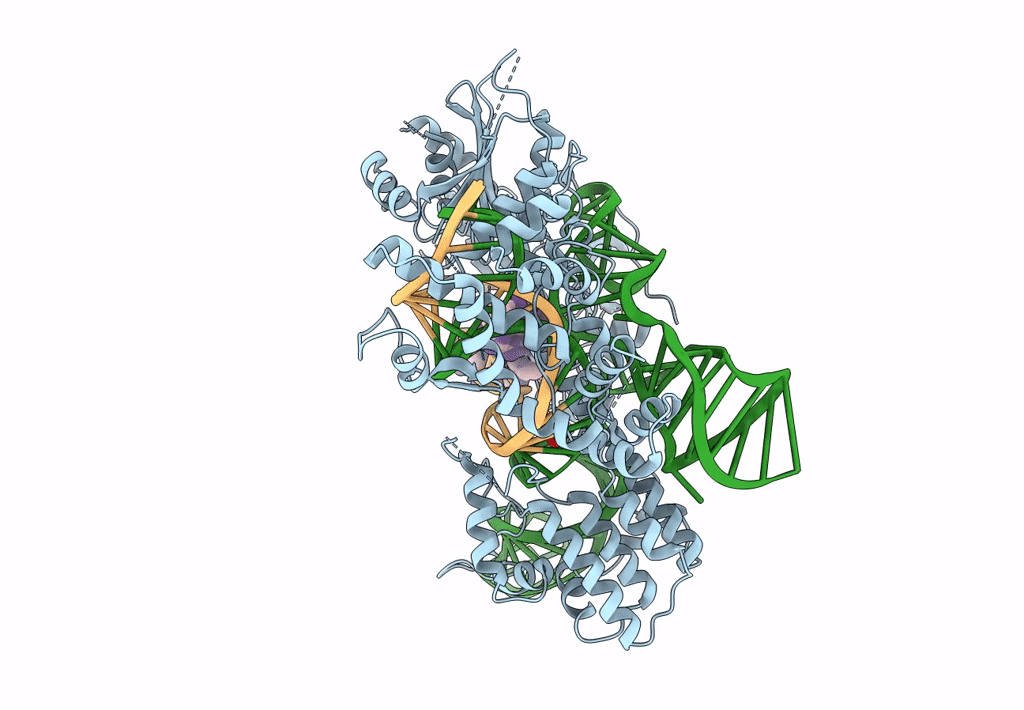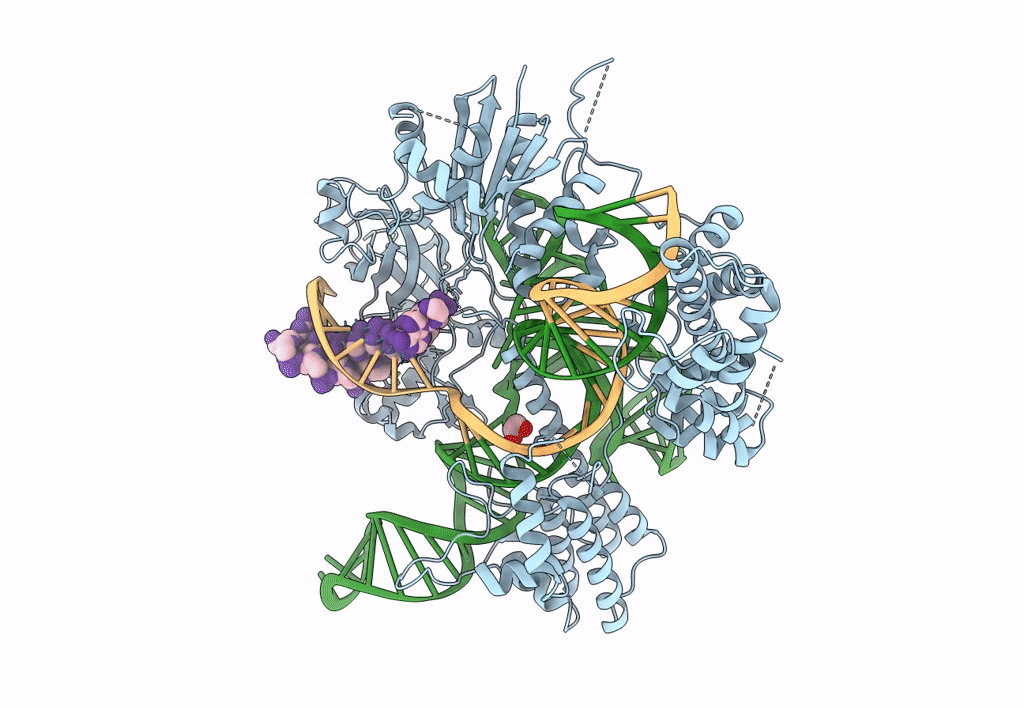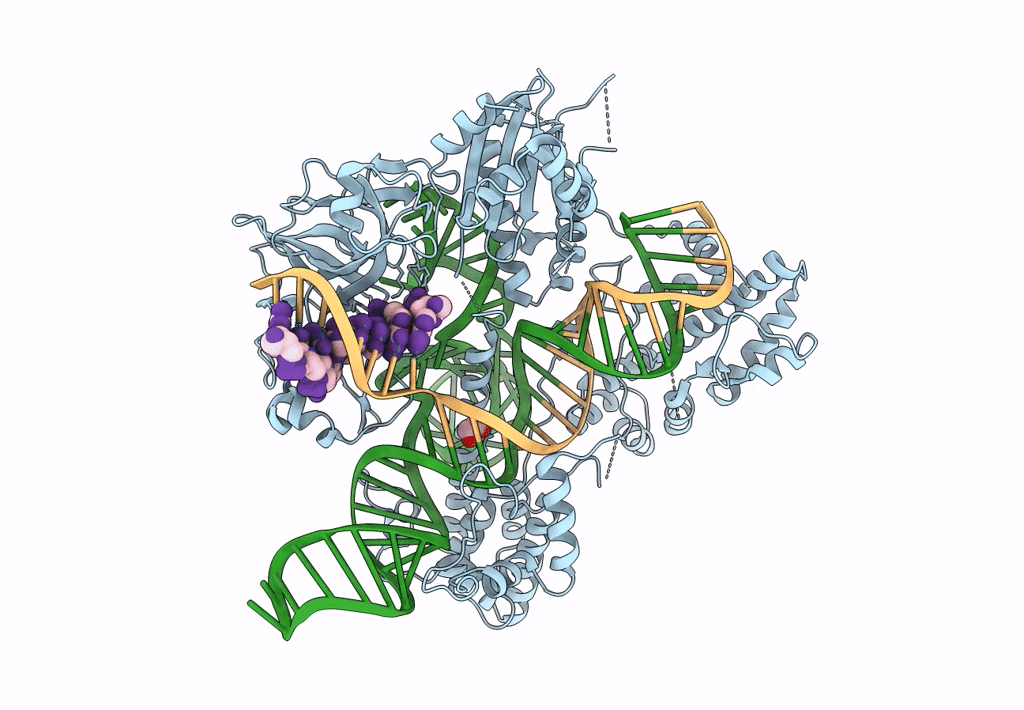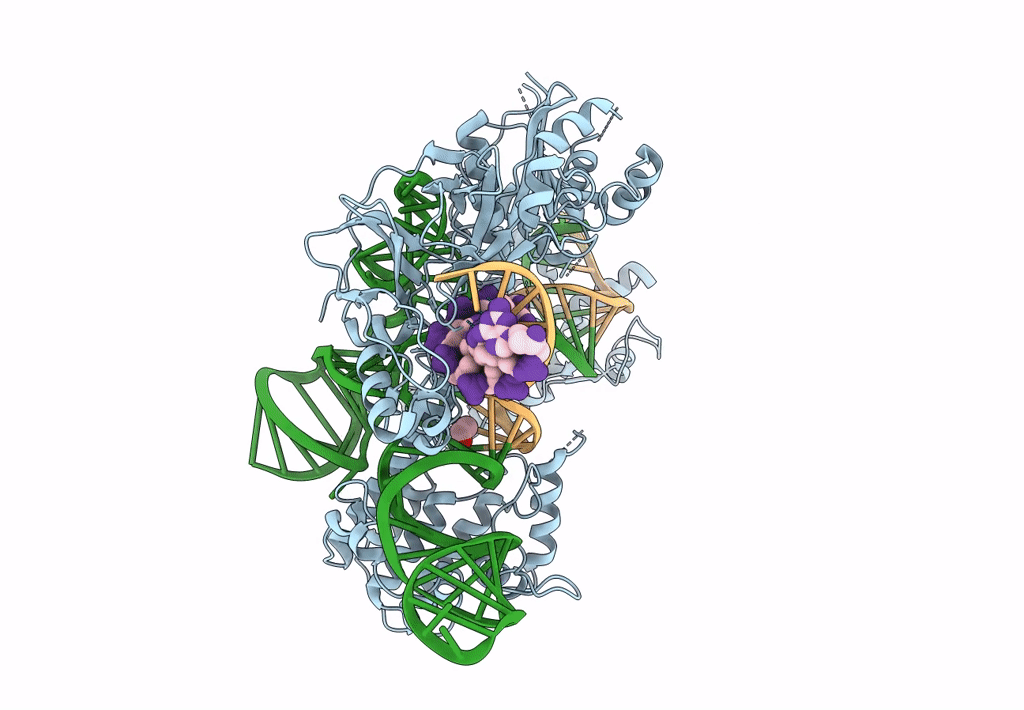
Title:
Crystal structure of Campylobacter jejuni Cas9 in complex with sgRNA and target DNA (AGAAACC PAM)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:2 (strain ATCC 700819 / NCTC 11168) (Taxon ID: 192222)
Campylobacter jejuni (Taxon ID: 197)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Campylobacter jejuni (Taxon ID: 197)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
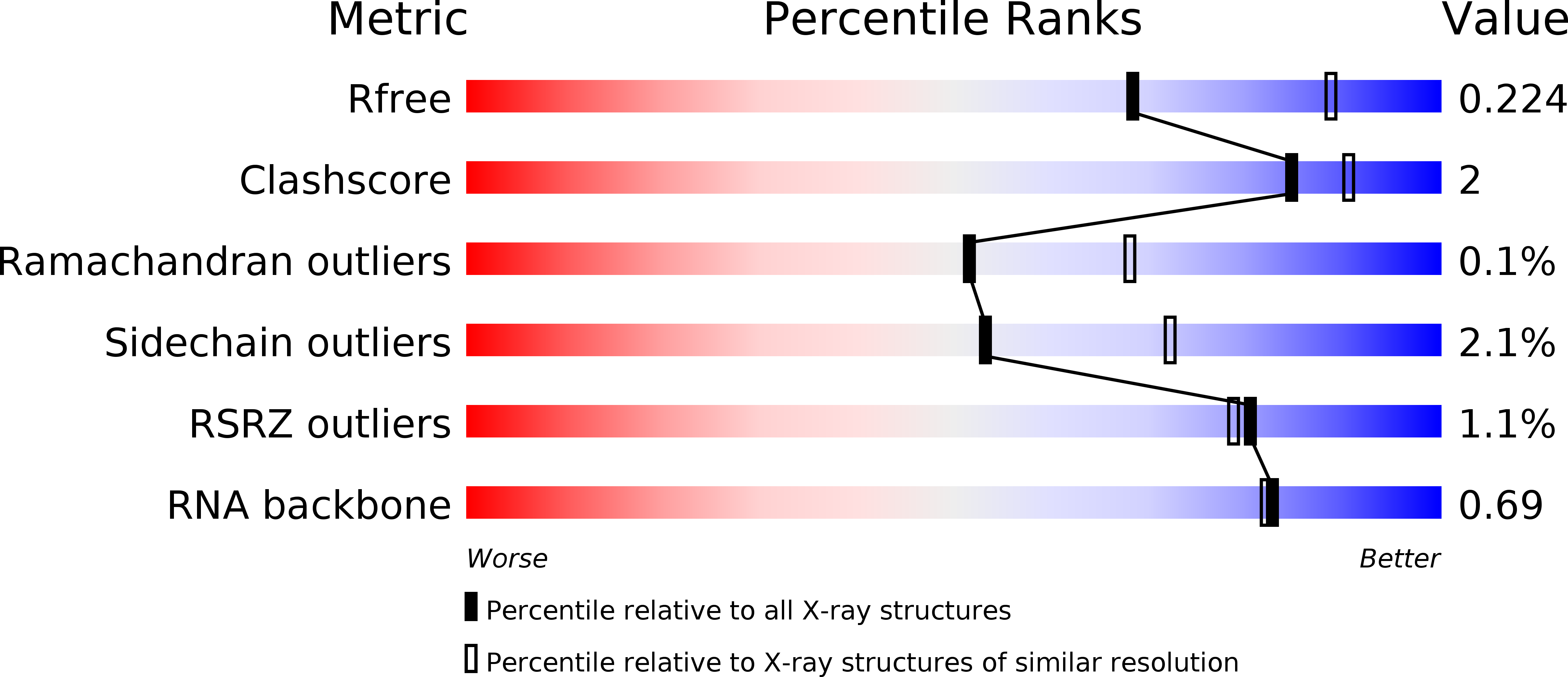
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 21 21 21