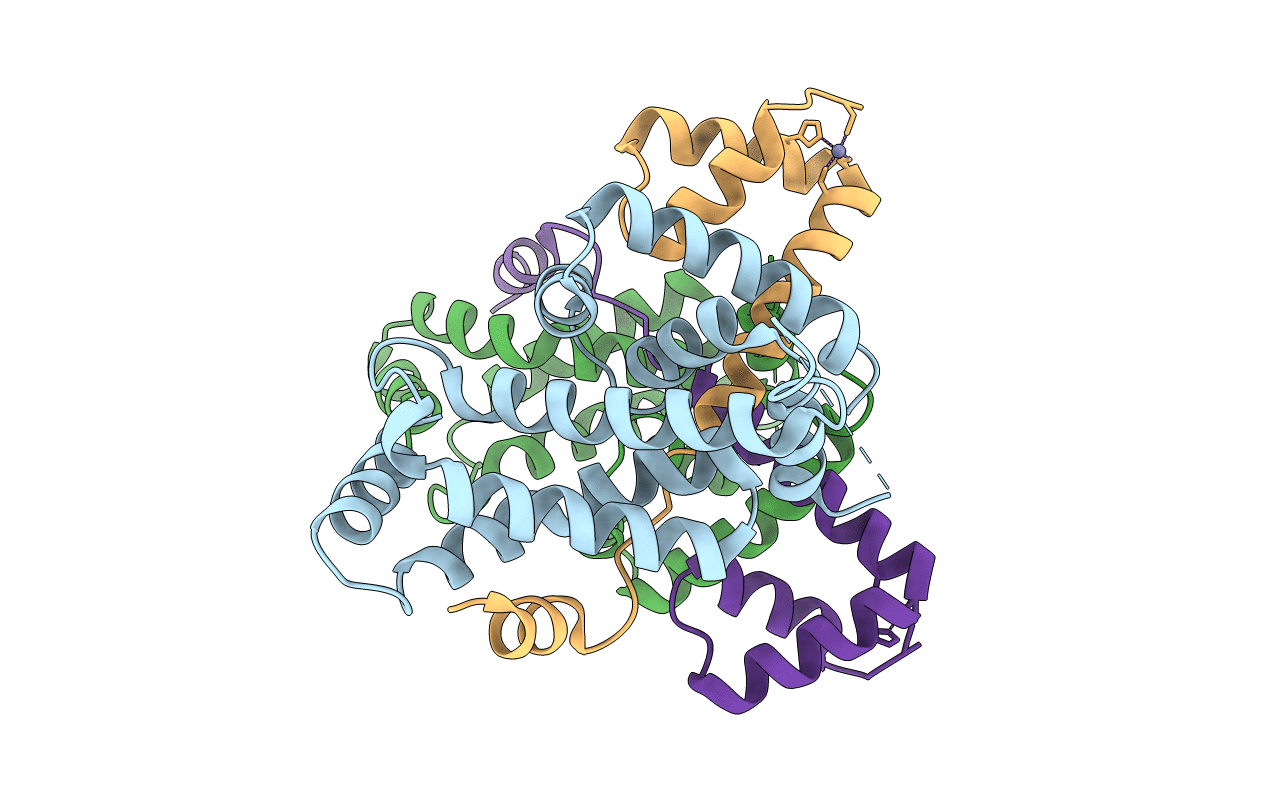
Deposition Date
2016-12-20
Release Date
2017-03-29
Last Version Date
2024-03-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5WUQ
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of SigW in complex with its anti-sigma RsiW, a zinc binding form
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 (Taxon ID: 224308)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.80 Å
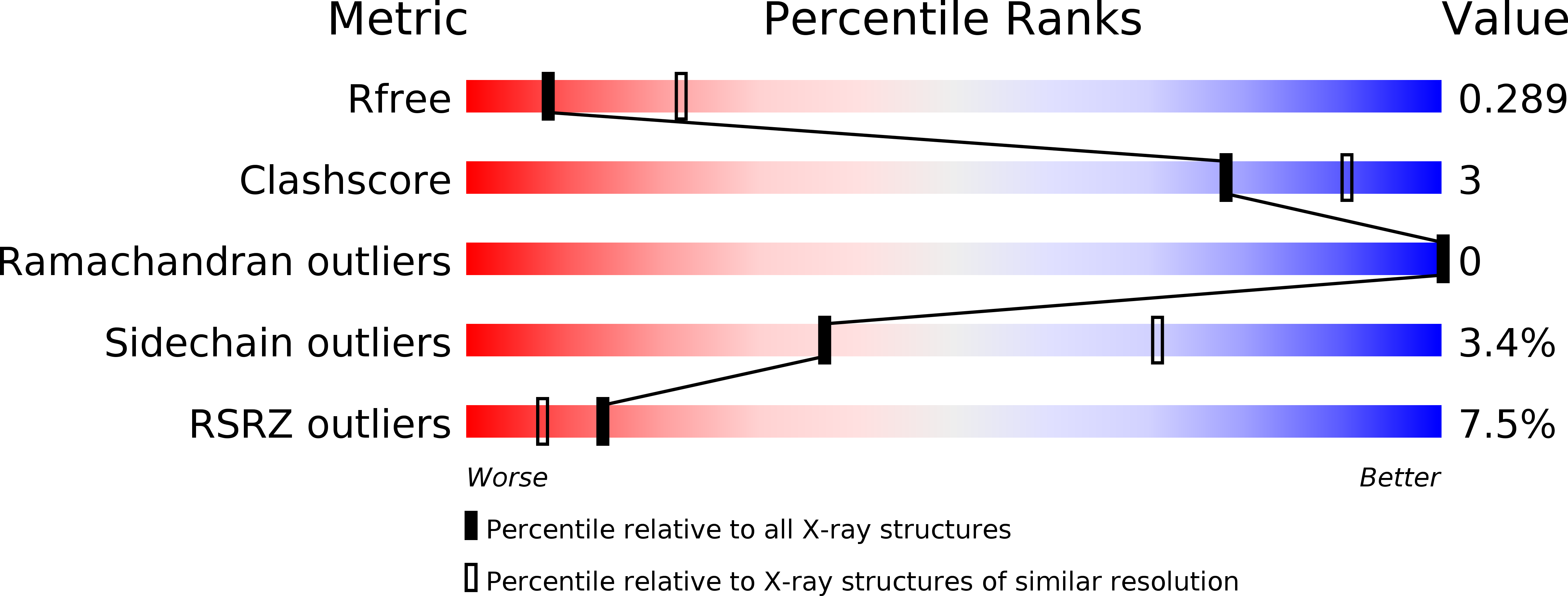
R-Value Free:
0.28
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 21 21 21