Deposition Date
2016-12-06
Release Date
2017-11-15
Last Version Date
2023-11-08
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5WSC
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal of pyruvate kinase (PYK) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in complex with Oxalate, soaked with allosteric activators AMP and Glucose 6-Phosphate
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
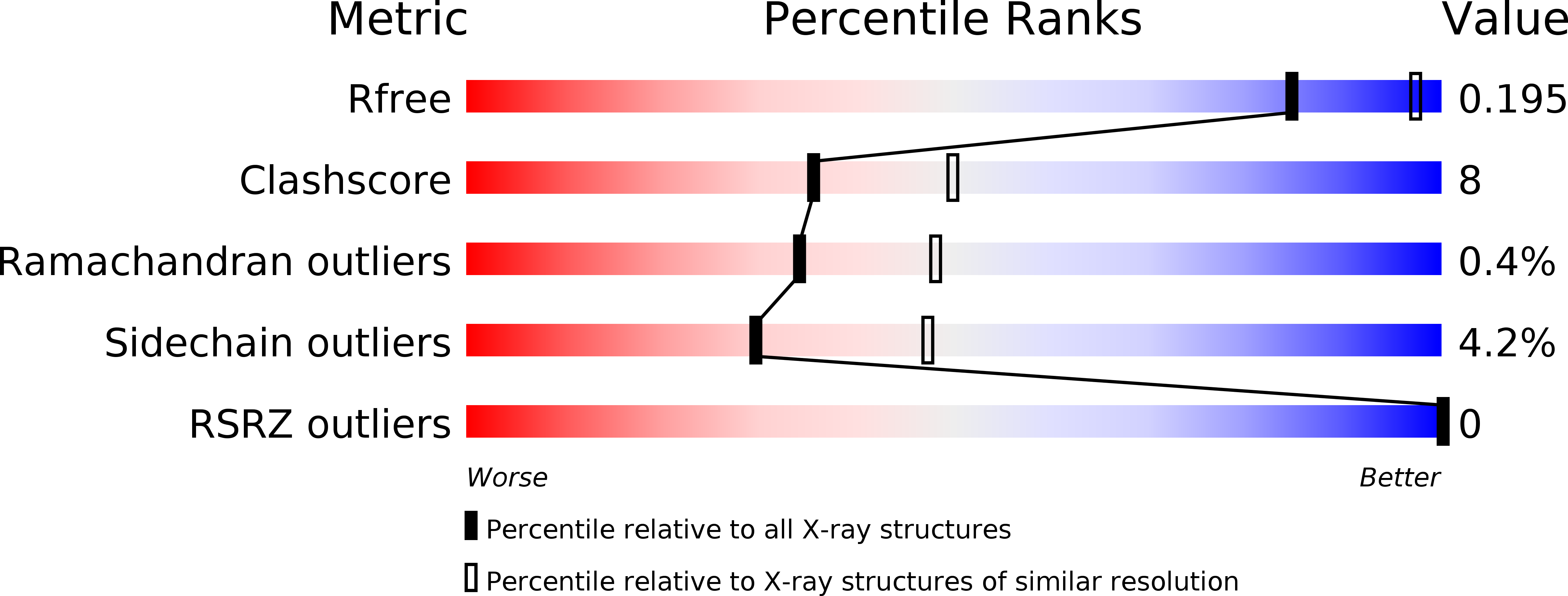
Resolution:
2.40 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 31