Deposition Date
2017-06-11
Release Date
2017-11-22
Last Version Date
2023-10-04
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5W4H
Keywords:
Title:
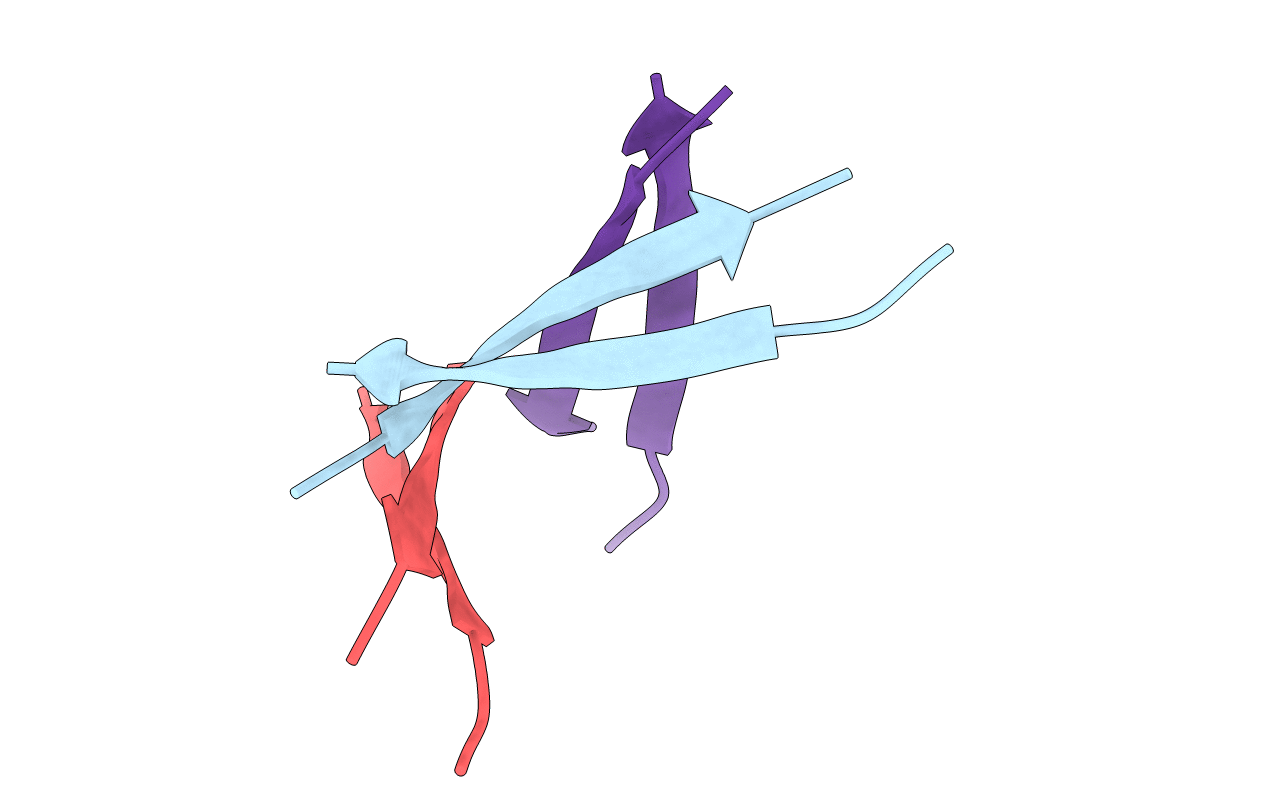
X-ray crystallographic structure of a beta-hairpin peptide mimic derived from Abeta 16-36. Synchrotron data set. (ORN)KLV(MEA)FAE(ORN)AIIGLMV.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
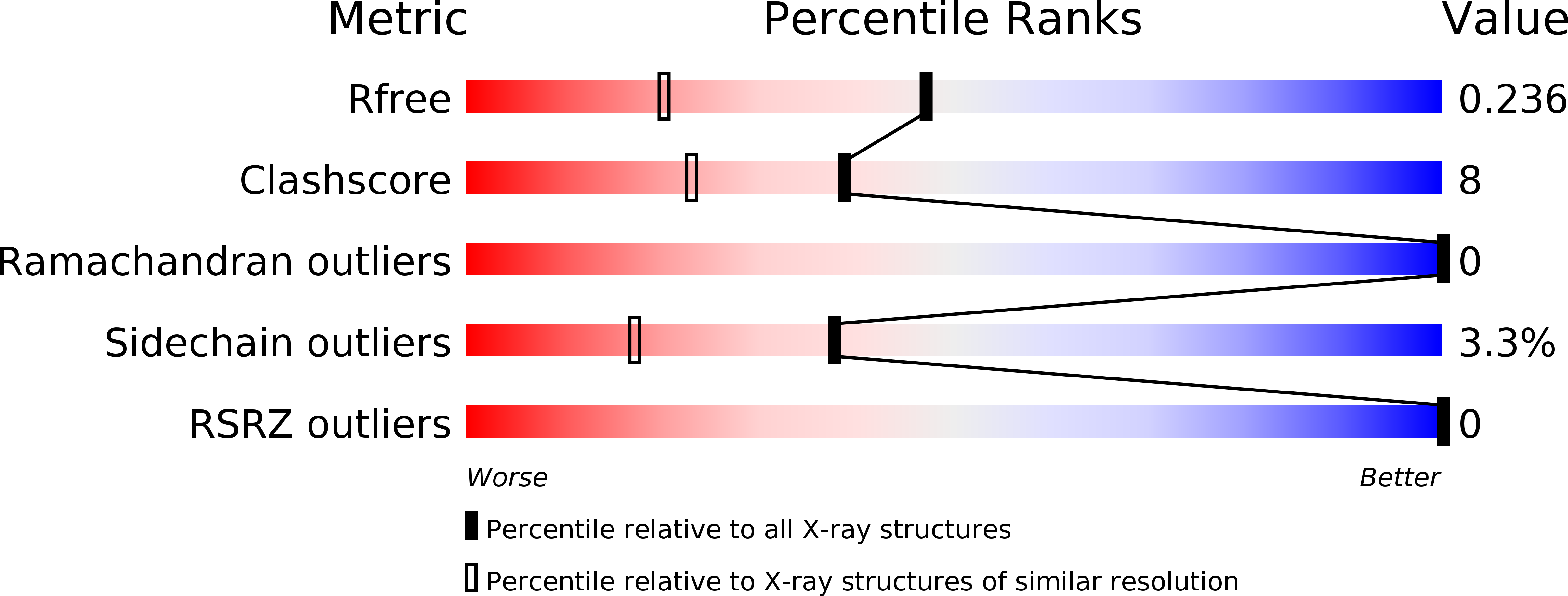
Resolution:
1.72 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 4 3 2