Deposition Date
2017-02-20
Release Date
2017-04-12
Last Version Date
2024-03-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5UW8
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of E. coli MCE protein MlaD, core MCE domain
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Taxon ID: 83334)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
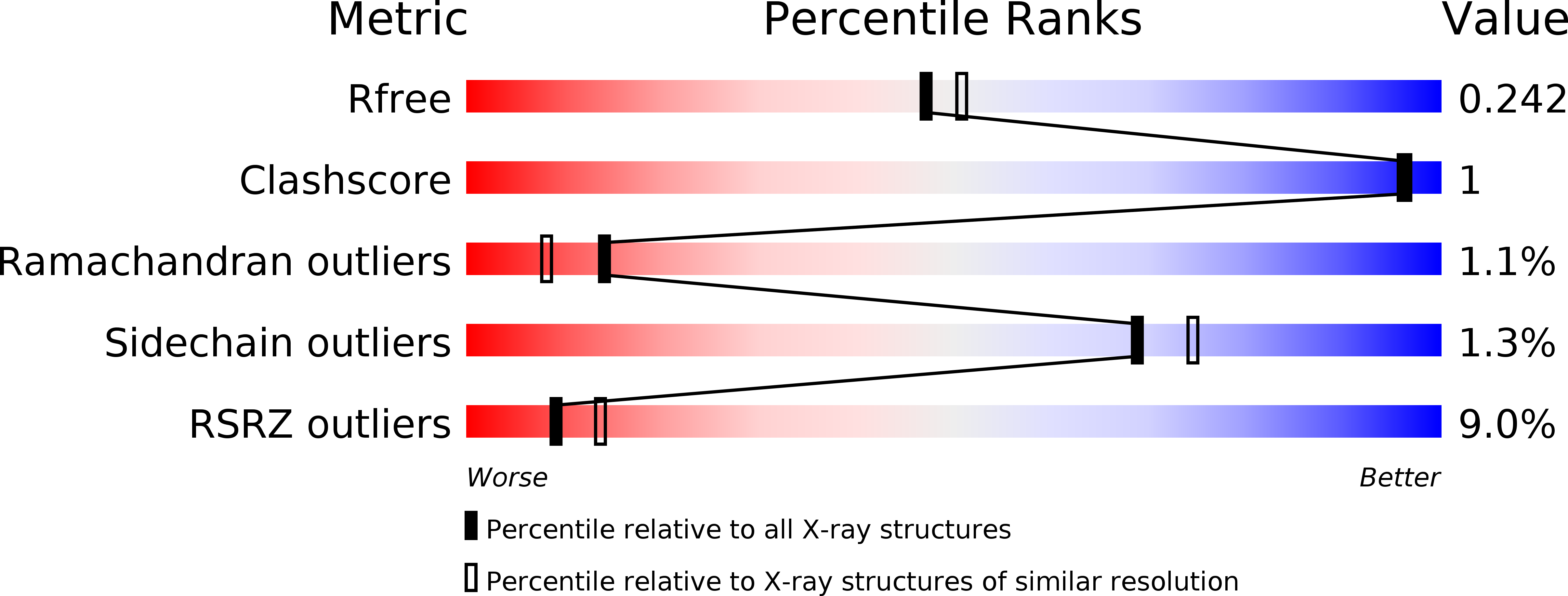
Resolution:
2.15 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
C 1 2 1