Deposition Date
2016-12-07
Release Date
2018-06-13
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5U5O
Keywords:
Title:
Bacterial adhesin from Mobiluncus mulieris containing intramolecular disulfide, isopeptide, and ester bond cross-links (space group P1)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mobiluncus mulieris (Taxon ID: 2052)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
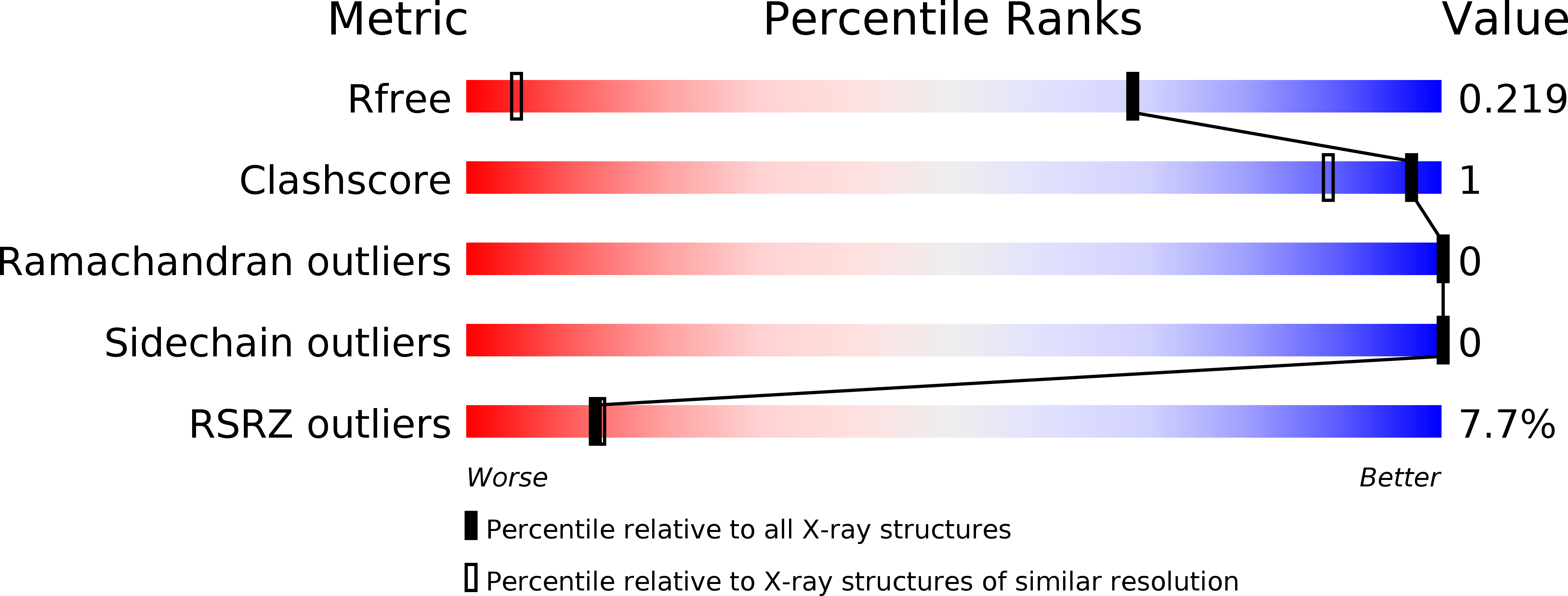
Resolution:
1.15 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 1