Deposition Date
2016-09-07
Release Date
2017-02-01
Last Version Date
2025-10-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5T89
Keywords:
Title:
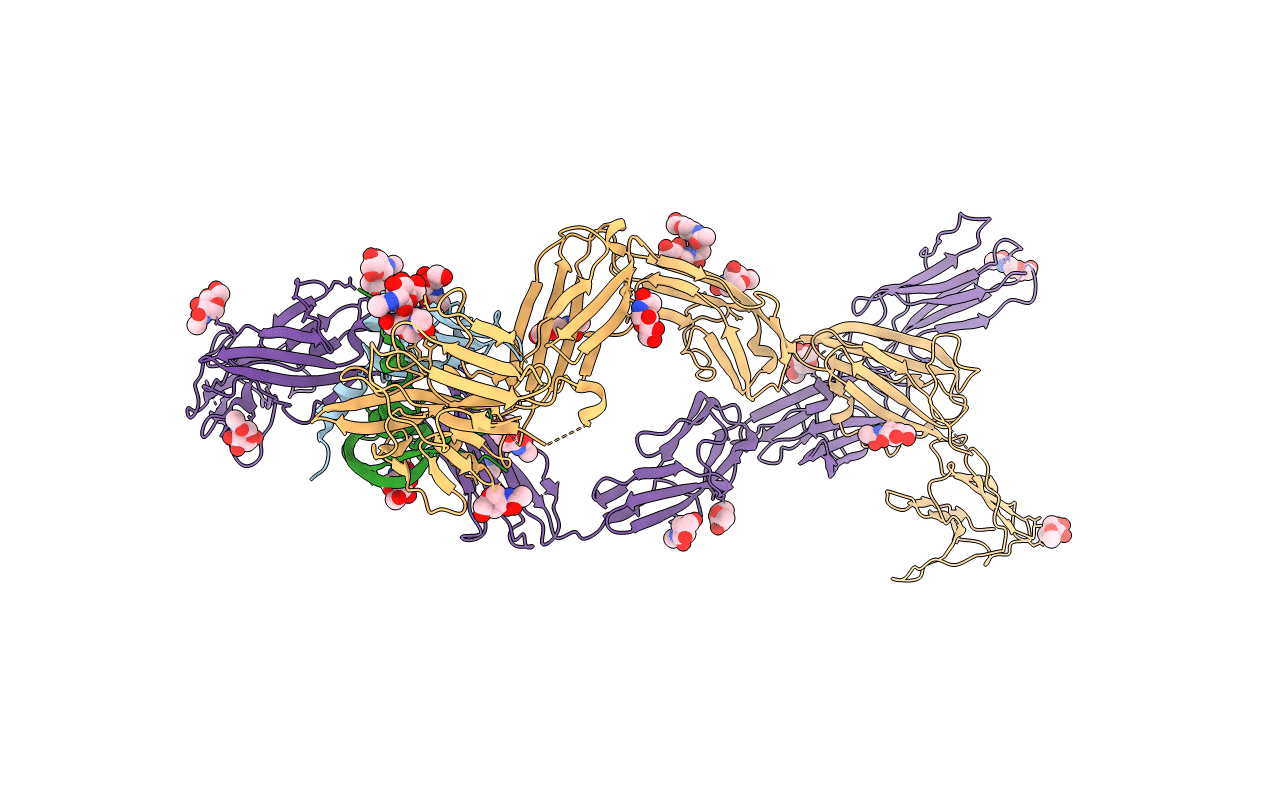
Crystal structure of VEGF-A in complex with VEGFR-1 domains D1-6
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
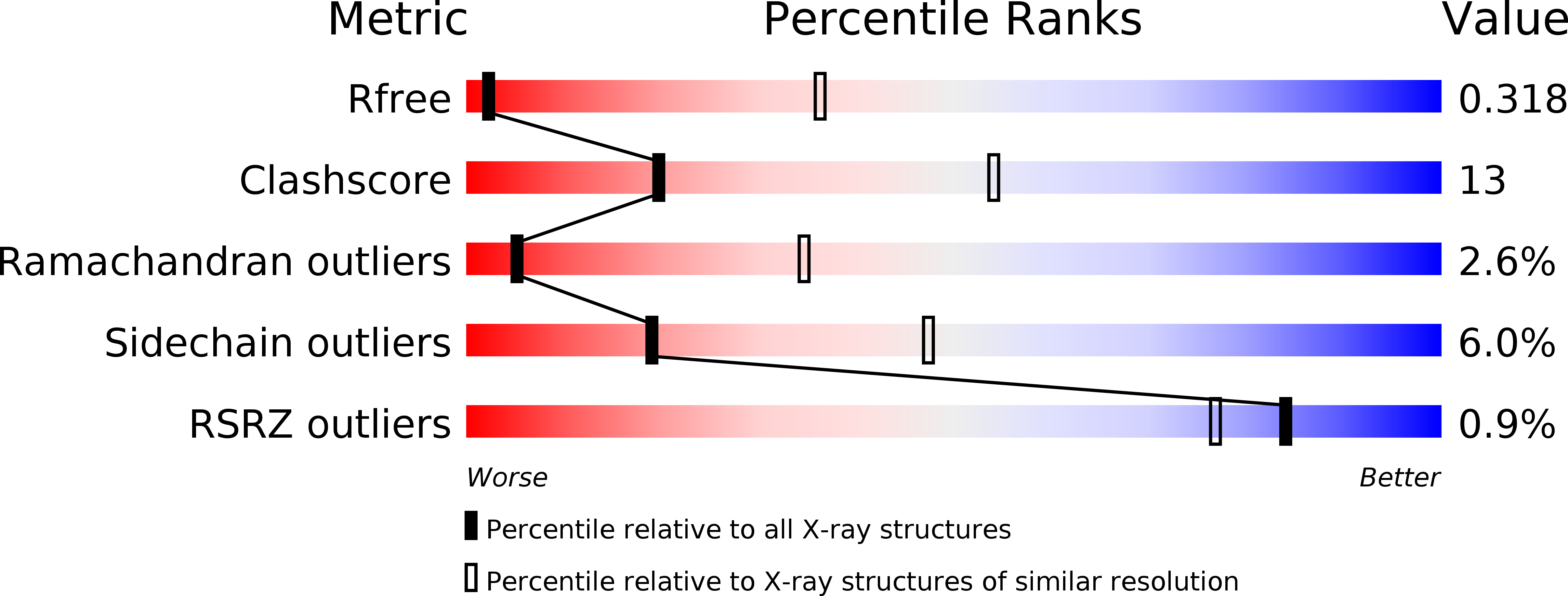
Resolution:
4.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.31
R-Value Work:
0.28
R-Value Observed:
0.28
Space Group:
C 1 2 1