Deposition Date
2016-09-04
Release Date
2017-10-11
Last Version Date
2024-10-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5T7G
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal Structure of Murine MHC-I H-2Dd in complex with Murine Beta2-Microglobulin and a Variant of Peptide (PT9) of HIV gp120 MN Isolate (IGPGRAFYT)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate MN) (Taxon ID: 11696)
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate MN) (Taxon ID: 11696)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
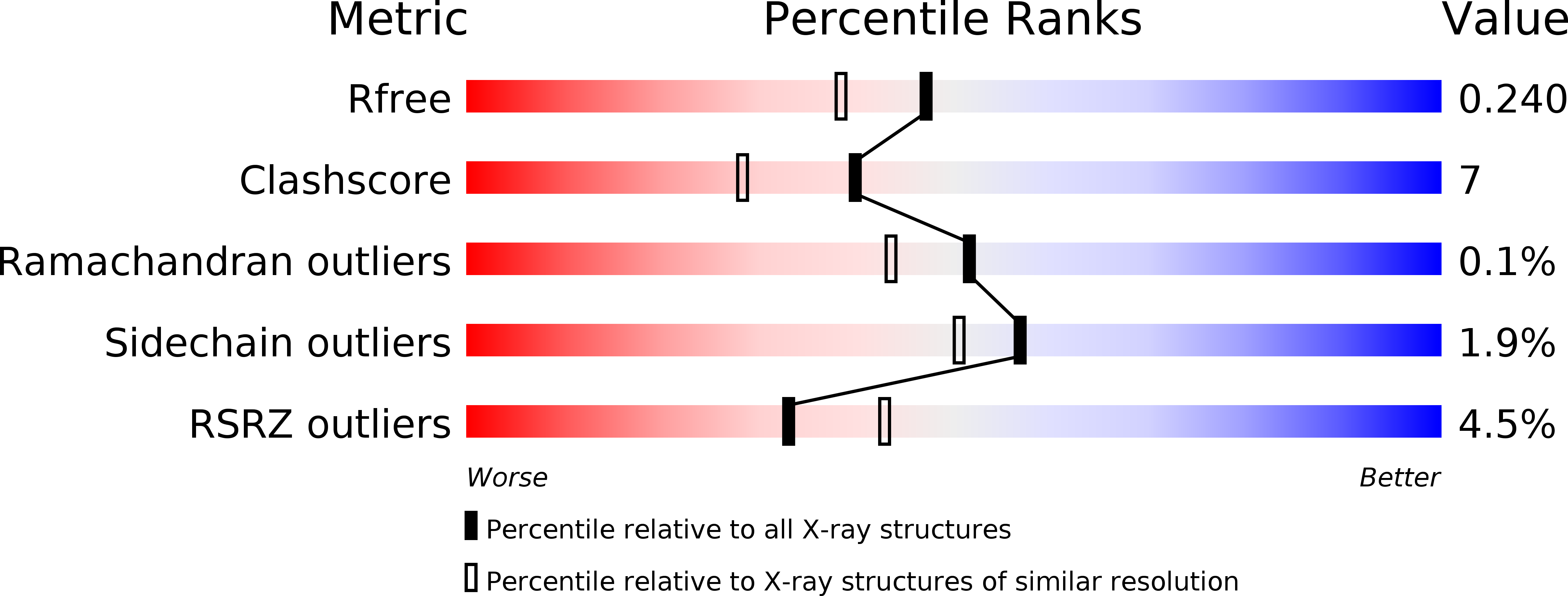
Resolution:
1.96 Å
R-Value Free:
0.23
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 21 21 21