Deposition Date
2016-08-31
Release Date
2017-08-23
Last Version Date
2023-10-04
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
5T5K
Keywords:
Title:
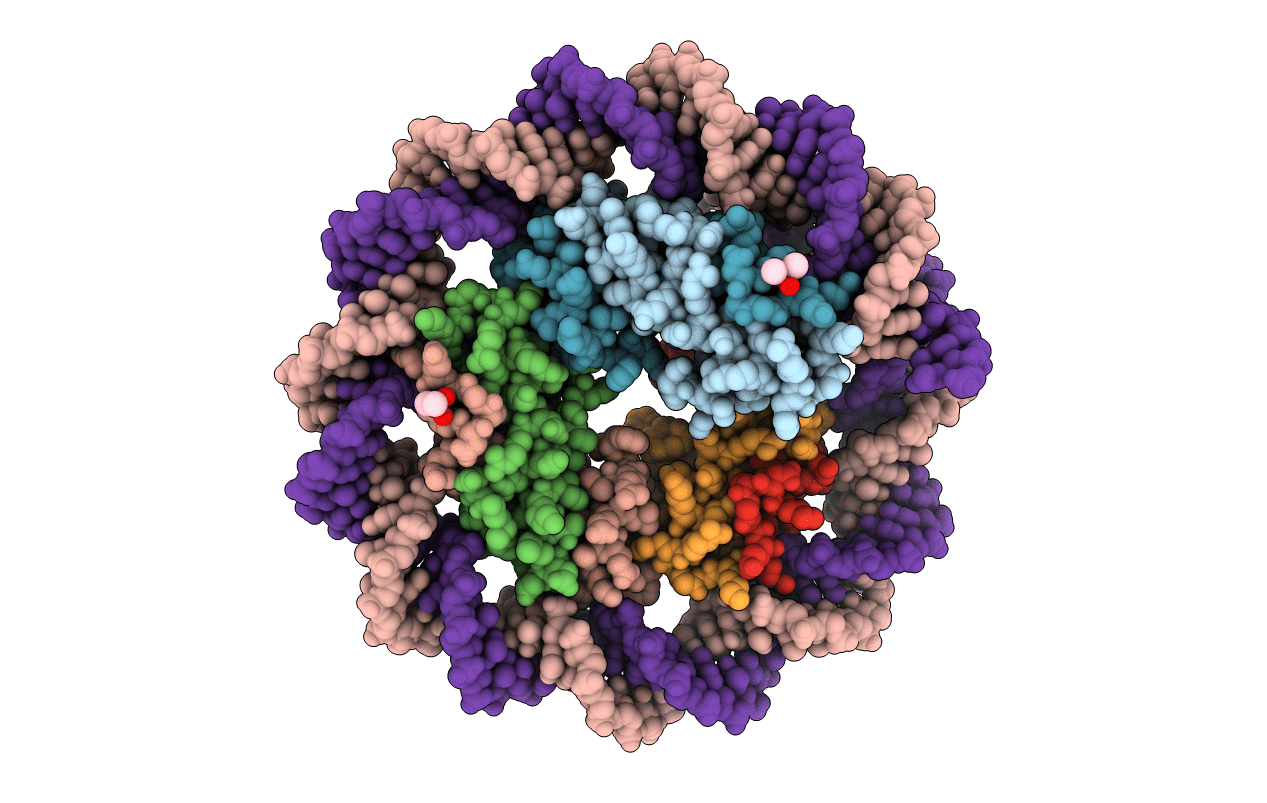
Structure of histone-based chromatin in Archaea
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Methanothermus fervidus (Taxon ID: 2180)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
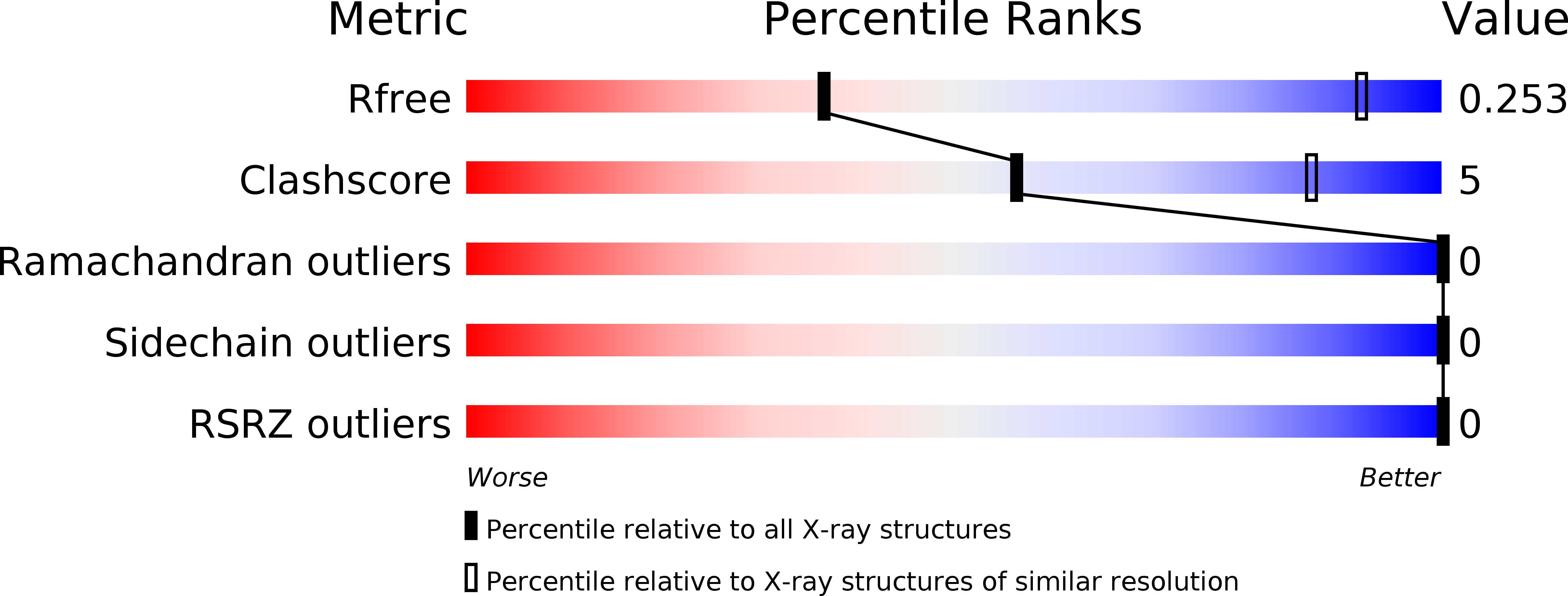
Resolution:
4.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
P 65